30% Tariffs On Chinese Goods: A 2025 Outlook
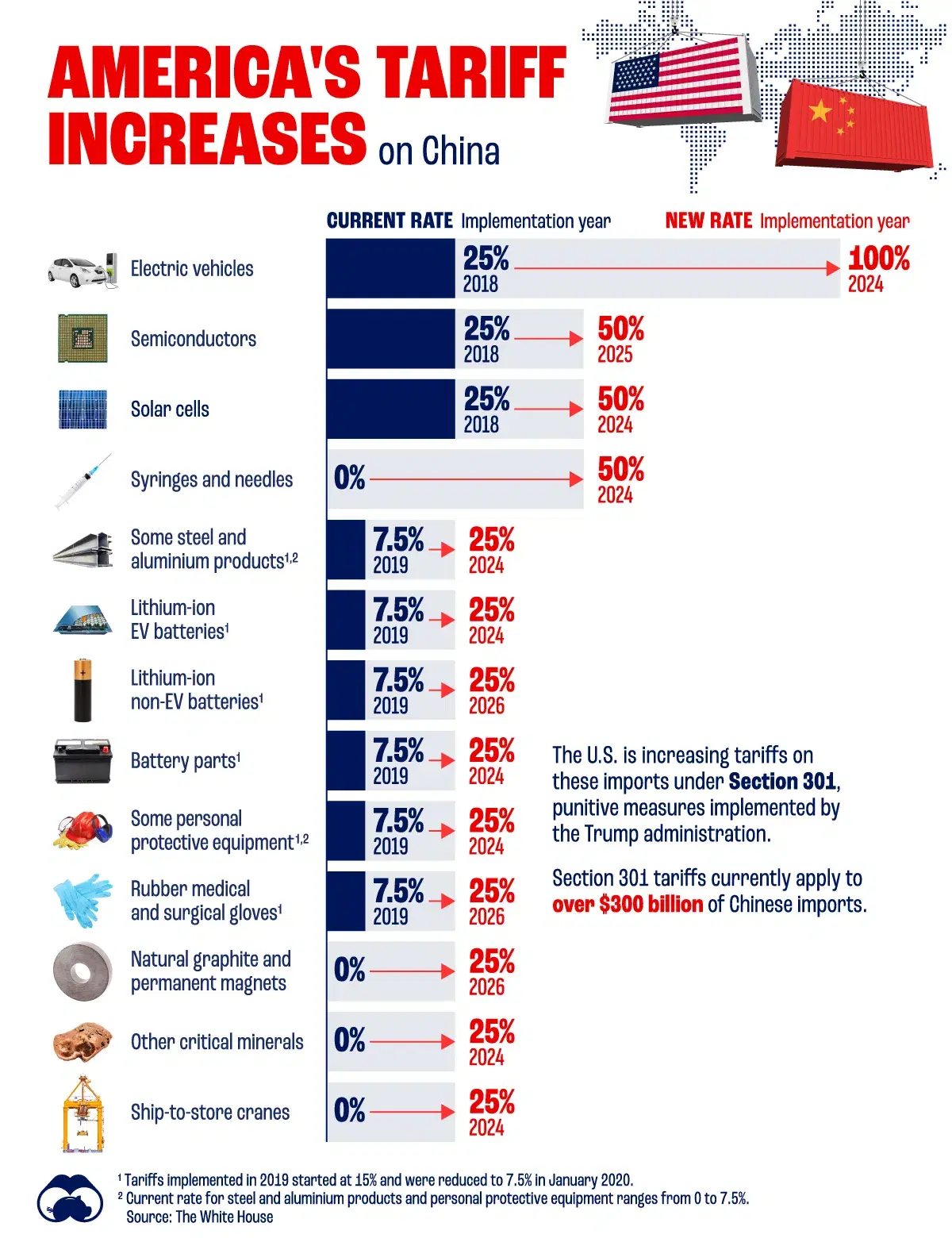
Table of Contents
Economic Impacts of the 30% Tariffs in 2025
The economic repercussions of the 30% tariffs on Chinese goods are multifaceted and far-reaching, significantly impacting consumers, businesses, and the global economy in 2025.
