A Look At F1 Greats: Successes And Failures After 40

Table of Contents
The Challenges of Age in F1
The physical and mental demands of Formula 1 racing are immense, making it a particularly challenging sport for older athletes. As drivers age, several factors can impact their performance.
Physical Demands
The physical strain of F1 racing is immense, even for younger drivers. The G-forces experienced during cornering, braking, and acceleration take a toll on the body, and this toll increases with age. Aging impacts reaction time, stamina, and neck strength – all crucial for optimal performance.
- Increased risk of injury: Older bodies are more susceptible to injuries and take longer to heal.
- Longer recovery times: The physical exertion of a race weekend leaves older drivers needing more time to recover between sessions.
- Need for specialized training regimens: Maintaining peak physical condition requires rigorous and specialized training programs tailored to the specific demands of F1 racing and the aging process.
For example, some veteran drivers have openly discussed the increased difficulty in maintaining neck strength, a critical factor in managing the G-forces experienced during high-speed cornering. The physical demands often contribute to a decline in performance as drivers age beyond 40.
Adapting to Technological Advancements
F1 technology advances relentlessly. New car designs, sophisticated electronics, and ever-changing regulations demand constant learning and adaptation. Older drivers often face steeper learning curves when adapting to these new systems.
- Difficulty mastering new car setups: Understanding and optimizing the complex setup of modern F1 cars requires significant time and effort. Older drivers might find this more challenging than their younger counterparts.
- Adjusting to different driving styles demanded by technological shifts: Technological advancements often necessitate changes in driving styles. Adapting to these changes can be difficult for drivers accustomed to older techniques.
- Reliance on engineering teams for adaptation: Experienced drivers frequently rely more heavily on their engineering teams to help bridge the knowledge gap presented by rapid technological changes.
Consider the contrast between a younger driver quickly mastering a new car's setup and a veteran driver struggling to find the optimal balance – the technological gap can be significant.
Notable Successes After 40
Despite the challenges, several F1 drivers have achieved remarkable success after turning 40, demonstrating that experience and strategic mastery can outweigh a decline in raw speed.
Strategic Mastery and Experience
Experience in F1 is invaluable. While younger drivers might possess superior reflexes, older drivers often demonstrate superior racecraft and tactical awareness.
- Superior racecraft: Years of experience translate into refined driving skills, enabling drivers to manage challenging situations with greater finesse.
- Tactical awareness: Experienced drivers excel at reading the race, anticipating opponents' moves, and strategically managing resources.
- Ability to manage tires and fuel efficiently: Conserving resources is crucial in F1. Experienced drivers often have a greater understanding of tire management and fuel efficiency.
- Mentorship of younger teammates: Older drivers can provide valuable guidance and support to younger teammates, boosting overall team performance.
Niki Lauda's incredible comeback after a near-fatal crash is a prime example of this strategic mastery, as is Alain Prost's calculated and consistently successful approach throughout his career.
Mentorship and Team Leadership
Beyond their on-track performance, experienced F1 drivers over 40 often play crucial roles as mentors and team leaders.
- Sharing knowledge with younger drivers: Older drivers can impart years of accumulated knowledge and insights, fostering a positive learning environment within the team.
- Improving team morale: Their experience and leadership can improve team morale, fostering a cohesive and productive environment.
- Providing valuable insights into car development: Their insights into car behavior and performance can be invaluable to engineers during car development.
Many examples exist of drivers who, past 40, significantly contributed to team dynamics and development beyond their driving abilities.
Failures and the End of the Line
While some drivers thrive after 40, others eventually face performance decline and the difficult decision to retire.
Performance Decline and the Pressure to Retire
The inevitable physical decline can impact performance, leading to consistent poor results and struggles against younger, faster drivers. The pressure to retire gracefully can be immense.
- Consistent poor results: Persistent underperformance puts pressure on both the driver and the team.
- Struggles to keep up with younger drivers: The speed and reflexes of younger drivers become increasingly difficult to match.
- Financial pressures to retire: Teams might opt for younger, less expensive drivers.
- Emotional challenges of accepting the end of a career: Retirement marks the end of a significant chapter in a driver's life, presenting emotional challenges.
Many drivers have faced these challenges, demonstrating that even the greatest F1 careers eventually come to an end.
The Psychological Impact of Aging Out
Retiring from F1 after years of competition can have a significant psychological impact.
- Dealing with diminished status: The transition from a high-profile athlete to a private citizen requires adjustment.
- Loss of identity tied to racing: For many drivers, their identity is heavily intertwined with their racing career. Retirement requires redefining their sense of self.
- Adaptation to life outside of F1: Finding new purpose and fulfillment after leaving such a demanding and high-profile career is crucial.
Examples abound of drivers successfully transitioning into new careers or enjoying fulfilling lives outside the sport, highlighting the adaptability and resilience of these individuals.
