Bank Of Canada: Navigating The Tightrope Of Inflation Control

Table of Contents
The Current Inflationary Landscape in Canada
Canada, like much of the world, is grappling with elevated inflation. Understanding the current inflationary landscape is crucial to comprehending the Bank of Canada's response. The impact on Canadian consumers is significant, eroding purchasing power and impacting household budgets.
-
Current CPI (Consumer Price Index) and its year-over-year change: As of [Insert most recent CPI data and percentage change here], the CPI reveals a [increase/decrease] in inflation compared to the same period last year. This figure reflects the overall cost of goods and services in Canada.
-
Key contributing factors to inflation: Several factors contribute to the current inflationary pressure in Canada. These include:
- Supply chain disruptions: Global supply chain bottlenecks continue to impact the availability and cost of goods.
- Energy prices: Fluctuations in global energy markets, particularly oil prices, significantly influence inflation.
- Demand-pull inflation: Increased consumer demand, fueled by factors like government stimulus and pent-up demand after lockdowns, contributes to price increases.
-
Impact on household budgets and purchasing power: Rising inflation directly reduces the purchasing power of Canadians. Essential goods and services become more expensive, squeezing household budgets and forcing many to make difficult choices.
-
Comparison to inflation rates in other G7 countries: Canada's inflation rate is [compare to other G7 countries – insert data here]. This comparison provides context for the challenges faced by the Bank of Canada relative to other developed economies.
The Bank of Canada's Monetary Policy Tools
The Bank of Canada employs several monetary policy tools to manage inflation and maintain price stability. These tools aim to influence the money supply and interest rates to curb inflationary pressures.
-
Overview of the overnight rate and its influence on other interest rates: The Bank of Canada's key policy instrument is the overnight rate – the target rate for the overnight borrowing and lending of funds between banks. Changes to this rate ripple through the financial system, affecting other interest rates such as mortgage rates, loan rates, and savings account interest. Recent Bank of Canada interest rate hikes reflect this approach.
-
Explanation of quantitative easing and its impact on money supply: Quantitative easing (QE) involves the Bank of Canada purchasing government bonds to increase the money supply. This is typically used during periods of low inflation or economic downturn. The opposite, quantitative tightening (QT), involves reducing the money supply by selling bonds.
-
Discussion of the effectiveness of past monetary policy decisions: The effectiveness of past monetary policy decisions varies depending on the economic context. Analyzing past interventions helps assess the potential impact of current strategies. For example, [cite specific examples and their outcomes].
-
Analysis of potential side effects of current monetary policy: Raising interest rates, while effective in curbing inflation, can also have negative consequences. For instance, higher interest rates can dampen economic growth and potentially impact the housing market.
Challenges and Risks Faced by the Bank of Canada
Controlling inflation is a complex undertaking, fraught with challenges and potential risks. The Bank of Canada must carefully navigate a tightrope between controlling inflation and fostering economic growth.
-
Balancing inflation control with economic growth: The primary challenge is finding the right balance between controlling inflation and sustaining economic growth. Aggressive interest rate hikes can curb inflation but risk triggering a recession.
-
Managing expectations and maintaining public confidence: The Bank of Canada's credibility is crucial. Effectively managing public expectations about inflation is essential for maintaining confidence in the economy.
-
Potential for unintended consequences of monetary policy adjustments: Monetary policy adjustments can have unintended consequences, making careful calibration and monitoring crucial. For example, higher interest rates can disproportionately affect certain sectors of the economy.
-
Global economic uncertainty and its impact on Canadian inflation: Global economic factors, such as geopolitical instability and supply chain disruptions, significantly impact Canadian inflation, adding another layer of complexity for the Bank of Canada.
The Role of Fiscal Policy in Inflation Control
Fiscal policy, encompassing government spending and taxation, plays a significant role in influencing inflation, often in coordination with monetary policy.
-
Examples of fiscal policies that can help combat inflation: Fiscal measures like reducing government spending or increasing taxes can help cool down an overheated economy and reduce demand-pull inflation.
-
Potential conflicts between fiscal and monetary policy: Conflicts can arise if fiscal and monetary policies are not aligned. For instance, expansionary fiscal policies (increased government spending) can counteract the Bank of Canada's efforts to control inflation through higher interest rates.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's battle to control inflation is an ongoing process, demanding a delicate balance between economic growth and price stability. The challenges are significant, encompassing global economic uncertainty, supply chain disruptions, and the potential for unintended consequences from monetary policy adjustments. Understanding the complexities of Bank of Canada inflation management, the tools employed, and the interplay with fiscal policy is crucial.
Call to action: Stay informed about the Bank of Canada's decisions regarding inflation control and their potential impact on your personal finances. Regularly check the Bank of Canada website for updates on Bank of Canada inflation rates and monetary policy announcements to make informed financial decisions. Understanding the Bank of Canada's approach to managing inflation is crucial for navigating the current economic climate.

