Assessing The Federal Reserve's Next Move: Inflation And Rate Hikes
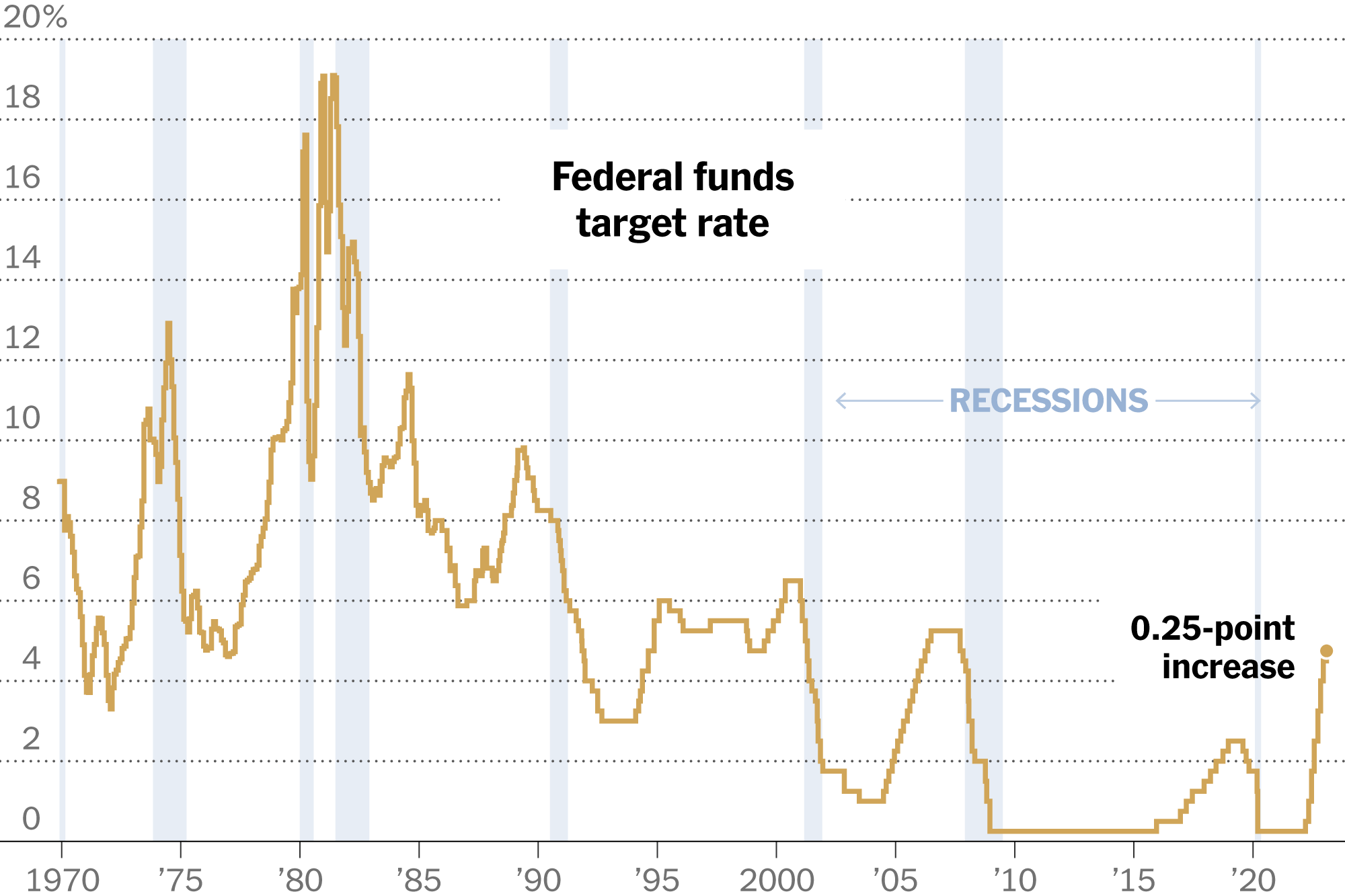
Table of Contents
Current Inflationary Pressures
Core Inflation and its Persistence
The persistence of core inflation, which excludes volatile food and energy prices, is a major headache for the Fed. Core inflation is a key indicator because it reflects underlying price pressures in the economy. Its stubborn refusal to decline suggests that inflationary pressures are deeply entrenched.
- Recent CPI and PCE data: Recent data from the Consumer Price Index (CPI) and Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, the Fed's preferred inflation gauge, continue to show elevated core inflation. While headline inflation may fluctuate, the persistent rise in core inflation signals that broader price increases are at play.
- Contributing factors: Several factors contribute to this persistent core inflation. Supply chain disruptions, though easing, continue to impact prices. Robust wage growth, while positive for workers, also fuels inflation if not matched by productivity gains. Strong consumer demand, fueled by pent-up savings and robust employment, keeps upward pressure on prices. The Fed needs to see substantial improvement in these areas before considering a pause in rate hikes.
