Creatine For Beginners: A Simple Explanation
Table of Contents
What is Creatine?
Creatine is a naturally occurring compound primarily found in red meat and fish. It plays a vital role in energy production within our muscles. While your body produces some creatine naturally, supplementation can significantly boost levels, leading to enhanced athletic performance. Several types of creatine exist, but creatine monohydrate stands out due to extensive research proving its effectiveness and safety. Other forms, such as creatine HCL and creatine ethyl ester, exist, but lack the same level of scientific backing.
- Creatine is a naturally occurring compound found in meat and fish. Your diet contributes to your creatine levels, but supplementation offers a more controlled and concentrated source.
- Creatine monohydrate is the most studied and effective form. Decades of research support its efficacy in improving strength, power, and muscle growth.
- It improves athletic performance by increasing energy availability in muscles. This translates to improved workout intensity and recovery.
How Creatine Works
Creatine's primary mechanism lies in its ability to enhance ATP (adenosine triphosphate) production. ATP is the primary energy currency of cells, fueling muscle contractions. Creatine helps replenish ATP stores more quickly, allowing for greater intensity and endurance during high-intensity exercise. This increased energy availability directly contributes to muscle growth and strength gains.
- Creatine increases phosphocreatine stores in muscles. Phosphocreatine is a high-energy compound that quickly regenerates ATP.
- Increased phosphocreatine leads to more ATP production during high-intensity exercise. This allows you to lift heavier weights, perform more repetitions, and push harder during training.
- This results in improved strength, power, and muscle growth. The increased energy availability directly supports muscle protein synthesis and hypertrophy (muscle growth).
How to Use Creatine Effectively
To maximize creatine's benefits, a two-phase approach is recommended: a loading phase followed by a maintenance phase. Consistency is key for optimal results. Furthermore, proper hydration is essential for creatine absorption and overall well-being.
- Loading Phase: Consume 20 grams of creatine monohydrate per day, divided into four 5-gram servings, for 5-7 days. This quickly saturates your muscles with creatine.
- Maintenance Phase: After the loading phase, switch to a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. This maintains elevated creatine levels in your muscles.
- Consume creatine with carbohydrates and protein for optimal absorption. This enhances the transport of creatine into your muscle cells.
- Drink plenty of water throughout the day. Adequate hydration is crucial for creatine absorption and prevents potential side effects like mild water retention.
Common Creatine Myths Debunked
Many misconceptions surround creatine use. Let's address some of the most common concerns:
-
Kidney damage: Studies consistently show that creatine is safe for healthy individuals when used as directed. Only in cases of pre-existing kidney conditions or excessive dosages might there be a risk.
-
Liver damage: There's no credible evidence linking creatine supplementation to liver damage in healthy individuals.
-
Excessive water retention: While mild water retention can occur, it's usually temporary and not harmful. This is often due to the increased intracellular water volume in muscles and is a normal physiological response.
-
Consult your doctor before starting any supplement regimen. This is especially important if you have any pre-existing health conditions.
Creatine and Your Diet
While creatine supplementation can significantly boost your results, it works best in conjunction with a balanced diet and regular exercise. A diet rich in protein is particularly important as it provides the building blocks for muscle growth and repair.
- Creatine works best when combined with a healthy diet and regular exercise. Think of creatine as a tool that enhances your efforts, not a magic bullet.
- Adequate protein intake is crucial for muscle growth and repair. Aim for a protein intake of 1.6-2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight.
- Combine creatine with a balanced diet for optimal results. A well-rounded diet provides all the necessary nutrients for optimal health and performance.
Conclusion
Creatine monohydrate is a safe and effective supplement that can significantly enhance athletic performance and muscle growth when used correctly. By following a proper loading and maintenance phase, and ensuring adequate hydration, you can maximize its benefits. Remember to consult your doctor before starting any new supplement.
Call to Action: Ready to experience the power of creatine? Start your journey to increased strength and muscle growth by learning more about creatine supplementation today! Research different reputable creatine monohydrate brands and choose one that meets your needs. Remember consistent use and a healthy lifestyle are key to successful creatine use.

