China's Unilateral Climate Action: Analyzing Xi's New Emissions Targets
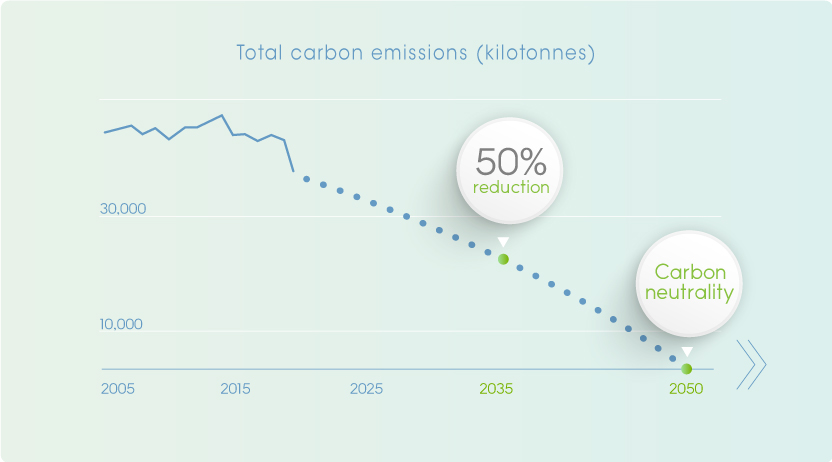
Table of Contents
Ambition and Scope of Xi's New Emissions Targets
Xi Jinping's announcements include several significant climate commitments. Crucially, China aims for carbon neutrality by 2060 and to peak its carbon dioxide emissions before 2030. These targets encompass various sectors, including energy production (a significant shift away from coal), industry, transportation, and agriculture.
Specific Targets Announced:
-
Carbon Neutrality by 2060: This ambitious goal signifies a net-zero emissions target, requiring significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and potentially large-scale carbon removal technologies.
-
Peak Emissions Before 2030: This intermediate target sets a crucial deadline for curbing the country's rapidly growing emissions. The specific level of emissions at the peak remains a subject of ongoing analysis and debate.
-
Sectoral Targets: While specific numerical targets for individual sectors are still emerging, the overall commitment suggests substantial decarbonization across all major sectors of the Chinese economy.
-
Comparison with previous targets: These targets represent a significant step up from previous commitments. While earlier pledges focused on emission intensity (emissions per unit of GDP), these new targets set absolute emission reduction goals.
-
International comparison: Compared to other major emitters, China's 2060 carbon neutrality target aligns with similar commitments from the European Union and the United States, although the timelines for peaking emissions differ. India, another major emitter, has yet to commit to a specific carbon neutrality date.
-
Strengths and weaknesses of the targets: The 2060 neutrality goal is ambitious, given China's current reliance on coal. However, the timeframe could be considered less ambitious than that of some developed nations. The success hinges critically on the speed and effectiveness of implementation strategies.
Feasibility and Implementation Challenges of China's Climate Plan
Transforming China's energy system and achieving these ambitious targets present substantial challenges.
Energy Transition Hurdles:
The most significant hurdle is transitioning away from coal, which remains the backbone of China's energy sector.
- Technological advancements needed: Massive investments in renewable energy technologies (solar, wind, hydropower), smart grids, and energy storage are crucial. Breakthroughs in carbon capture, utilization, and storage (CCUS) technologies will also be essential.
- Policy and regulatory framework: A robust policy and regulatory framework is required to incentivize renewable energy adoption, phase out coal-fired power plants, and promote energy efficiency across various sectors. Clear carbon pricing mechanisms and stricter emission standards are likely necessary.
- Economic and social impacts: The transition away from coal will inevitably lead to job displacement in coal-dependent regions. This necessitates comprehensive just transition policies to support affected workers and communities through retraining, job creation in renewable energy sectors, and social safety nets.
Geopolitical Implications of China's Independent Climate Action
China's unilateral climate action has significant geopolitical ramifications.
