Bank Of Canada And Trump Tariffs: Assessing The April Rate Cut Consideration
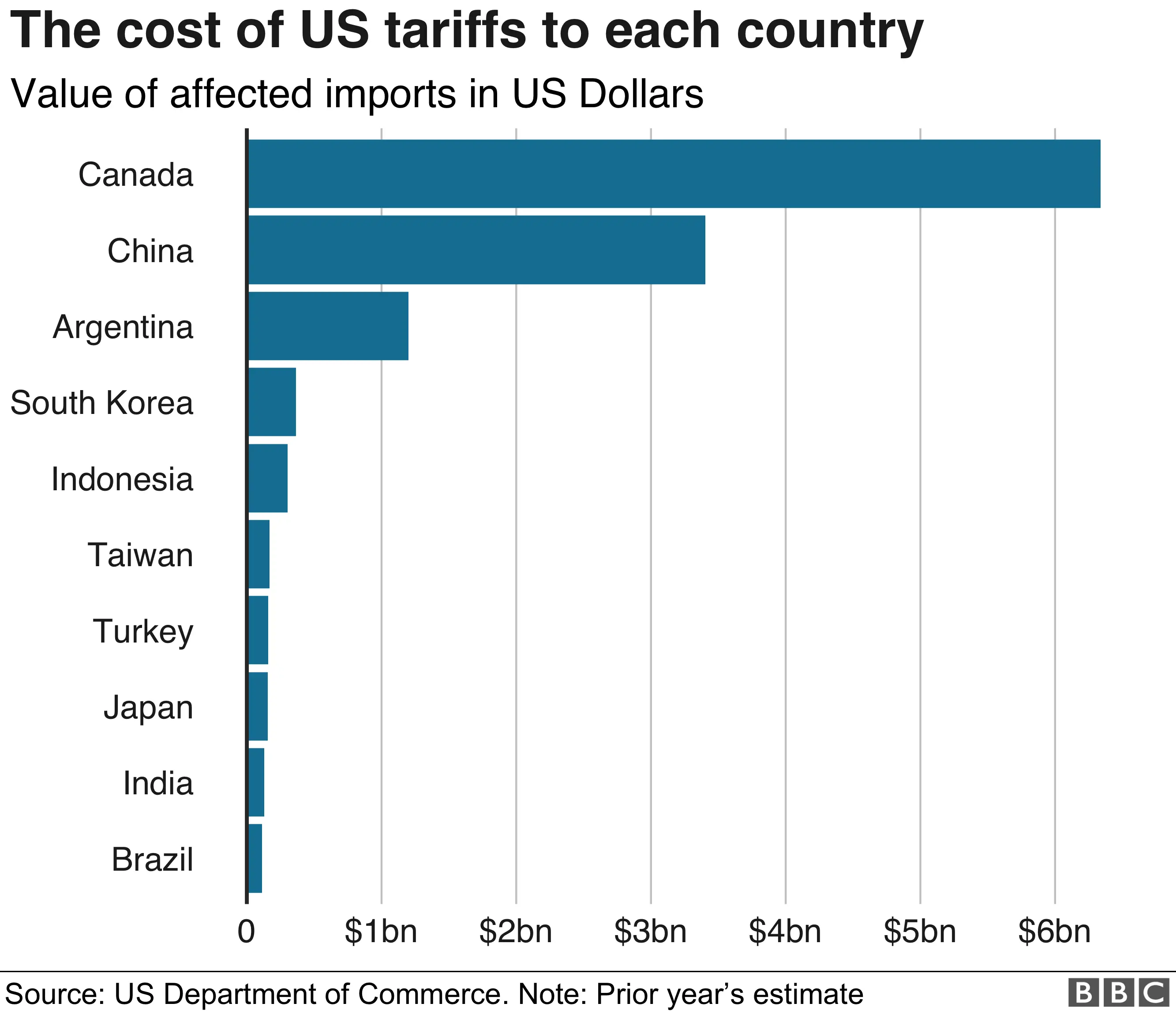
Table of Contents
The Economic Impact of Trump Tariffs on Canada
The Trump administration's imposition of tariffs on various Canadian goods significantly impacted the Canadian economy. Key sectors, including lumber, agriculture, and the automotive industry, bore the brunt of these trade barriers. The tariffs resulted in a considerable decrease in Canadian exports to the US, significantly reducing trade volume between the two nations. This trade disruption led to a slowdown in Canadian GDP growth and, in some sectors, contributed to inflationary pressures.
- Specific examples of tariff impacts: The lumber industry faced substantial export losses due to increased tariffs, impacting employment and profitability in British Columbia and other lumber-producing provinces. The agricultural sector, particularly dairy and pork producers, also experienced reduced market access and lower prices due to tariffs. The automotive sector faced disruptions to supply chains and increased production costs.
- Quantifiable data: Data from Statistics Canada could be cited here to illustrate the decline in GDP growth and potentially increased unemployment rates following the imposition of tariffs. For example, specific figures on the reduction in export volumes and the impact on various industry sectors would strengthen this section. Charts and graphs visually depicting this decline in trade would be highly beneficial.
- Decline in Trade: The imposition of tariffs led to a noticeable decrease in bilateral trade between Canada and the US, impacting businesses reliant on this trade relationship. This could be visually illustrated with a line graph demonstrating the decrease in trade volume over the period in question.
