2% Decline In U.S. GDP: Analysis Of Spending And Tariff Effects
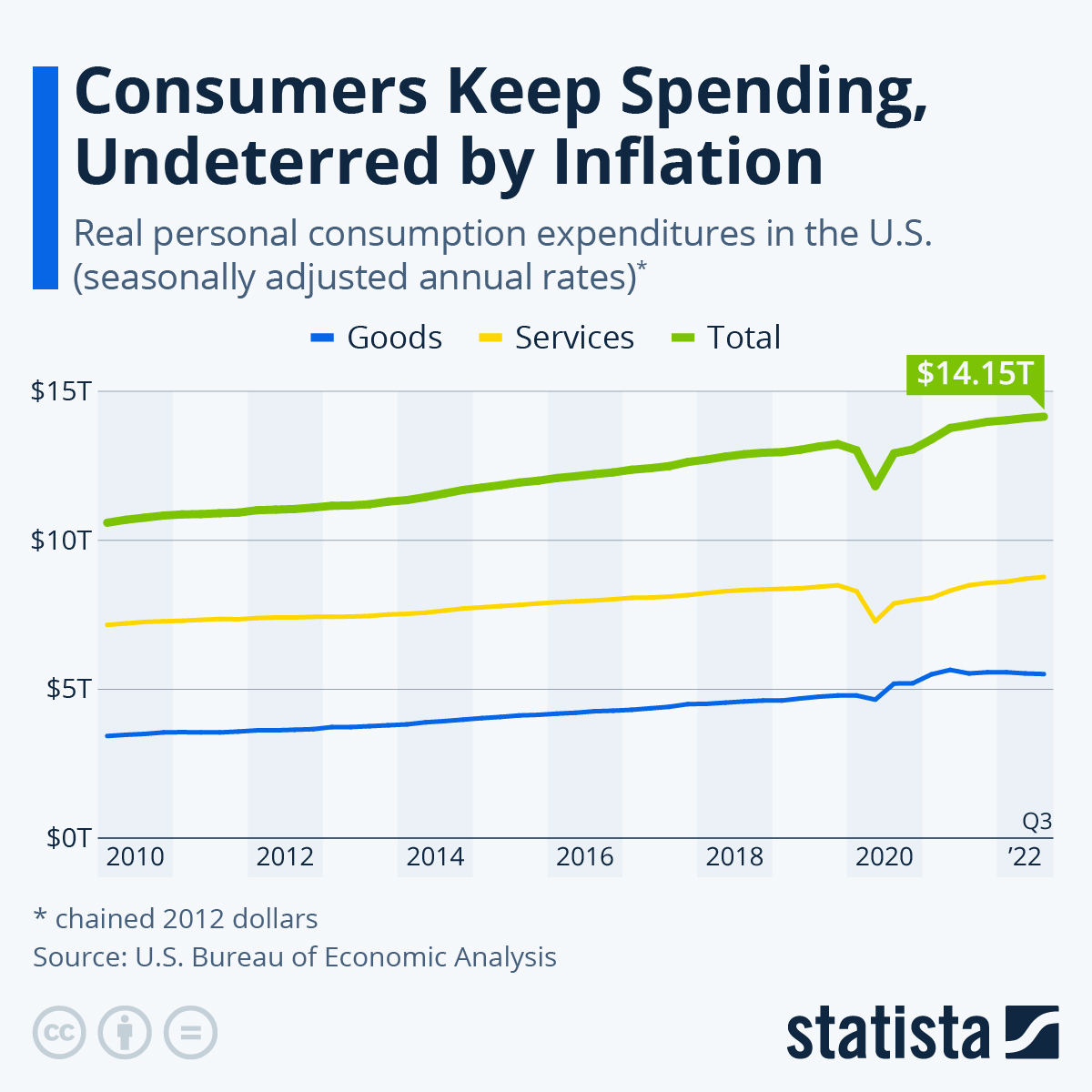
Table of Contents
The Role of Consumer Spending in the GDP Decline
Consumer spending forms a substantial portion of the U.S. GDP, making its decline a critical factor in the overall economic downturn.
Decreased Consumer Confidence and its Impact
The decline in consumer spending is largely attributed to decreased consumer confidence. Several factors have contributed to this:
- Inflationary pressures: High inflation, eroding purchasing power, has led consumers to curtail spending on non-essential items. The Consumer Price Index (CPI) has consistently remained above the Federal Reserve's target, impacting consumer sentiment.
- Interest rate hikes: The Federal Reserve's efforts to curb inflation through interest rate hikes have increased borrowing costs, making it more expensive for consumers to finance purchases, particularly large ones like homes and automobiles.
- Retail sales decline: Data shows a significant decline in retail sales across various sectors, reflecting reduced consumer spending. For instance, sales in the automotive sector have notably decreased due to higher interest rates and decreased affordability.
Keywords: "consumer confidence index," "inflation impact on spending," "interest rate hikes," "retail sales decline."
Shifting Spending Patterns and Their Contribution
Consumers are adapting to the economic climate by prioritizing essential goods over discretionary spending. This shift in spending habits is clearly observable:
- Essential goods dominance: Spending on necessities like groceries and utilities has increased, while discretionary spending on entertainment, travel, and dining out has significantly decreased.
