Bank Of Canada Interest Rates: Retail Sales Data Weighs On Decision
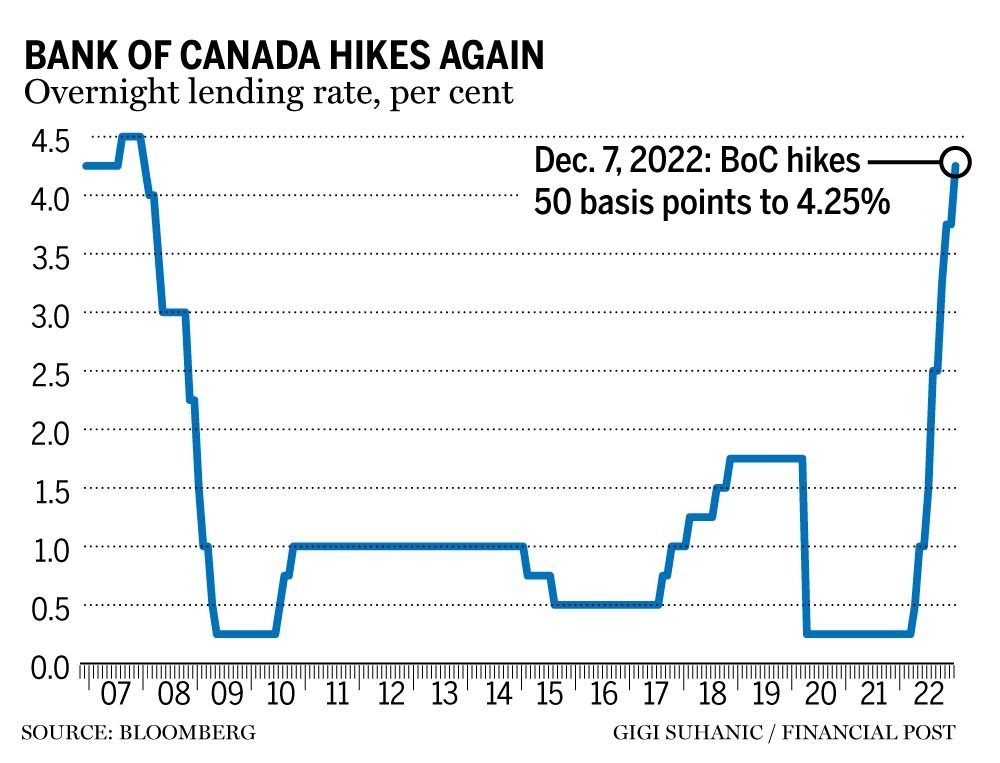
Table of Contents
Retail Sales Slump: A Key Indicator for the Bank of Canada
Retail sales data serves as a crucial barometer of consumer spending and overall economic health. Strong retail sales typically indicate robust consumer confidence and economic growth, while a decline often signals weakening demand and potential economic slowdown. The Bank of Canada closely monitors these figures to gauge the effectiveness of its monetary policy.
-
Recent Retail Sales Figures: Recent data has shown a concerning downturn in retail sales. For example, [Insert specific data, e.g., July 2024 saw a 0.5% month-over-month decline, and a 2% year-over-year decrease]. [Insert another data point, e.g., This follows a similarly weak performance in June, indicating a persistent trend].
-
Causes for the Decline: Several factors are likely contributing to this retail sales slump. High inflation continues to erode consumer purchasing power, forcing many Canadians to cut back on discretionary spending. Furthermore, rising interest rates are increasing borrowing costs, making large purchases like homes and vehicles less accessible. Weakening consumer confidence, fueled by economic uncertainty, further exacerbates the situation.
-
Softening Consumer Demand: Weak retail sales strongly suggest softening consumer demand. This indicates a potential slowdown in economic growth, which is a major consideration for the Bank of Canada when setting interest rates. A significant decline could signal a need for more accommodative monetary policy.
[Insert a relevant chart or graph here, clearly labeled and showing the trend of retail sales over the past several months or years.]
Inflation Remains a Central Concern Despite Retail Sales Dip
Despite the recent dip in retail sales, inflation remains a primary concern for the Bank of Canada. The central bank's mandate is to maintain price stability, targeting an inflation rate of around 2%.
-
Current Inflation Rate and Impact: Canada's current inflation rate is still [Insert current inflation rate], significantly above the Bank of Canada's target. This persistent inflation necessitates a cautious approach to monetary policy, even in the face of weakening retail sales.
-
Inflation vs. Economic Growth: The Bank of Canada faces a delicate balancing act: controlling inflation without triggering a significant economic recession. Raising interest rates combats inflation but risks slowing down economic growth and potentially increasing unemployment.
-
Stagflation Risk: The combination of high inflation and slow economic growth – stagflation – poses a significant challenge. The Bank of Canada will be closely monitoring economic indicators to assess the risk of this scenario unfolding and adjust its interest rate policy accordingly.