Impact on Global Climate Negotiations:
China's approach, while ambitious, also presents a unique challenge to global climate negotiations.
- China's role in international climate finance: While China has increased its contribution to climate finance for developing nations, the level of its commitment and the transparency of its funding mechanisms remain subjects of ongoing discussion.
- Potential for collaboration and competition: China's independent actions create both opportunities for collaboration (e.g., technology sharing) and potential competition (e.g., in renewable energy markets) with other countries.
- Influence on other developing nations: China's actions will undoubtedly influence other developing nations, potentially accelerating their own climate commitments or shaping their approaches to climate change mitigation.
Domestic Policy and Public Opinion on China's Climate Goals
Public support and domestic policies are vital for the success of China's climate goals.
Public Awareness and Support:
While awareness of climate change is growing in China, public understanding of the necessary policy changes and their personal implications remains a challenge.
- Government initiatives for public awareness: The Chinese government has launched several campaigns and educational programs to raise public awareness on climate change and promote sustainable lifestyles.
- Challenges in public engagement: Gaining public acceptance for potentially disruptive policies, like carbon pricing or restrictions on energy consumption, requires careful communication and engagement.
- Role of media and civil society: The role of media and civil society organizations in shaping public opinion and advocating for climate action is significant but faces constraints within China's political system.
Conclusion: Evaluating China's Independent Path to Climate Action
China's unilateral climate action, embodied in Xi Jinping's new emissions targets, presents a complex picture. The 2060 carbon neutrality goal is undeniably ambitious, yet the pathway to achieving it is fraught with challenges related to energy transition, policy implementation, and economic and social adjustments. The geopolitical implications are also significant, influencing international climate cooperation and shaping the actions of other nations. Successfully navigating these complexities requires technological innovation, strong policy frameworks, robust public engagement, and effective international collaboration. Further research and discussion on China's unilateral climate action and the implications of Xi Jinping's new emissions targets are crucial for effective global climate change mitigation. Explore related resources and engage in conversations to contribute to a deeper understanding of this critical issue.

Featured Posts
-
 Bayern Munich Extends Bundesliga Lead To Six Points
Apr 25, 2025
Bayern Munich Extends Bundesliga Lead To Six Points
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Auto Dealers Double Down On Opposition To Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 25, 2025
Auto Dealers Double Down On Opposition To Electric Vehicle Regulations
Apr 25, 2025 -
 Is Apple Tv S Next Crime Thriller Its Masterpiece A Look At The Genres Ascent On The Platform
Apr 25, 2025
Is Apple Tv S Next Crime Thriller Its Masterpiece A Look At The Genres Ascent On The Platform
Apr 25, 2025 -
 House Of Hair Newton Aycliffe Earns Top Ten Spot In Local Echo Awards
Apr 25, 2025
House Of Hair Newton Aycliffe Earns Top Ten Spot In Local Echo Awards
Apr 25, 2025 -
 2024 Nfl Mock Draft Projecting The Saints Next Running Back
Apr 25, 2025
2024 Nfl Mock Draft Projecting The Saints Next Running Back
Apr 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 The China Factor Analyzing The Difficulties Faced By Bmw Porsche And Other Auto Brands
Apr 26, 2025
The China Factor Analyzing The Difficulties Faced By Bmw Porsche And Other Auto Brands
Apr 26, 2025 -
 The Growing Problem Of Betting On Natural Disasters Focus On Los Angeles
Apr 26, 2025
The Growing Problem Of Betting On Natural Disasters Focus On Los Angeles
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires A Case Study In Disaster Speculation
Apr 26, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires A Case Study In Disaster Speculation
Apr 26, 2025 -
 How Middle Management Drives Company Growth And Employee Development
Apr 26, 2025
How Middle Management Drives Company Growth And Employee Development
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Analyzing The Trend People Betting On The Los Angeles Wildfires
Apr 26, 2025
Analyzing The Trend People Betting On The Los Angeles Wildfires
Apr 26, 2025