Featured Posts
-
 New Trans Australia Run Attempt Threatens Existing Record
May 22, 2025
New Trans Australia Run Attempt Threatens Existing Record
May 22, 2025 -
 Half Dome Secures Major Victorian Account With Abn Group
May 22, 2025
Half Dome Secures Major Victorian Account With Abn Group
May 22, 2025 -
 Cong Usb Co Hai Lo Vuong Nho Tim Hieu Y Nghia Va Cong Dung
May 22, 2025
Cong Usb Co Hai Lo Vuong Nho Tim Hieu Y Nghia Va Cong Dung
May 22, 2025 -
 Taming The Love Monster A Journey To Self Acceptance And Positive Self Image
May 22, 2025
Taming The Love Monster A Journey To Self Acceptance And Positive Self Image
May 22, 2025 -
 Southern French Alps Weather Storm Brings Unexpected Snow
May 22, 2025
Southern French Alps Weather Storm Brings Unexpected Snow
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
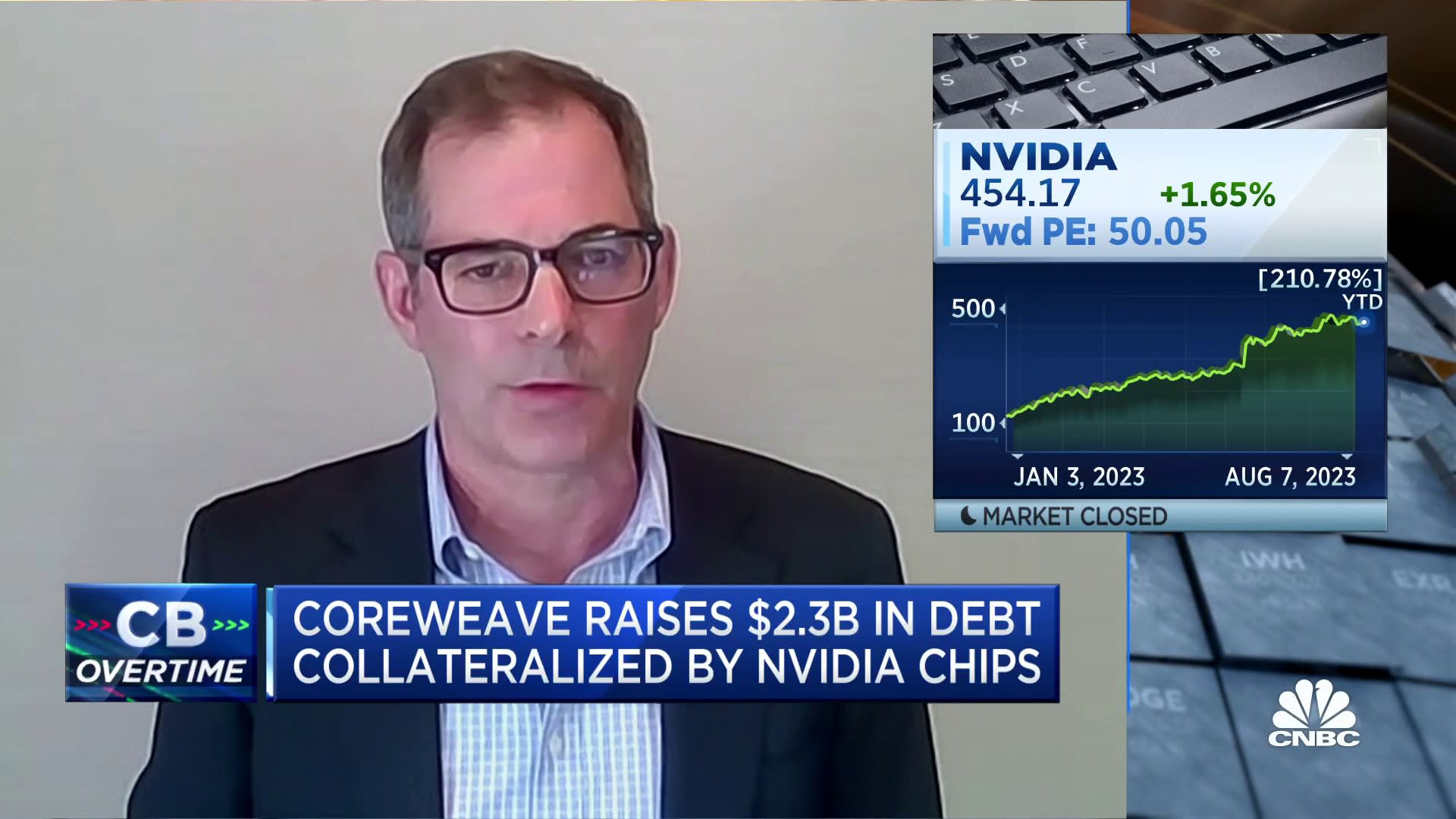 Investigating The Reasons Behind Core Weave Inc Crwv S Stock Appreciation On Tuesday
May 22, 2025
Investigating The Reasons Behind Core Weave Inc Crwv S Stock Appreciation On Tuesday
May 22, 2025 -
 Cau Duong Lien Tinh Binh Duong Tay Ninh Huong Dan And Ban Do
May 22, 2025
Cau Duong Lien Tinh Binh Duong Tay Ninh Huong Dan And Ban Do
May 22, 2025 -
 Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Lien Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Dong Nai Kien Nghi Duong Cao Toc 4 Lan Xe Xuyen Rung Ma Da Noi Lien Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Thong Tin Chinh Thuc Cau Ma Da Se Khoi Cong Vao Thang 6 Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025
Thong Tin Chinh Thuc Cau Ma Da Se Khoi Cong Vao Thang 6 Ket Noi Dong Nai Va Binh Phuoc
May 22, 2025 -
 Cau Ma Da Noi Dong Nai Binh Phuoc Du Kien Khoi Cong Thang 6
May 22, 2025
Cau Ma Da Noi Dong Nai Binh Phuoc Du Kien Khoi Cong Thang 6
May 22, 2025
