Algorithms And Mass Violence: Exploring Corporate Responsibility In Radicalization

Table of Contents
We will define key terms to establish a common understanding. Algorithms, in this context, refer to the sets of rules and statistical models used by online platforms to personalize content, recommend connections, and display advertisements. Mass violence encompasses acts of violence targeting multiple victims, often motivated by ideological or political aims. Radicalization is the process by which individuals adopt extreme political, social, or religious beliefs and are prepared to engage in violence to achieve their objectives. This article argues that corporations have a moral and potentially legal responsibility to mitigate the role their algorithms play in facilitating radicalization and mass violence.
The Role of Algorithms in Spreading Extremist Ideologies
Algorithms are not inherently malicious, but their design and implementation on social media and other online platforms significantly contribute to the spread of extremist ideologies. The ways in which algorithms facilitate this spread are multifaceted and deeply concerning.
Echo Chambers and Filter Bubbles
Algorithmic personalization creates echo chambers and filter bubbles. These personalized feeds reinforce pre-existing beliefs by showing users only content that aligns with their views, limiting exposure to diverse perspectives and potentially radicalizing them further.
- Examples: Facebook's newsfeed, YouTube's recommendation system, and Twitter's trending topics algorithm all contribute to the formation of echo chambers.
- Psychological Mechanisms: Confirmation bias, the tendency to favor information confirming pre-existing beliefs, is heavily amplified within these echo chambers. This leads to increased polarization and a decreased ability to critically evaluate opposing viewpoints.
Targeted Advertising and Content Recommendation
Algorithms are used to target individuals with extremist propaganda, increasing the likelihood of radicalization. Extremist groups leverage these systems to precisely reach vulnerable populations with tailored messages.
- Examples: Targeted Facebook ads promoting extremist groups, YouTube recommendations suggesting radical content to users with similar viewing histories.
- Challenges: Detecting and mitigating such targeted advertising is incredibly difficult due to the sophisticated techniques employed by extremist groups and the sheer volume of content online.
Algorithmic Amplification of Hate Speech and Violence
Algorithms prioritize engagement over safety, unintentionally (or intentionally) amplifying hateful content and increasing the risk of real-world violence. The pursuit of maximizing user engagement often leads to the prioritization of sensational or emotionally charged content, including hate speech and violent extremism.
- Examples: Trending topics on Twitter that amplify hate speech, YouTube's recommendation algorithm suggesting increasingly radical videos.
- Technical Limitations: Identifying and removing harmful content effectively is a significant technical challenge, due to the scale of the internet and the constant evolution of extremist tactics.
Corporate Responsibility and Ethical Considerations
The pervasive influence of algorithms on the spread of extremist ideologies raises crucial questions about corporate responsibility and ethical considerations.
Duty of Care and Prevention
Corporations have a duty of care to protect their users from harmful content and prevent the spread of extremist ideologies. This involves proactive measures to mitigate the risks associated with their algorithms.
- Best Practices: Implementing robust content moderation systems, designing algorithms that prioritize safety over engagement, and investing in artificial intelligence to detect hate speech and extremist content.
- Legal and Ethical Frameworks: Existing laws regarding online safety and hate speech, along with emerging ethical guidelines, are relevant in defining this duty of care.
Transparency and Accountability
Greater transparency in algorithmic design and decision-making, along with increased accountability for the consequences of algorithmic choices, is essential. This includes understanding how algorithms contribute to the spread of harmful content and taking responsibility for the impact.
- Measures for Increased Transparency: Algorithmic audits conducted by independent experts, public reports detailing the design and impact of algorithms, and open-source algorithmic components.
- Balancing Transparency and Proprietary Interests: This is a significant challenge, as companies often view their algorithms as trade secrets. However, the societal impact of these algorithms necessitates a shift towards greater transparency.
Collaboration and Regulation
Collaboration between corporations, governments, and civil society is crucial in addressing the problem of algorithmic-driven radicalization. A multi-stakeholder approach is needed to develop effective strategies for preventing online radicalization.
