Bank Of Canada Interest Rate Outlook: Job Losses And The Potential For Further Cuts
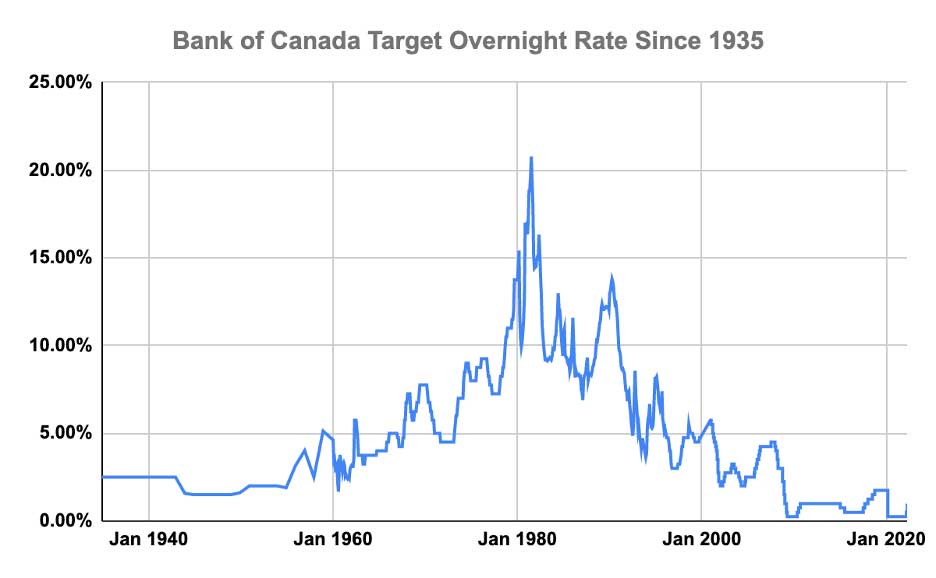
Table of Contents
Rising Unemployment and its Impact on the Canadian Economy
The Canadian unemployment rate is a key indicator of the country's economic health, directly influencing consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic growth. Recent unemployment figures show [insert current data and source, e.g., a 5.2% unemployment rate in August 2024, according to Statistics Canada]. This represents [insert analysis, e.g., a slight increase from the previous month, indicating a potential softening of the labor market].
- Impact on Consumer Confidence and Spending: Rising unemployment erodes consumer confidence, leading to decreased spending. Job insecurity makes individuals more cautious about making large purchases, impacting sectors like retail, automotive, and housing.
- Effect on Business Investment and Economic Growth: Businesses are less likely to invest in expansion or new projects when facing uncertain economic conditions and weakening consumer demand. This further slows down economic growth, creating a negative feedback loop.
- Regional Variations in Unemployment: Unemployment rates vary significantly across Canada. [Insert data and examples of regions with higher or lower unemployment and reasons why]. Understanding these regional disparities is crucial for targeted policy interventions.
- Illustrative Data: [Include a relevant chart or graph visualizing recent unemployment trends, clearly labelled with data sources].
Inflation and the Bank of Canada's Mandate
The Bank of Canada's primary mandate is to maintain price stability for the benefit of Canadians. This means keeping inflation within its target range of 1-3%. The current inflation rate is [insert current data and source]. [Analyze if this is within the target range, and explain if it is above or below the target and reasons why].
- Relationship Between Inflation, Unemployment, and Interest Rates: The Bank of Canada uses interest rates as a key monetary policy tool to influence both inflation and unemployment. Lower interest rates generally stimulate economic activity and employment, but can also fuel inflation. Conversely, higher interest rates curb inflation but may lead to higher unemployment.
- Impact of Interest Rate Cuts on Inflation: Interest rate cuts make borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending and investment, which can increase demand-pull inflation. However, if the economy is already operating below its potential, the impact on inflation might be minimal.
- Trade-offs: The Bank of Canada faces a difficult balancing act. Stimulating employment through lower interest rates risks increasing inflation, while combating inflation through higher rates can lead to job losses. The optimal policy depends on a careful assessment of the current economic situation.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Economic Slowdown
The Bank of Canada has historically responded to economic downturns with interest rate cuts and, in more severe cases, quantitative easing (QE). [Provide examples of past responses and their effectiveness].
