Analyzing The Economic Impact Of The Student Loan Debt Crisis
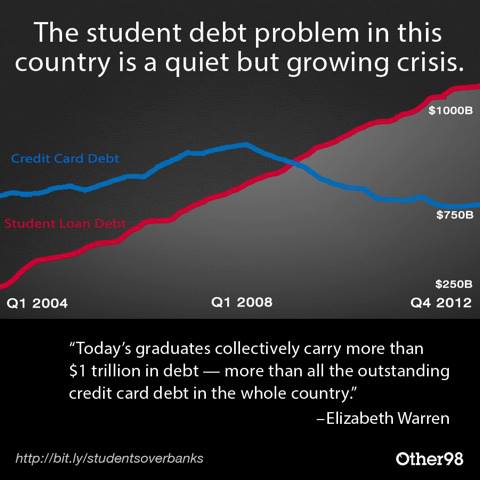
Table of Contents
Impact on Individual Finances and Consumer Spending
The weight of student loan debt significantly impacts borrowers' financial well-being and their ability to participate fully in the economy.
Reduced Disposable Income: Student loan payments often consume a substantial portion of borrowers' income, leaving less for essential expenses and discretionary spending. This has a ripple effect throughout the economy.
- Reduced consumer spending hampers economic growth. Less money available for purchases means decreased demand for goods and services, slowing overall economic expansion.
- Increased reliance on credit cards and high-interest loans exacerbates financial strain. Borrowers may resort to high-cost credit to meet their needs, further trapping them in a cycle of debt.
- Delayed major life milestones like homeownership and starting a family. The financial burden of student loans can postpone significant life events, impacting long-term financial stability and family formation.
Impact on Savings and Investment: The burden of student loan debt often translates to decreased savings and limited investment opportunities, hindering long-term financial security.
- Lower retirement savings contributions. With less disposable income, borrowers may struggle to contribute adequately to retirement plans, jeopardizing their financial future.
- Inability to save for emergencies or unexpected expenses. Lack of savings leaves borrowers vulnerable to financial shocks, potentially leading to further debt accumulation.
- Limited access to homeownership and wealth-building opportunities. High student loan debt can significantly reduce the chances of homeownership, a primary avenue for wealth building in many societies.
Macroeconomic Effects and National Economic Growth
The student loan debt crisis has profound macroeconomic effects, impacting national economic growth and overall prosperity.
Dampened Consumer Demand: Reduced consumer spending, a direct consequence of high student loan debt, negatively impacts aggregate demand, slowing down overall economic growth.
- Businesses experience decreased sales and profits. Lower consumer spending directly translates to reduced business revenue and profitability.
- Slowdown in job creation due to reduced economic activity. Weak consumer demand can lead to businesses scaling back operations and reducing hiring.
- Potential for deflationary pressures. Sustained low consumer demand can contribute to deflationary pressures, potentially harming the economy.
Impact on Entrepreneurship and Innovation: High student loan debt can deter individuals from pursuing entrepreneurial ventures, hindering innovation and economic dynamism.
- Fear of financial risk due to existing debt burden. The weight of student loan debt can discourage individuals from taking on the risks associated with starting a business.
- Limited access to capital for new ventures. Existing debt may make it difficult for borrowers to secure additional funding for new business ventures.
- Reduced entrepreneurial activity compared to countries with lower student debt. Countries with lower student loan burdens often see higher rates of entrepreneurship and innovation.
Sectoral Impacts and Related Industries
The student loan debt crisis significantly impacts various sectors of the economy, creating both opportunities and challenges.
Higher Education Industry: The student loan crisis raises concerns about the sustainability of the higher education model and the affordability of college tuition.
- Pressure to increase tuition despite affordability concerns. Colleges may increase tuition to compensate for declining government funding, further exacerbating the debt crisis.
- Increased reliance on student loan funding for institutional budgets. Colleges increasingly depend on student loan revenue, creating a financial incentive to maintain high tuition costs.
- Potential for declining enrollment if affordability issues aren't addressed. The high cost of education coupled with significant debt may deter potential students from pursuing higher education.
Financial Services Industry: The student loan debt crisis creates opportunities and challenges for the financial services industry, including debt collection agencies and loan servicers.
- Growth of the debt collection industry. The increasing number of delinquent student loans fuels the growth of the debt collection industry.
- Increased demand for student loan refinancing and consolidation services. The complexity of student loan repayment creates a demand for refinancing and consolidation services.
- Ethical concerns surrounding predatory lending practices. The student loan industry has faced criticism regarding predatory lending practices targeting vulnerable borrowers.
Conclusion
The student loan debt crisis presents a significant economic challenge with far-reaching consequences. From reduced consumer spending and dampened economic growth to its impact on entrepreneurship and the higher education industry, the implications are profound and require urgent attention. Addressing this crisis demands a multifaceted approach, including exploring loan forgiveness programs, promoting affordable higher education, and implementing responsible lending practices. Understanding the full economic impact of the student loan debt crisis is crucial for developing effective solutions and fostering a more economically sustainable and equitable future. We must act now to mitigate the severe consequences of the student loan debt crisis and create a system that promotes access to affordable higher education without crippling future generations with unsustainable debt.

Featured Posts
-
 Cek Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Timur Hujan 6 Mei 2024
May 28, 2025
Cek Prakiraan Cuaca Jawa Timur Hujan 6 Mei 2024
May 28, 2025 -
 Mundial De Atletismo Nanjing 2023 La Seleccion Espanola Confirmada
May 28, 2025
Mundial De Atletismo Nanjing 2023 La Seleccion Espanola Confirmada
May 28, 2025 -
 Personal Loan Interest Rates A Complete Guide For 2024
May 28, 2025
Personal Loan Interest Rates A Complete Guide For 2024
May 28, 2025 -
 Georgia Senate Race 2026 Ossoffs Focus On Protecting Healthcare
May 28, 2025
Georgia Senate Race 2026 Ossoffs Focus On Protecting Healthcare
May 28, 2025 -
 Avis Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go Performances Et Fonctionnalites
May 28, 2025
Avis Samsung Galaxy S25 Ultra 256 Go Performances Et Fonctionnalites
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Air Jordan June 2025 Release Dates Everything You Need To Know
May 29, 2025
Air Jordan June 2025 Release Dates Everything You Need To Know
May 29, 2025 -
 The Family Of Taylor Dearden A Closer Look
May 29, 2025
The Family Of Taylor Dearden A Closer Look
May 29, 2025 -
 Hl Ansf Alqwmu Tamlat Fy Dhkra Alastqlal
May 29, 2025
Hl Ansf Alqwmu Tamlat Fy Dhkra Alastqlal
May 29, 2025 -
 Flagowa Inwestycja Pcc Analiza Potencjalnych Opoznien I Zwiekszonych Kosztow
May 29, 2025
Flagowa Inwestycja Pcc Analiza Potencjalnych Opoznien I Zwiekszonych Kosztow
May 29, 2025 -
 Taylor Dearden Information On Her Family Background
May 29, 2025
Taylor Dearden Information On Her Family Background
May 29, 2025