- Successful Collaborations and Regulatory Frameworks: Examples include initiatives promoting media literacy, government regulations targeting online hate speech, and collaborations between tech companies and civil society organizations to combat online extremism.
- Ongoing Debate: The debate surrounding online regulation and freedom of speech is ongoing and complex, requiring careful consideration of both individual rights and the collective need for online safety.
Algorithms and Mass Violence: A Call for Corporate Accountability
Algorithms play a significant role in facilitating the spread of extremist ideologies and the resulting mass violence. Corporations have a moral and legal responsibility to mitigate these risks. We must demand that corporations take proactive steps to address the role their algorithms play in fueling algorithms and mass violence. This requires a collective effort involving corporations, policymakers, and civil society to develop effective strategies for preventing online radicalization and promoting a safer digital environment. The future of online safety and the prevention of mass violence hinges on a fundamental shift in corporate responsibility toward algorithmic transparency and ethical design. Demand better from the tech giants – demand accountability for algorithms and mass violence.

Featured Posts
-
 Hl Stnjh Alatfaqyat Aljdydt Fy Hl Azmt Almyah Byn Alardn Wswrya
May 30, 2025
Hl Stnjh Alatfaqyat Aljdydt Fy Hl Azmt Almyah Byn Alardn Wswrya
May 30, 2025 -