Conclusion
This look at F1 drivers over 40 reveals a complex picture. While the physical and technological challenges are undeniable, the strategic brilliance, experience, and leadership qualities of older drivers can still significantly contribute to a team's success. Ultimately, the longevity of an F1 driver's career depends on a combination of physical fitness, adaptability, and the ability to navigate the evolving landscape of the sport. To further explore the fascinating careers of these seasoned professionals, keep searching for more insights into F1 drivers over 40, and their unique contributions to the world of Formula 1.

Featured Posts
-
 Jamie Foxxs All Star Weekend The Casting Of Robert Downey Jr And Representation
May 26, 2025
Jamie Foxxs All Star Weekend The Casting Of Robert Downey Jr And Representation
May 26, 2025 -
 Kuluep Krizi Doert Oenemli Oyuncu Sorusturmada
May 26, 2025
Kuluep Krizi Doert Oenemli Oyuncu Sorusturmada
May 26, 2025 -
 Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Aksi Pembalap Di Race Sprint 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025
Live Streaming Moto Gp Inggris Saksikan Aksi Pembalap Di Race Sprint 20 00 Wib
May 26, 2025 -
 Staying Safe During Flash Floods Essential Information On Flood Alerts
May 26, 2025
Staying Safe During Flash Floods Essential Information On Flood Alerts
May 26, 2025 -
 Jenson Fw 22 Extended Features And Details
May 26, 2025
Jenson Fw 22 Extended Features And Details
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Lotto Officials Confirm Winning Euro Millions Ticket Locations In Ireland
May 28, 2025
Lotto Officials Confirm Winning Euro Millions Ticket Locations In Ireland
May 28, 2025 -
 Six Figure Euro Millions Prizes Claimed Locations Revealed In Ireland
May 28, 2025
Six Figure Euro Millions Prizes Claimed Locations Revealed In Ireland
May 28, 2025 -
 Irelands Euro Millions Winners Locations Of Six Figure Prizes Confirmed
May 28, 2025
Irelands Euro Millions Winners Locations Of Six Figure Prizes Confirmed
May 28, 2025 -
 Six Weeks Remain To Claim Your 1 Million National Lottery Win
May 28, 2025
Six Weeks Remain To Claim Your 1 Million National Lottery Win
May 28, 2025 -
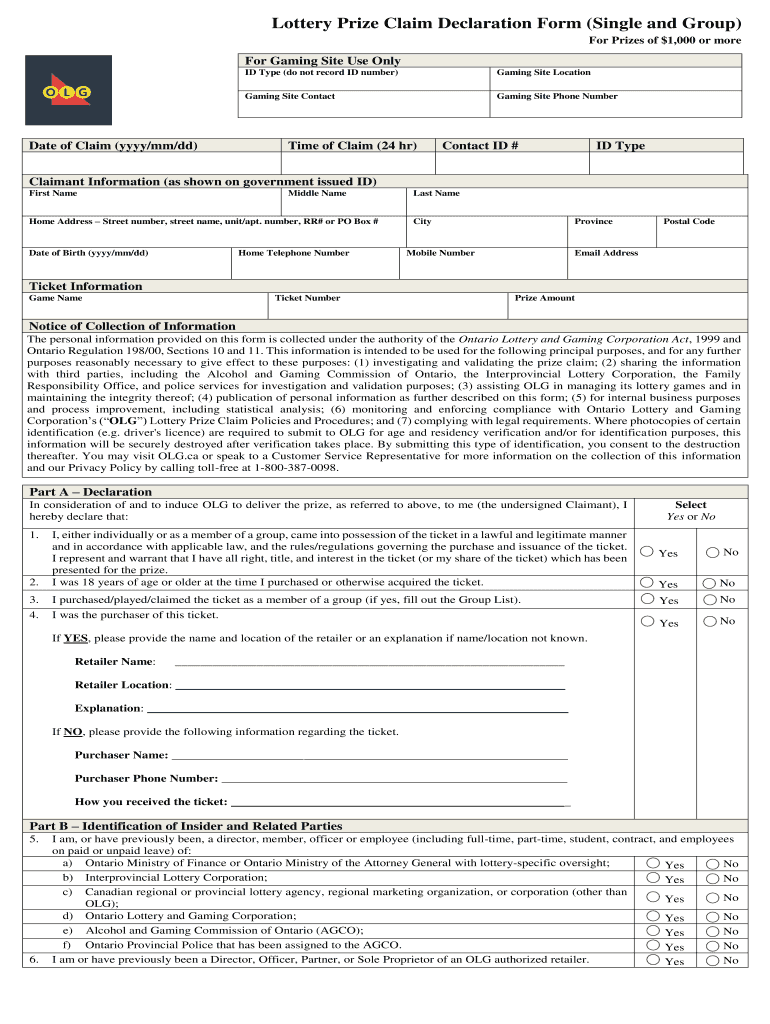 1 Million National Lottery Prize Winner Urged To Claim Before Deadline
May 28, 2025
1 Million National Lottery Prize Winner Urged To Claim Before Deadline
May 28, 2025