The Impact of Global Factors on US Inflation
Global events significantly influence US inflation, complicating the Fed's decision-making process. The war in Ukraine, for example, has drastically increased energy prices, impacting inflation worldwide, including in the US.
- Global supply chains and commodity prices: Disruptions to global supply chains, partly stemming from geopolitical instability, continue to elevate the prices of various goods. Commodity prices, particularly energy and food, remain volatile and sensitive to global events.
- Geopolitical instability: Geopolitical uncertainty creates volatility in global markets, impacting inflation through various channels including energy prices, supply chain disruptions, and investor sentiment. This makes it difficult for the Fed to accurately predict future inflationary trends.
The Fed's Tools and Strategies
The Federal Funds Rate and its Mechanism
The Fed's primary tool for influencing inflation is the federal funds rate – the target rate that banks charge each other for overnight loans. Adjustments to this rate ripple through the entire financial system.
- Defining the federal funds rate: The federal funds rate is a short-term interest rate that serves as a benchmark for other interest rates in the economy.
- Impact on borrowing costs: Raising the federal funds rate increases borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, reducing demand and potentially curbing inflation. Lowering the rate has the opposite effect.
- Ripple effect on investment and economic activity: Changes in the federal funds rate significantly impact investment decisions and overall economic activity. Higher rates can cool down an overheated economy, while lower rates can stimulate growth.
Quantitative Tightening (QT) and its Role
Quantitative tightening (QT) is another tool the Fed employs to control inflation. It involves reducing the money supply by allowing Treasury securities and agency mortgage-backed securities to mature without reinvestment.
- Defining quantitative tightening: QT is the opposite of quantitative easing (QE), where the Fed buys assets to increase the money supply.
- Reducing market liquidity: QT reduces the amount of money circulating in the economy, putting downward pressure on inflation by lessening demand.
- Impact on bond yields and market stability: QT can lead to higher bond yields, potentially impacting market stability. The Fed carefully monitors these effects to avoid unintended consequences.
Potential Economic Scenarios and Risks
The Risk of a Recession
Aggressive rate hikes increase the risk of a recession. The Fed must carefully balance its inflation-fighting efforts with the need to avoid triggering a significant economic downturn.
- Current economic indicators: The Fed closely monitors key economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer confidence to assess the state of the economy and gauge the impact of its policies.
- Relationship between interest rate hikes and recessionary risk: History shows a correlation between aggressive interest rate hikes and subsequent recessions. The lag effect, where the impact of monetary policy takes time to materialize, adds complexity.
- Economic forecasts: Various economic forecasts predict different probabilities of a recession, depending on the pace and magnitude of future rate hikes and other economic factors.
Balancing Inflation Control with Economic Growth
The Fed faces the challenging task of controlling inflation without significantly hindering economic growth. This requires a delicate balancing act.
- The trade-off between inflation control and economic growth: There’s often an inverse relationship between inflation control and economic growth. Aggressive measures to curb inflation can lead to slower growth and potentially job losses.
- Consequences of prioritizing one over the other: Prioritizing inflation control too aggressively could lead to a recession, while prioritizing economic growth too much could allow inflation to spiral out of control.
- The Fed's communication strategy: The Fed's communication strategy, including its statements and press conferences, is crucial in managing market expectations and guiding economic activity.
Conclusion
The Federal Reserve's decision on future interest rate hikes is a complex balancing act. While high inflation demands action, the risk of triggering a recession remains significant. The Fed's approach will depend on incoming economic data, the persistence of core inflation, and global economic developments. Understanding the various factors at play is critical for investors and businesses alike.
Call to Action: Stay informed on the latest developments from the Federal Reserve regarding interest rates and inflation. Regularly monitor economic indicators and analysis to effectively assess the Federal Reserve’s next move and its implications for your financial planning. Continuously researching Federal Reserve interest rate hikes and related keywords will help you stay ahead of the curve.

Featured Posts
-
 Barys San Jyrman Hl Syudwn Asmh Fy Sjlat Abtal Awrwba
May 09, 2025
Barys San Jyrman Hl Syudwn Asmh Fy Sjlat Abtal Awrwba
May 09, 2025 -
 F1 News Alpine Boss Delivers Direct Message To Doohan
May 09, 2025
F1 News Alpine Boss Delivers Direct Message To Doohan
May 09, 2025 -
 20 23
May 09, 2025
20 23
May 09, 2025 -
 Inter Milans Shock De Ligt Pursuit Loan Move With Option To Buy
May 09, 2025
Inter Milans Shock De Ligt Pursuit Loan Move With Option To Buy
May 09, 2025 -
 Vegas Golden Knights Defeat Columbus Blue Jackets 4 0 Hills Stellar Goaltending Leads The Way
May 09, 2025
Vegas Golden Knights Defeat Columbus Blue Jackets 4 0 Hills Stellar Goaltending Leads The Way
May 09, 2025