 Nyc Lush Spa 30 Minute Bubble Bath Booking 75
May 30, 2025
Nyc Lush Spa 30 Minute Bubble Bath Booking 75
May 30, 2025 -
 Deutsche Bank Appointed Depositary Bank For Epiroc Adr Programs
May 30, 2025
Deutsche Bank Appointed Depositary Bank For Epiroc Adr Programs
May 30, 2025 -
 Unprecedented Late Winter Storm In San Diego
May 30, 2025
Unprecedented Late Winter Storm In San Diego
May 30, 2025 -
 Addressing Heatwave Mortality Lessons From 311 Deaths In England
May 30, 2025
Addressing Heatwave Mortality Lessons From 311 Deaths In England
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Deadly Wildfires Rage In Eastern Manitoba Update On Contained And Uncontained Fires
May 31, 2025
Deadly Wildfires Rage In Eastern Manitoba Update On Contained And Uncontained Fires
May 31, 2025 -
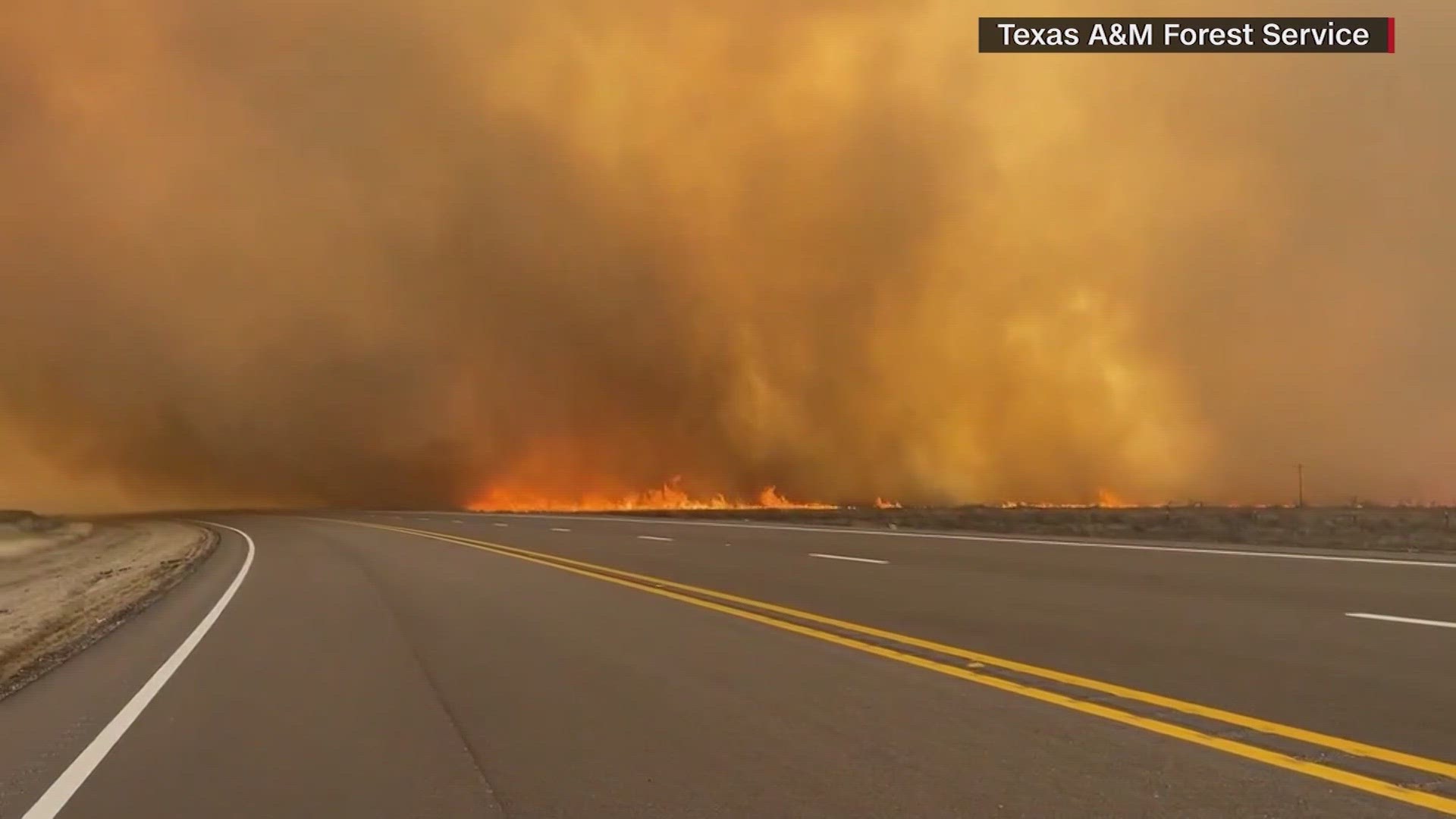 Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Renewal
May 31, 2025
Texas Panhandle Wildfire A Year Of Recovery And Renewal
May 31, 2025 -
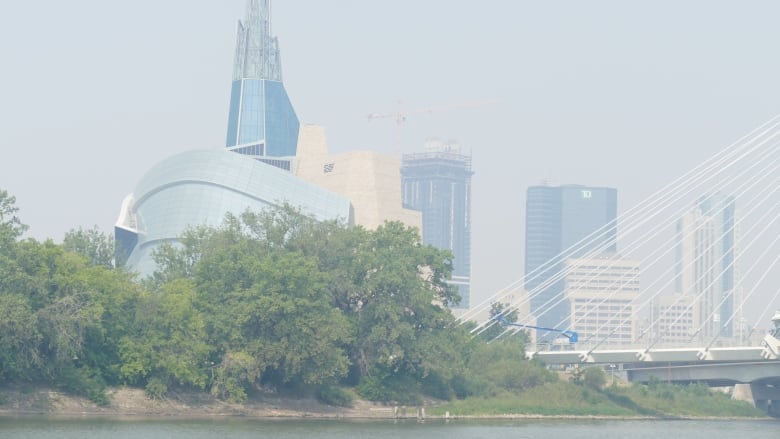 Eastern Manitoba Wildfires Ongoing Battle Against Uncontrolled Fires
May 31, 2025
Eastern Manitoba Wildfires Ongoing Battle Against Uncontrolled Fires
May 31, 2025 -
 Beauty From The Ashes Texas Panhandles Wildfire Recovery One Year Later
May 31, 2025
Beauty From The Ashes Texas Panhandles Wildfire Recovery One Year Later
May 31, 2025 -
 Newfoundland Wildfires Emergency Response To Widespread Destruction
May 31, 2025
Newfoundland Wildfires Emergency Response To Widespread Destruction
May 31, 2025