Impact on US Consumers
Increased prices for a wide range of consumer goods remain a significant concern. The 30% tariffs directly translate to higher costs for imported products, forcing consumers to absorb these increased prices or adjust their purchasing habits. This effect is amplified by inflation, creating a double burden on household budgets.
- Increased prices: Consumers will likely continue to experience higher prices for electronics, clothing, furniture, and countless other goods imported from China.
- Shifting consumer spending: Consumers may reduce spending on affected goods, opt for cheaper alternatives, or shift their purchasing power towards domestically produced goods.
- Inflationary pressures: The tariffs contribute to broader inflationary pressures, eroding purchasing power and impacting the overall cost of living.
Impact on US Businesses
Businesses relying heavily on Chinese imports face significant challenges. Manufacturers and retailers experience increased production costs, reduced competitiveness, and potential for business closures or relocation.
- Increased production costs: The tariffs directly increase the cost of imported goods, squeezing profit margins for businesses.
- Reduced competitiveness: US businesses face difficulty competing with foreign companies that source goods from countries without similar tariffs.
- Business closures and relocation: Some businesses may be forced to close due to unsustainable costs, while others may choose to relocate their operations to reduce reliance on Chinese imports. This includes exploring reshoring (returning production to the US) and nearshoring (moving production to nearby countries).
Impact on the Global Economy
The disruption of global supply chains caused by the tariffs continues to impact the global economy. The ripple effects are felt by countries beyond the US and China, altering trade patterns and potentially slowing global economic growth.
- Disrupted supply chains: The tariffs have forced businesses to find alternative suppliers, leading to delays, increased costs, and logistical complexities.
- Shifts in global trade patterns: Countries may seek new trading partners, leading to a restructuring of global trade routes and relationships.
- Impact on the WTO: The tariffs challenge the principles of the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the multilateral trading system, potentially leading to further trade disputes and fragmentation.
Political and Geopolitical Implications in 2025
The 30% tariffs on Chinese goods have profound political and geopolitical implications, shaping US-China relations and impacting international trade organizations.
US-China Relations
Tension between the US and China remains a significant concern. While the tariffs themselves might be adjusted or removed, the underlying tensions in the relationship persist, influencing future trade negotiations and diplomatic efforts.
- Continued trade negotiations: The possibility of future trade agreements or further escalation of trade disputes remains uncertain.
- Strained diplomatic relations: The trade war has damaged diplomatic relations between the US and China, impacting broader areas of cooperation.
- Potential for de-escalation or further conflict: The future trajectory of US-China relations depends on various factors including political will, economic pressures, and global geopolitical shifts.
Impact on International Trade Organizations
The 30% tariffs and the broader US-China trade war have challenged the effectiveness of the WTO and other international trade organizations. The emphasis on unilateral action raises questions about the future of multilateralism and global trade governance.
- Challenges to the WTO: The tariffs undermine the WTO's rules-based trading system and its ability to resolve trade disputes effectively.
- Impact on trade liberalization: The trade war has slowed progress on trade liberalization and raised doubts about the future of global trade cooperation.
- Potential for new trade agreements: The rise of regional trade agreements and bilateral deals may further fragment the global trading system.
Adaptation and Mitigation Strategies in 2025
Businesses and governments are actively pursuing strategies to mitigate the long-term effects of the tariffs. These strategies focus on reshoring, supply chain diversification, and technological innovation.
Reshoring and Nearshoring
The trend of companies relocating manufacturing back to the US or to nearby countries continues. This presents both opportunities and considerable challenges.
- Increased production costs: Reshoring can be expensive, requiring significant investment in infrastructure and labor.