Featured Posts
-
 Millions In Losses Insider Threat Exposes Office365 Executive Vulnerabilities
May 17, 2025
Millions In Losses Insider Threat Exposes Office365 Executive Vulnerabilities
May 17, 2025 -
 Trump Tariffs How They Affected My Phone Battery Replacement
May 17, 2025
Trump Tariffs How They Affected My Phone Battery Replacement
May 17, 2025 -
 Simplified Surface Lineup Analyzing Microsofts Recent Changes
May 17, 2025
Simplified Surface Lineup Analyzing Microsofts Recent Changes
May 17, 2025 -
 T Mobile Data Breaches Result In 16 Million Penalty A Three Year Timeline
May 17, 2025
T Mobile Data Breaches Result In 16 Million Penalty A Three Year Timeline
May 17, 2025 -
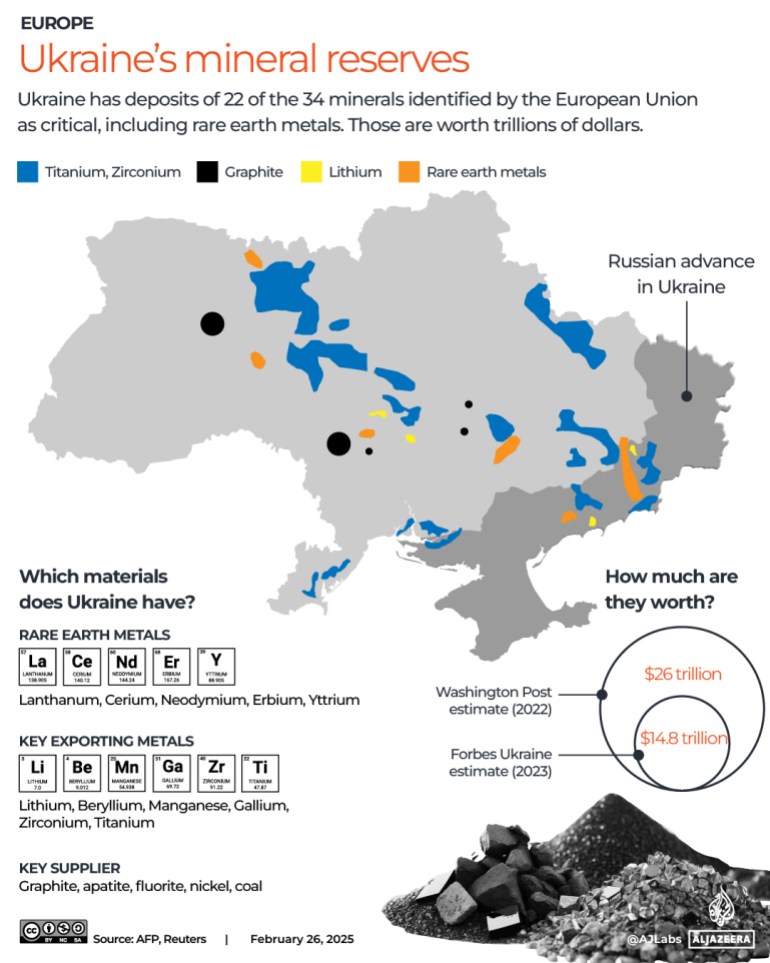 Rare Earth Minerals Fueling A New Cold War
May 17, 2025
Rare Earth Minerals Fueling A New Cold War
May 17, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Nba Analyst Perkins Critiques Brunsons Podcast
May 17, 2025
Nba Analyst Perkins Critiques Brunsons Podcast
May 17, 2025 -
 Detroit Pistons Loss Crew Chief Admits Final Second Non Call Error
May 17, 2025
Detroit Pistons Loss Crew Chief Admits Final Second Non Call Error
May 17, 2025 -
 Week In Review Turning Failures Into Success
May 17, 2025
Week In Review Turning Failures Into Success
May 17, 2025 -
 Crew Chief Admits Wrong Call Cost Detroit Pistons Game
May 17, 2025
Crew Chief Admits Wrong Call Cost Detroit Pistons Game
May 17, 2025 -
 A Look Back Failures And What We Learned
May 17, 2025
A Look Back Failures And What We Learned
May 17, 2025