The Bank of Canada's Mandate and Policy Tools
The Bank of Canada operates under a dual mandate: maintaining price stability and fostering full employment. Its primary policy tool for achieving these objectives is adjusting interest rates. Lowering interest rates (a rate cut) aims to stimulate economic activity by reducing borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, encouraging investment and spending. This increased economic activity, in theory, leads to job creation and higher GDP growth.
- Inflation Target: The Bank of Canada typically targets an inflation rate of around 2%. Deviations from this target, either upward or downward, influence their policy decisions.
- Interest Rate Impacts: A reduction in the Bank Rate influences other lending rates, such as mortgage rates and business loan rates, making borrowing cheaper and encouraging investment and consumption.
- Past Rate Cuts: The Bank of Canada has utilized rate cuts in the past to counter economic downturns. Examples of these past instances, along with their effectiveness, would provide context and credibility.
Analyzing the April Rate Cut Consideration in the Context of Trump Tariffs
In April (insert specific year), faced with the ongoing negative impacts of the Trump tariffs, the Bank of Canada carefully considered a rate cut. The economic situation was characterized by (insert relevant economic indicators from that period, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation rates). Arguments for a rate cut centered on stimulating the economy and mitigating the negative consequences of the trade dispute. Arguments against a rate cut emphasized potential risks such as increased inflation or the creation of asset bubbles.
- Economic Indicators: Detailed analysis of relevant economic data from April (insert year) is essential to fully assess the situation. Specific numbers related to employment, inflation, and other key indicators will enhance the credibility of this section.
- Positive Effects of a Rate Cut: A rate cut could have potentially increased consumer spending, boosted business investment, and created jobs.
- Negative Effects of a Rate Cut: Concerns existed that a rate cut could fuel inflation, potentially leading to instability in the economy and creating asset bubbles in the housing or stock markets.
Alternative Policy Responses Considered by the Bank of Canada
Besides interest rate adjustments, the Bank of Canada explored other policy options to counter the negative economic effects of the Trump tariffs. These included quantitative easing (QE) and forward guidance. Quantitative easing involves the Bank purchasing government bonds to increase the money supply, while forward guidance involves communicating the Bank's future intentions regarding interest rates. Each approach has its advantages and disadvantages, with effectiveness depending on economic conditions.
- Quantitative Easing (QE): QE could have injected liquidity into the market, but the potential for inflationary pressures would need careful consideration.
- Forward Guidance: Clearly communicating the Bank's intentions could have influenced market expectations and reduced uncertainty, but it may not be sufficient in the face of significant economic shocks.
- Reasons for Policy Choice: The Bank ultimately chose its specific policy response based on a thorough assessment of the economic situation and a consideration of the potential risks and benefits of each option.
Conclusion: Bank of Canada and Trump Tariffs: A Retrospective on the April Rate Cut Consideration
The impact of Trump's tariffs on the Canadian economy was significant, forcing the Bank of Canada to carefully weigh various policy responses. The April rate cut consideration was a critical moment, reflecting the challenge of balancing price stability with full employment in the face of externally imposed economic shocks. The effectiveness of the chosen policy response (or lack thereof) can be assessed by reviewing subsequent economic data.
Understanding the complexities surrounding the Bank of Canada and Trump Tariffs requires ongoing analysis. Continue exploring the impacts of international trade policies on monetary policy decisions to gain a deeper understanding of these critical interactions.

Featured Posts
-
 Justice Department Ends Louisiana School Desegregation Order A New Chapter
May 02, 2025
Justice Department Ends Louisiana School Desegregation Order A New Chapter
May 02, 2025 -
 Understanding Michael Sheens Million Pound Donation
May 02, 2025
Understanding Michael Sheens Million Pound Donation
May 02, 2025 -
 Rechtszaak Gemeente Kampen Eist Stroomnetaansluiting Van Enexis
May 02, 2025
Rechtszaak Gemeente Kampen Eist Stroomnetaansluiting Van Enexis
May 02, 2025 -
 Lost Fortnite Skins Which Ones Are Gone Forever
May 02, 2025
Lost Fortnite Skins Which Ones Are Gone Forever
May 02, 2025 -
 Savor The Flavors Culinary Delights On Windstar Cruises
May 02, 2025
Savor The Flavors Culinary Delights On Windstar Cruises
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Joseph Sur Tf 1 Avis Complet Sur La Nouvelle Serie Policiere
May 03, 2025
Joseph Sur Tf 1 Avis Complet Sur La Nouvelle Serie Policiere
May 03, 2025 -
 Soutien Financier A La Republique De Maurice Signature D Un Accord
May 03, 2025
Soutien Financier A La Republique De Maurice Signature D Un Accord
May 03, 2025 -
 Financement De Projets A Maurice Signature D Un Accord D Aide Financiere
May 03, 2025
Financement De Projets A Maurice Signature D Un Accord D Aide Financiere
May 03, 2025 -
 Dedicace Les Tuche 5 Comprendre Le Message Du Realisateur
May 03, 2025
Dedicace Les Tuche 5 Comprendre Le Message Du Realisateur
May 03, 2025 -
 Projet D Aide Financiere A Maurice Signature Et Protocole D Accord
May 03, 2025
Projet D Aide Financiere A Maurice Signature Et Protocole D Accord
May 03, 2025