- Infrastructure requirements: Adequate infrastructure is crucial for supporting reshored manufacturing, including transportation, energy, and technology.
- Labor market implications: Reshoring can create jobs but may also lead to labor shortages in certain sectors.
Diversification of Supply Chains
Businesses are actively diversifying their supply chains to reduce dependence on Chinese imports. This involves finding alternative suppliers in other countries.
- Finding alternative suppliers: Businesses are exploring sources in Southeast Asia, India, Mexico, and other regions.
- Logistical complexities: Managing multiple suppliers across different geographic locations adds logistical complexities.
- Quality control: Ensuring consistent quality and reliability from new suppliers requires careful vetting and monitoring. Technology plays an increasingly important role here, with sophisticated supply chain management software offering visibility and control.
Technological Innovation
Technological advancements play a key role in mitigating the impact of tariffs. Automation and other technological innovations can reduce reliance on imports and boost productivity.
- Automation and robotics: Increased automation can reduce labor costs and lessen reliance on imported components.
- 3D printing and additive manufacturing: These technologies can enable on-demand manufacturing and reduce reliance on global supply chains.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: AI and machine learning can optimize supply chains, improve efficiency, and predict potential disruptions.
Conclusion
The 30% tariffs on Chinese goods have had a profound and lasting impact on the global economy, US-China relations, and the international trading system. Looking ahead to 2025, the long-term effects are still unfolding. While some businesses have adapted through reshoring, nearshoring, and supply chain diversification, the overall economic and political landscape remains uncertain. The impact on consumers through increased prices and inflation will likely persist. Understanding the ongoing implications of these tariffs is crucial for businesses and consumers alike. To stay informed about the evolving situation and potential future developments regarding 30% tariffs on Chinese goods, continue your research by consulting reputable sources such as the World Trade Organization, the US Department of Commerce, and leading economic research institutions. Engage in discussions and share your perspectives to contribute to a better understanding of this crucial issue.

Featured Posts
-
 Toekomst Nederlandse Defensie Industrie Steun Voor Uitbreiding
May 18, 2025
Toekomst Nederlandse Defensie Industrie Steun Voor Uitbreiding
May 18, 2025 -
 Find Easy A On Bbc Three Hd Your Complete Tv Guide
May 18, 2025
Find Easy A On Bbc Three Hd Your Complete Tv Guide
May 18, 2025 -
 Taylor Swifts Reputation Taylors Version A Sneak Peek At Whats To Come
