Cross-Border Crime: Analysis And Enhancement Of Investigative Mechanisms
Table of Contents
H2: The Evolving Landscape of Cross-Border Crime
The nature of cross-border crime is constantly evolving, adapting to technological advancements and shifting global dynamics. Understanding this evolving landscape is critical to developing effective countermeasures.
H3: Types of Transnational Criminal Activities
Transnational crime encompasses a wide range of illicit activities that transcend national borders. Key examples include:
- Drug trafficking and smuggling: The global trade in illicit drugs, including heroin, cocaine, and fentanyl, fuels violence, addiction, and organized crime. Combating this requires international collaboration to disrupt supply chains and target key players.
- Human trafficking and smuggling: This heinous crime involves the exploitation of vulnerable individuals for forced labor, sexual exploitation, and other forms of servitude. Effective investigation requires collaboration between law enforcement, NGOs, and international organizations.
- Cybercrime: The digital age has facilitated a surge in cybercrime, including data breaches, online fraud, and identity theft. These crimes often involve perpetrators in multiple countries, making investigation and prosecution challenging.
- Arms trafficking and illegal weapons proliferation: The illicit trade in weapons fuels conflict, violence, and instability globally. Tracing the flow of arms and disrupting trafficking networks requires sophisticated investigative techniques and international cooperation.
- Money laundering and financial crimes: Criminals use complex financial systems to conceal the origins of illicit funds. Identifying and tracking these funds requires expertise in financial investigations and international collaboration.
- Terrorism financing: The funding of terrorist activities often involves cross-border transactions and the use of sophisticated financial mechanisms. Investigating and disrupting these financial flows is vital to counter-terrorism efforts.
- Environmental crime: Illegal logging, wildlife trafficking, and other environmental crimes have significant global implications. Tackling these crimes requires international collaboration and robust enforcement mechanisms.
H3: Challenges Posed by Globalization and Technology
Globalization and technological advancements have significantly impacted the landscape of international crime:
- Increased ease of movement for criminals: Open borders and advanced transportation networks make it easier for criminals to operate across jurisdictions.
- Use of encrypted communication and dark web technologies: Criminals utilize encrypted communication channels and the dark web to conceal their activities and evade detection. This requires law enforcement to develop advanced forensic techniques and expertise in dark web investigation.
- Sophisticated money laundering techniques: Criminals employ increasingly sophisticated methods to launder illicit proceeds, making it challenging to trace the flow of funds. This necessitates advanced financial intelligence and international cooperation to track cryptocurrency crime and digital assets.
- Challenges in tracking digital assets and cryptocurrency transactions: The rise of cryptocurrencies presents new challenges for investigators due to the decentralized and pseudonymous nature of these transactions.
H2: Limitations of Traditional Investigative Approaches
Traditional investigative approaches often face significant limitations when dealing with cross-border crime.
H3: Jurisdictional Barriers and Legal Discrepancies
- Difficulties in obtaining evidence across borders: International legal frameworks often create hurdles in obtaining evidence from foreign jurisdictions.
- Varying legal definitions and standards of proof: Differences in national laws and legal standards can complicate investigations and prosecutions.
- Lack of consistent extradition treaties: The absence of comprehensive extradition treaties can hinder the prosecution of cross-border criminals.
H3: Resource Constraints and Capacity Building
- Understaffing and lack of training in law enforcement agencies: Many law enforcement agencies lack the personnel and training needed to effectively investigate complex cross-border crimes.
- Limited resources for forensic analysis and technological advancements: Access to cutting-edge forensic technology and expertise is often limited, particularly in developing countries.
H2: Enhancing Investigative Mechanisms for Cross-Border Crime
Overcoming the challenges of cross-border crime requires a multi-pronged approach.
H3: Strengthening International Cooperation
Effective cross-border crime investigation requires close collaboration between nations. This includes:
- Improved information sharing between law enforcement agencies: Establishing secure and efficient channels for information exchange is essential.
- Joint investigations and task forces: Creating joint task forces allows for the pooling of resources and expertise.
- Harmonization of legal frameworks and procedures: Standardizing legal definitions and procedures can simplify cross-border investigations.
H3: Leveraging Technological Advancements
Technology plays a crucial role in enhancing investigative capabilities:
- Use of data analytics and artificial intelligence for crime prediction: Data analytics can help identify patterns and predict potential threats.
- Enhanced surveillance technologies and cyber forensics: Advanced surveillance and cyber forensics tools are essential for investigating digital crimes.
- Development of secure communication channels for international collaboration: Secure communication channels are vital for sharing sensitive information.
H3: Improving Public Awareness and Prevention Strategies
Public awareness and preventative measures are also critical:
- Educating the public about the risks of cross-border crime: Raising public awareness can help prevent individuals from becoming victims.
- Implementing anti-money laundering measures: Robust anti-money laundering regulations are necessary to disrupt the financial networks supporting criminal activities.
- Promoting responsible use of technology: Promoting cybersecurity awareness can help individuals and organizations protect themselves from cybercrime.