-
Bank of Canada's Inflation Target: The Bank of Canada's inflation target is 2 percent, averaged over time. While recent measures have helped bring inflation down from its peak, it remains stubbornly above target, requiring further action to be considered. [Insert any recent statements made by the Bank of Canada regarding their inflation targets and strategies].
Other Factors Influencing the Bank of Canada's Decision
Beyond retail sales and inflation, several other factors influence the Bank of Canada's interest rate decisions.
-
Global Economic Conditions: Global economic uncertainty, including potential recessions in major economies like the US, significantly impacts Canada's economy. These external factors weigh heavily on the Bank of Canada's deliberations. The Federal Reserve's interest rate decisions also play a significant role.
-
Canadian Dollar Exchange Rate: The value of the Canadian dollar relative to other currencies affects the cost of imports and exports, impacting inflation and overall economic growth. A weaker Canadian dollar can contribute to higher inflation.
-
Employment Data and Housing Market: Employment figures and housing market trends provide additional insights into the health of the Canadian economy. Strong employment and a stable housing market generally support higher interest rates, while weakness in these areas might suggest a need for lower rates.
-
Other Key Economic Indicators: The Bank of Canada also considers a broad range of other economic indicators, including manufacturing sales, business investment, and consumer confidence, when making its interest rate decisions. These factors provide a comprehensive picture of the overall economic landscape.
Predicting the Bank of Canada's Next Move
Given the conflicting signals from weak retail sales and persistent inflation, several scenarios are possible for the next interest rate announcement:
-
Rate Hike: A rate hike remains a possibility if the Bank of Canada prioritizes inflation control over supporting economic growth. This would be more likely if inflation remains stubbornly high and other economic indicators remain strong.
-
Rate Cut: A rate cut is less likely given the current inflationary pressures but could be considered if the economic slowdown intensifies significantly, posing a greater threat than inflation.
-
Maintaining the Status Quo: The most probable scenario might be maintaining the current interest rate, allowing the Bank of Canada to assess the impact of previous rate hikes and monitor incoming economic data before making any further adjustments.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's upcoming interest rate decision is a complex one, heavily influenced by recent weak retail sales data, persistent inflationary pressures, and global economic uncertainties. While the retail sales slump suggests a cooling economy, stubborn inflation continues to necessitate careful consideration. The central bank must navigate a delicate balance between controlling inflation and avoiding a significant economic slowdown.
Call to Action: Stay informed about the upcoming Bank of Canada interest rate announcement and its potential impact on your finances. Continuously monitor Bank of Canada interest rates and related economic news to make informed financial decisions. Understanding the nuances of Canadian interest rate policy is crucial for effective financial planning.

Featured Posts
-
 Pogacars Unstoppable Solo Performance Secures Tour Of Flanders
May 26, 2025
Pogacars Unstoppable Solo Performance Secures Tour Of Flanders
May 26, 2025 -
 Dr Terrors House Of Horrors Tips For A Frightening Experience
May 26, 2025
Dr Terrors House Of Horrors Tips For A Frightening Experience
May 26, 2025 -
 Flash Flood Warning South Florida Residents Urged To Prepare For Heavy Rain
May 26, 2025
Flash Flood Warning South Florida Residents Urged To Prepare For Heavy Rain
May 26, 2025 -
 Avenir Des Locaux Rtbf Au Palais Des Congres De Liege Un Projet En Suspens
May 26, 2025
Avenir Des Locaux Rtbf Au Palais Des Congres De Liege Un Projet En Suspens
May 26, 2025 -
 Rtbf Et Rtl Belgium Contre L Iptv Les Raisons De Leur Offensive
May 26, 2025
Rtbf Et Rtl Belgium Contre L Iptv Les Raisons De Leur Offensive
May 26, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Le Depute Laurent Jacobelli Rn Un Portrait
May 30, 2025
Le Depute Laurent Jacobelli Rn Un Portrait
May 30, 2025 -
 Marine Le Pen Et 2027 Jacobelli Alerte Sur Une Possible Exclusion De La Candidate
May 30, 2025
Marine Le Pen Et 2027 Jacobelli Alerte Sur Une Possible Exclusion De La Candidate
May 30, 2025 -
 Laurent Jacobelli Actions Et Positions Politiques A L Assemblee Nationale
May 30, 2025
Laurent Jacobelli Actions Et Positions Politiques A L Assemblee Nationale
May 30, 2025 -
 Biographie Et Mandat De Laurent Jacobelli Depute Rn De La Moselle
May 30, 2025
Biographie Et Mandat De Laurent Jacobelli Depute Rn De La Moselle
May 30, 2025 -
 Hanouna Le Pen 2027 Jacobelli S Inquiete D Une Exclusion De La Candidate
May 30, 2025
Hanouna Le Pen 2027 Jacobelli S Inquiete D Une Exclusion De La Candidate
May 30, 2025