May 18, 2025
Taylor Swifts Reputation Taylors Version A Sneak Peek At Whats To Come
May 18, 2025 -
 Reddits New Policy Cracking Down On Violent Content Upvotes
May 18, 2025
Reddits New Policy Cracking Down On Violent Content Upvotes
May 18, 2025 -
 The Dark Side Of Gambling Betting On The Devastation Of The Los Angeles Wildfires
May 18, 2025
The Dark Side Of Gambling Betting On The Devastation Of The Los Angeles Wildfires
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Great Wolf Lodge Suffolk Boy Hailed A Hero For Saving Drowning Child
May 18, 2025
Great Wolf Lodge Suffolk Boy Hailed A Hero For Saving Drowning Child
May 18, 2025 -
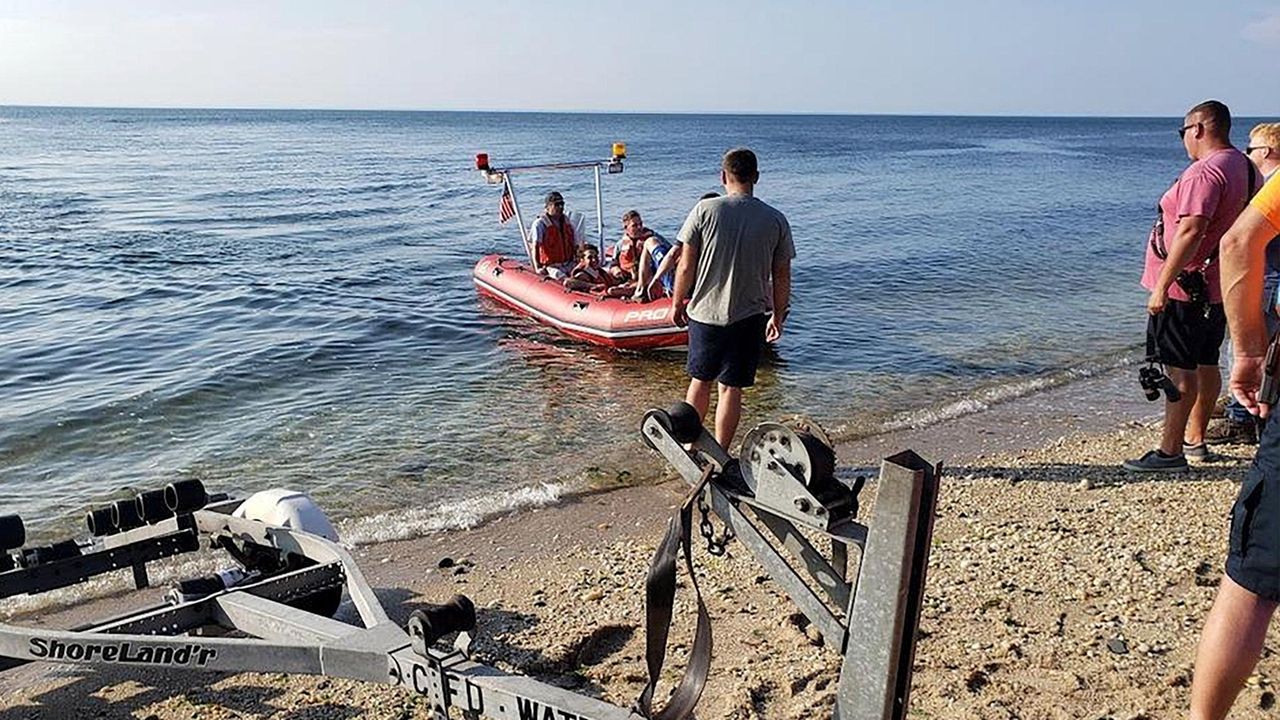 Suffolk Teen Praised For Bravery After Drowning Rescue At Great Wolf Lodge
May 18, 2025
Suffolk Teen Praised For Bravery After Drowning Rescue At Great Wolf Lodge
May 18, 2025 -
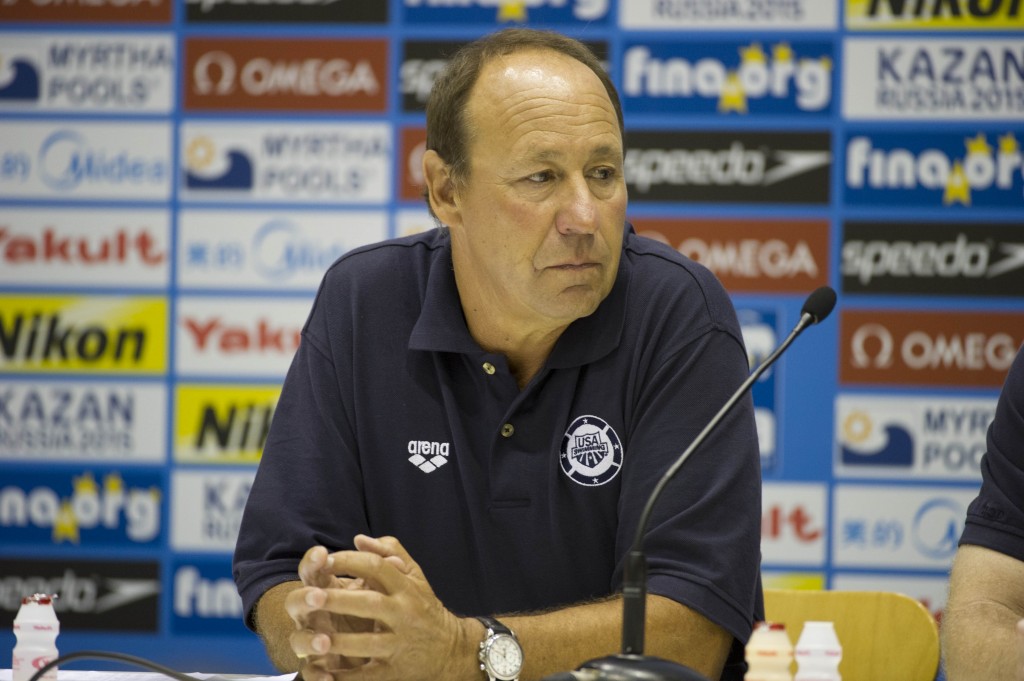 Swim With Mike A Support Network For Trojan Swimmers
May 18, 2025
Swim With Mike A Support Network For Trojan Swimmers
May 18, 2025 -
 Suffolk Boys Heroic Rescue At Great Wolf Lodge Saving A Drowning Child
May 18, 2025
Suffolk Boys Heroic Rescue At Great Wolf Lodge Saving A Drowning Child
May 18, 2025 -
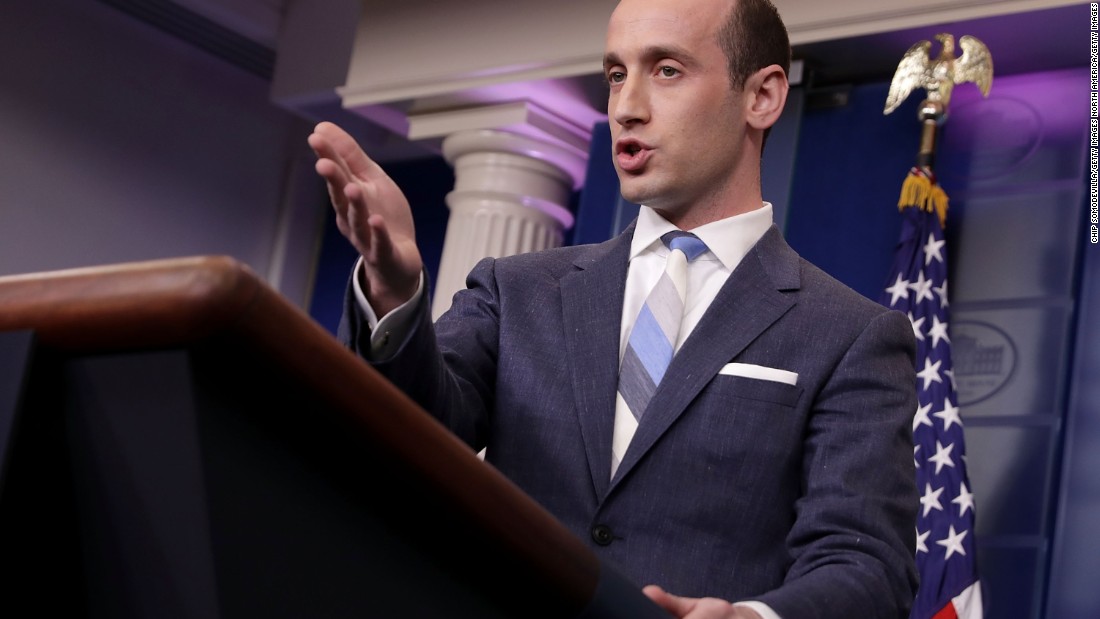 Stephen Miller Eyed For National Security Advisor Role Amidst Waltz Speculation
May 18, 2025
Stephen Miller Eyed For National Security Advisor Role Amidst Waltz Speculation
May 18, 2025
