Analyzing The Canadian Dollar's Overvaluation Against The Greenback
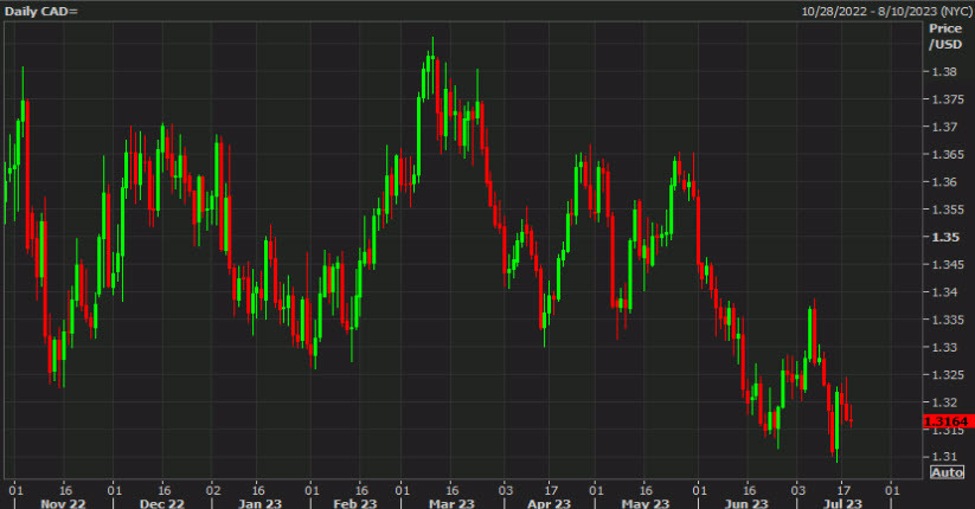
Table of Contents
Factors Contributing to CAD Overvaluation
Several interconnected factors contribute to the potential overvaluation of the Canadian dollar against the greenback. Let's delve into the key drivers:
Strong Commodity Prices
Canada's economy is heavily reliant on its natural resources. High prices for oil, natural gas, and other commodities significantly boost the Canadian dollar. Increased global demand for these resources leads to a surge in Canadian exports, increasing the demand for CAD and strengthening its value against the USD.
- Canadian commodity prices: The price of West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil, a key benchmark, directly impacts the CAD. Similarly, natural gas prices and the price of other Canadian exports like lumber and potash play a significant role.
- CAD strength: As commodity prices rise, so does the CAD, making Canadian exports more expensive for international buyers. This is a double-edged sword; while it benefits producers, it can hurt overall export volume.
- Resource-based economy: Canada's dependence on its resource sector makes it particularly vulnerable to fluctuations in global commodity markets. This inherent volatility impacts the CAD's strength.
Interest Rate Differentials
The Bank of Canada's monetary policy plays a crucial role in influencing the CAD/USD exchange rate. Higher interest rates in Canada compared to the United States attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the CAD. This influx of capital strengthens the Canadian dollar.
- Interest rate policy: The Bank of Canada's decisions on interest rates directly impact the attractiveness of Canadian investments. Higher rates incentivize foreign investors seeking higher returns.
- Bank of Canada: The Bank's actions are closely watched by global markets, and any changes in its monetary policy can significantly affect the CAD/USD exchange rate.
- CAD interest rates: A widening gap between Canadian and US interest rates generally strengthens the CAD.
- USD interest rates: Conversely, a rise in US interest rates can weaken the CAD as investors shift their funds to higher-yielding US assets.
Geopolitical Factors
Global events significantly influence currency markets. Geopolitical instability or uncertainty can impact the CAD/USD exchange rate, depending on how it affects the perceived safety of each currency.
- Geopolitical risk: Events like the war in Ukraine create uncertainty and can lead investors to seek safe-haven assets. The CAD, often viewed as a relatively stable currency, might benefit in such situations.
- Safe-haven currency: While the USD is traditionally considered a safe-haven currency, the CAD can sometimes benefit from flight-to-safety flows depending on the specific geopolitical event.