3. Conclusion:
Combating cross-border crime requires a comprehensive and collaborative approach. By strengthening international cooperation, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering public awareness, we can significantly enhance our ability to investigate and prosecute transnational criminal activities. The persistent and evolving nature of cross-border crime demands ongoing analysis, adaptation of strategies, and a sustained commitment to improving investigative mechanisms. We must continue to invest in training, technology, and international partnerships to effectively address this persistent threat to global security. Let's work together to strengthen our response to cross-border crime.

Featured Posts
-
 How To Play Doom Games A Chronological Playthrough
May 13, 2025
How To Play Doom Games A Chronological Playthrough
May 13, 2025 -
 Funeral For Teenager Killed In School Stabbing
May 13, 2025
Funeral For Teenager Killed In School Stabbing
May 13, 2025 -
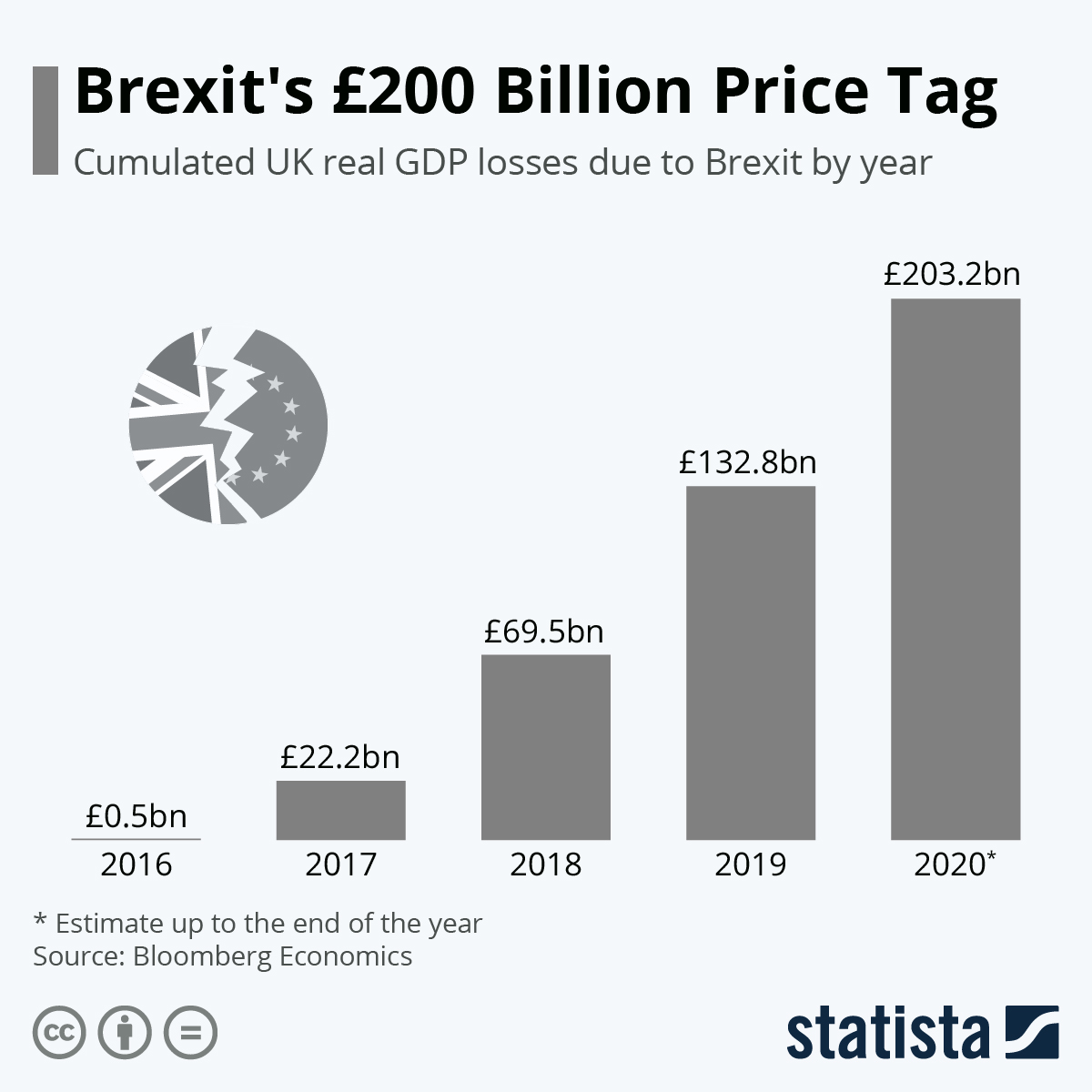 Brexits Impact Spanish Border Towns On The Brink
May 13, 2025
Brexits Impact Spanish Border Towns On The Brink
May 13, 2025 -
 Springwatch Japan Best Spots For Cherry Blossom Viewing
May 13, 2025
Springwatch Japan Best Spots For Cherry Blossom Viewing
May 13, 2025 -
 Catch Leonardo Di Caprio In A Thrilling New Spy Film On Netflix
May 13, 2025
Catch Leonardo Di Caprio In A Thrilling New Spy Film On Netflix
May 13, 2025