- Potential for Further Interest Rate Cuts: Given the rising unemployment and potential economic slowdown, the likelihood of further interest rate cuts is a significant consideration. [Analyze potential scenarios and their impacts].
- Other Monetary Policy Tools: Besides interest rate adjustments, the Bank of Canada could consider other tools such as QE—a policy where the central bank creates new money to purchase assets, injecting liquidity into the financial system. [Discuss the pros and cons of QE in this context].
- Effectiveness of Past Interventions: Analyzing the effectiveness of previous monetary policy interventions is crucial in predicting the impact of future actions. [Discuss the past responses and analyze their success rates and unintended consequences].
- Risks and Benefits: Further stimulus measures carry both risks and benefits. While stimulating the economy, they could also lead to increased inflation or asset bubbles. A cautious approach is necessary.
Predicting Future Bank of Canada Interest Rate Decisions
Predicting future Bank of Canada interest rate decisions requires analyzing various economic indicators and forecasts. [Cite relevant economic forecasts and their methodologies].
- Analysis of Economic Indicators and Forecasts: Key indicators to watch include GDP growth, inflation rates, consumer confidence, and housing starts. [Explain the importance of each indicator].
- Market Expectations: Market participants' expectations regarding future interest rate movements heavily influence financial markets. [Explain how market sentiment is formed and why it matters].
- Impact of Global Economic Events: Global economic conditions, such as international trade tensions or global recessions, can significantly influence the Bank of Canada’s decisions. [Discuss potential global factors].
- Uncertainty: Forecasting economic conditions is inherently uncertain. [Discuss the inherent limitations and potential surprises].
- Prediction: Based on current trends, [provide a reasoned prediction about the likelihood of further interest rate cuts, including caveats and qualifications].
Conclusion
This analysis of the Bank of Canada interest rate outlook highlights the complex interplay between rising unemployment, inflation targets, and the need for economic stimulus. While job losses present a significant challenge, the Bank of Canada’s response will depend on a careful assessment of inflation and overall economic conditions. The potential for further interest rate cuts remains a key area of focus.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the evolving Bank of Canada interest rate outlook and its impact on your financial planning. Regularly check reliable sources for updates on Canadian interest rates and economic news to make informed decisions. Understanding the Bank of Canada interest rate outlook is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 Juan Sotos Post Kay Interview Surge Coincidence Or Causation
May 12, 2025
Juan Sotos Post Kay Interview Surge Coincidence Or Causation
May 12, 2025 -
 More Than Just A Meeting The Shane Lowry Experience
May 12, 2025
More Than Just A Meeting The Shane Lowry Experience
May 12, 2025 -
 Latest Injury News Chicago Bulls And New York Knicks
May 12, 2025
Latest Injury News Chicago Bulls And New York Knicks
May 12, 2025 -
 Is John Wicks Return In John Wick 5 Impossible Even For Keanu Reeves
May 12, 2025
Is John Wicks Return In John Wick 5 Impossible Even For Keanu Reeves
May 12, 2025 -
 Where To Watch The Ny Knicks Vs Cleveland Cavaliers Game Time Tv Channel And Live Stream Options
May 12, 2025
Where To Watch The Ny Knicks Vs Cleveland Cavaliers Game Time Tv Channel And Live Stream Options
May 12, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Gerard Hernandez Parle De Chantal Ladesou Je Ne Comprends Pas Toujours Ce Qu Elle Me Dit
May 12, 2025
Gerard Hernandez Parle De Chantal Ladesou Je Ne Comprends Pas Toujours Ce Qu Elle Me Dit
May 12, 2025 -
 Rare Eye Condition A Guide To Bilateral Anophthalmia For Parents And Healthcare Professionals
May 12, 2025
Rare Eye Condition A Guide To Bilateral Anophthalmia For Parents And Healthcare Professionals
May 12, 2025 -
 Bilateral Anophthalmia Current Research And Future Treatment Options
May 12, 2025
Bilateral Anophthalmia Current Research And Future Treatment Options
May 12, 2025 -
 Usmnt Weekend A Hat Trick For Haji And Key Match Updates
May 12, 2025
Usmnt Weekend A Hat Trick For Haji And Key Match Updates
May 12, 2025 -
 Kieran Stevenson And Ipswich Town Looking Ahead
May 12, 2025
Kieran Stevenson And Ipswich Town Looking Ahead
May 12, 2025