- Increased savings rate: Some consumers are opting to increase their savings rate to build a financial buffer against economic uncertainty. This shift away from spending contributes to the overall decline in GDP.
- Economic indicators: Data from the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) shows a clear correlation between the shifting spending patterns and the overall decline in consumer spending contribution to the GDP.
Keywords: "discretionary spending," "essential goods," "savings rate," "spending habits."
The Impact of Reduced Investment on GDP Growth
Reduced investment plays a significant role in the current GDP contraction. Businesses are hesitant to invest due to prevailing economic uncertainty.
Business Investment and Economic Uncertainty
Several factors contribute to the reluctance of businesses to invest:
- Geopolitical instability: Global geopolitical tensions and uncertainties create a climate of risk aversion, causing businesses to postpone or cancel investment projects.
- Supply chain disruptions: Lingering supply chain disruptions and inflationary pressures increase the uncertainty around production costs and timelines, dampening investment enthusiasm.
- Capital expenditure decline: Data indicates a substantial decline in capital expenditure by businesses, confirming the impact of economic uncertainty on investment decisions.
Keywords: "business investment," "capital expenditure," "economic uncertainty," "supply chain disruptions," "geopolitical risk."
The Effect of Rising Interest Rates on Investment
Higher interest rates significantly impact investment decisions:
- Increased borrowing costs: Rising interest rates make borrowing more expensive, increasing the cost of capital for businesses undertaking investment projects. This directly discourages investment.
- Housing market slowdown: The housing market, a significant component of investment, has experienced a slowdown due to higher mortgage rates, impacting construction and related industries.
- Manufacturing investment decline: Higher borrowing costs also negatively affect investment in the manufacturing sector, which requires substantial capital expenditure. This is reflected in decreased manufacturing investment figures.
Keywords: "interest rate impact," "borrowing costs," "housing market slowdown," "manufacturing investment."
Analyzing the Effects of Tariffs on the U.S. Economy
Tariffs have played a role in contributing to the economic slowdown.
Tariff Impact on Import Prices and Inflation
Tariffs increase the price of imported goods, leading to higher inflation:
- Increased import prices: Tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, reducing consumer purchasing power and negatively impacting aggregate demand.
- Tariff impact on inflation: This increase in import prices contributes significantly to overall inflation, further squeezing consumer spending.
- Examples: Specific examples of tariffs on particular goods and their impact on prices can be cited here using data from relevant sources.
Keywords: "tariff impact on inflation," "import prices," "trade war," "protectionism."
Tariffs and Their Effect on Global Trade Relations
Tariffs have broader implications for global trade relations:
- Retaliatory tariffs: The imposition of tariffs by the U.S. often leads to retaliatory tariffs from other countries, negatively impacting U.S. exports.
- Trade relations deterioration: The overall impact is a deterioration in global trade relations, creating further economic uncertainty.
- Export decline: Data shows a decline in U.S. exports in certain sectors due to retaliatory tariffs.
Keywords: "trade relations," "retaliatory tariffs," "global trade," "export decline."
Conclusion: Understanding the 2% U.S. GDP Decline and Looking Ahead
The 2% decline in U.S. GDP is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of factors. Decreased consumer confidence leading to reduced spending, reduced business investment due to economic uncertainty and high interest rates, and the impact of tariffs on inflation and global trade relations all contributed significantly to this economic slowdown. Understanding these interconnected elements is crucial for navigating the current economic landscape.
Key Takeaways: The primary drivers of the GDP decline are a decrease in consumer spending due to inflation and interest rate hikes, a reduction in business investment fueled by economic uncertainty, and the negative impact of tariffs on prices and global trade.
Future Outlook: The outlook for the U.S. economy remains uncertain. The Federal Reserve's actions to combat inflation will continue to influence interest rates and consumer spending. The resolution of geopolitical uncertainties and supply chain disruptions will also play a critical role. Government policy responses will be crucial in shaping future economic growth.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving situation by regularly monitoring updates on GDP growth, consumer spending, and the impact of trade policies. Understanding U.S. GDP fluctuations is essential for making informed decisions and navigating the complexities of the current economic climate. Analyzing future GDP growth requires continued vigilance and a deep understanding of the factors influencing economic performance.

Featured Posts
-
 Guelsen Bubikoglu Ndan Esi Tuerker Inanoglu Icin Dolu Dolu Anilar
May 31, 2025
Guelsen Bubikoglu Ndan Esi Tuerker Inanoglu Icin Dolu Dolu Anilar
May 31, 2025 -
 Your Good Life A Personalized Plan For Success
May 31, 2025
Your Good Life A Personalized Plan For Success
May 31, 2025 -
 The Good Life A Roadmap To A Richer More Fulfilling Life
May 31, 2025
The Good Life A Roadmap To A Richer More Fulfilling Life
May 31, 2025 -
 One Night Only Brandon Inge Back In The Dugout In Kalamazoo
May 31, 2025
One Night Only Brandon Inge Back In The Dugout In Kalamazoo
May 31, 2025 -
 The Good Life Project Practical Steps For Lasting Happiness
May 31, 2025
The Good Life Project Practical Steps For Lasting Happiness
May 31, 2025