- Global economic uncertainty: Periods of global economic uncertainty can lead to increased volatility in the CAD/USD exchange rate as investors reassess their risk exposure.
- CAD/USD volatility: Geopolitical factors are a major source of short-term volatility in the CAD/USD exchange rate.
US Dollar Weakness
The overvaluation of the CAD might also be partly attributed to a weakening US dollar. Various factors can contribute to USD weakness.
- USD weakness: A weakening USD generally makes other currencies, including the CAD, appear stronger by comparison.
- US inflation: High inflation in the United States erodes the purchasing power of the USD, potentially leading to its depreciation.
- Federal Reserve policy: The Federal Reserve's monetary policy decisions significantly impact the USD's value. Changes in interest rates or quantitative easing programs can affect the USD's strength.
Implications of CAD Overvaluation
A strong Canadian dollar has both positive and negative implications for various stakeholders:
Impact on Canadian Exports
A strong CAD makes Canadian goods and services more expensive for international buyers, potentially harming export growth. This negatively impacts Canadian businesses that rely on exports.
- Canadian exports: A high CAD reduces the competitiveness of Canadian exports in global markets.
- Trade balance: A strong CAD can lead to a widening trade deficit as imports become cheaper and exports become more expensive.
- Competitiveness: Canadian businesses face increased challenges in competing with producers from countries with weaker currencies.
Impact on Canadian Businesses
Canadian businesses, particularly those involved in international trade, face significant challenges due to a strong CAD.
- Canadian businesses: Increased import costs can squeeze profit margins, while reduced export revenue can hurt overall profitability.
- Import costs: A strong CAD makes imports cheaper, but this benefit is often offset by lower export revenues.
- Profit margins: Businesses might see reduced profit margins as the cost of imported goods remains unchanged, while export revenue diminishes.
- International trade: Companies involved in international trade are particularly vulnerable to currency fluctuations.
Impact on Canadian Investors
Canadian investors holding CAD and USD assets must consider the impact of currency fluctuations on their portfolios.
- Canadian investments: Investors holding primarily CAD-denominated assets might see reduced returns when the CAD appreciates against other currencies.
- Currency risk: Understanding currency risk and implementing appropriate hedging strategies is vital for managing portfolio risk.
- Portfolio diversification: Diversifying investments across different currencies and asset classes can help mitigate currency risk.
- Investment strategies: Investors need to adapt their investment strategies to account for the potential impact of CAD fluctuations.
Conclusion: Understanding the Canadian Dollar's Overvaluation
The potential overvaluation of the Canadian dollar against the greenback is a complex issue driven by a combination of strong commodity prices, interest rate differentials, geopolitical factors, and US dollar weakness. This overvaluation presents significant challenges for Canadian exporters and businesses, impacting their competitiveness and profitability. Investors must also carefully consider currency risk when managing their portfolios. To navigate these complexities, stay informed about the Canadian dollar's value, monitor the CAD/USD exchange rate closely, and consult financial advisors for guidance on navigating the Canadian dollar's fluctuations. Learn more about analyzing the Canadian dollar's performance to make informed decisions.

Featured Posts
-
 2025 Bitcoin Conference Seouls Hub For Global Leaders
May 08, 2025
2025 Bitcoin Conference Seouls Hub For Global Leaders
May 08, 2025 -
 Oklahoma City Thunder Vs Houston Rockets Where To Watch Betting Preview And Game Predictions
May 08, 2025
Oklahoma City Thunder Vs Houston Rockets Where To Watch Betting Preview And Game Predictions
May 08, 2025 -
 Ahtsab Edaltwn Ka Khatmh Lahwr Myn 5 Edaltyn Bnd
May 08, 2025
Ahtsab Edaltwn Ka Khatmh Lahwr Myn 5 Edaltyn Bnd
May 08, 2025 -
 Hollywood Shutdown Double Strike Cripples Film And Television
May 08, 2025
Hollywood Shutdown Double Strike Cripples Film And Television
May 08, 2025 -
 Check Todays Lotto Results Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025
Check Todays Lotto Results Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025
