Declining Measles Cases In The United States: What's Behind The Trend?
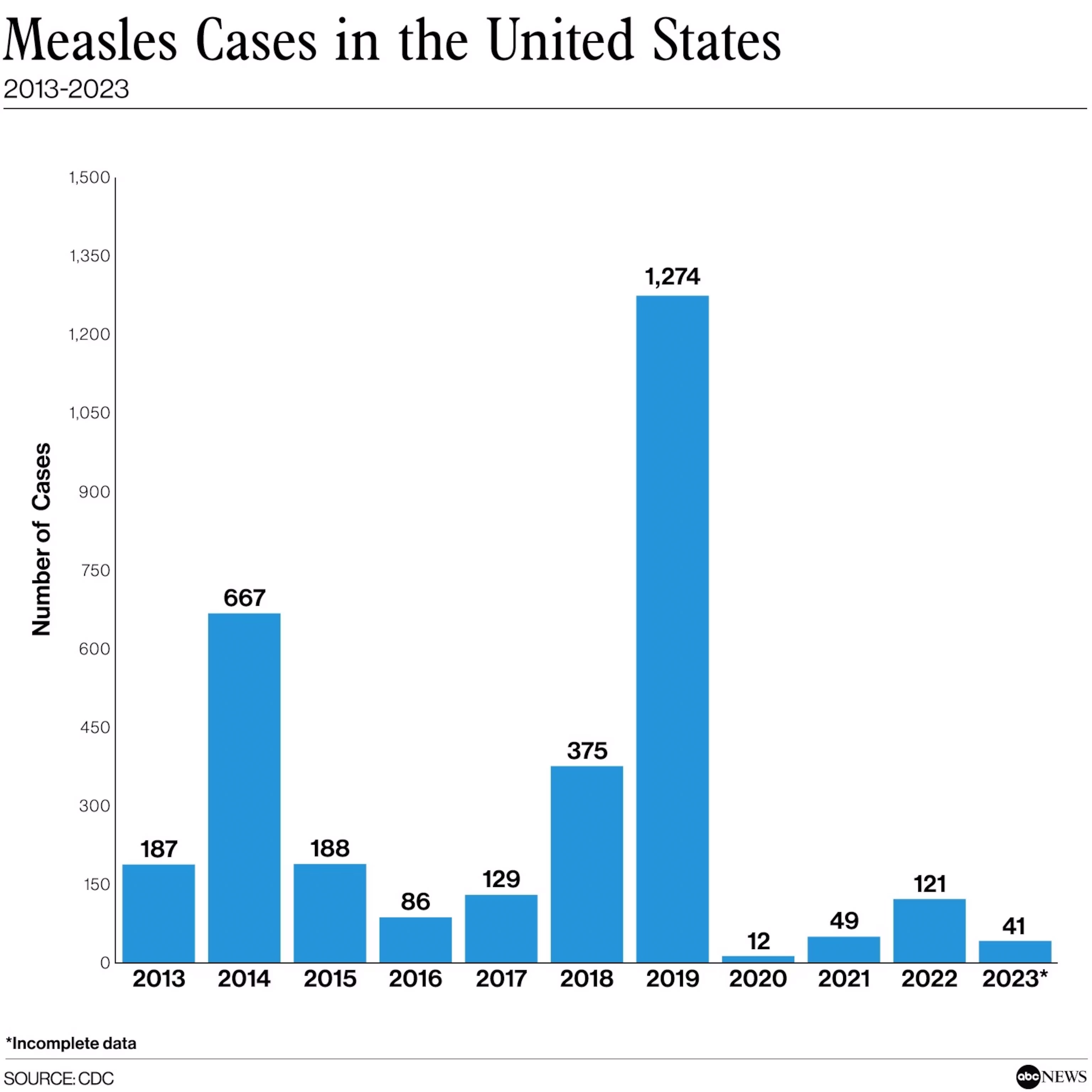
Table of Contents
The Impact of High Vaccination Rates on Measles Eradication
The MMR (measles, mumps, rubella) vaccine is the cornerstone of measles prevention. Its effectiveness in preventing measles infection is exceptionally high, significantly reducing the risk of outbreaks. High vaccination coverage rates across the US are directly correlated with the dramatic decline in measles cases.
- Percentage of children vaccinated against measles: The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) reports that vaccination rates for measles have consistently remained above 90% for several years in many states. This high level of immunity within the population contributes significantly to herd immunity.
- Effectiveness of the MMR vaccine in preventing infection: The MMR vaccine is over 97% effective at preventing measles after two doses. This exceptionally high efficacy makes it a powerful tool in disease control.
- Impact of herd immunity on measles transmission: Herd immunity, achieved through high vaccination rates, protects even those who cannot be vaccinated due to medical reasons. When a significant portion of the population is immune, the virus struggles to spread, effectively breaking the chain of transmission.
Concerns about vaccine safety are understandable, but it's crucial to acknowledge the overwhelming scientific consensus supporting the safety and efficacy of the MMR vaccine. Extensive research has consistently shown that the benefits of vaccination far outweigh any potential risks. The CDC and other reputable health organizations provide detailed information addressing these concerns.
Enhanced Public Health Surveillance and Response Systems
Early detection and rapid response are critical in controlling measles outbreaks. Advancements in disease surveillance technology, including sophisticated data analysis tools, enable public health officials to identify and respond to outbreaks swiftly. Improved reporting mechanisms and efficient contact tracing significantly limit the spread of the virus.
- Role of the CDC in monitoring measles cases: The CDC plays a central role in monitoring measles cases nationwide, collecting and analyzing data to track trends and identify potential outbreaks.
- Effectiveness of contact tracing in preventing further spread: Contact tracing involves identifying and monitoring individuals who may have been exposed to the virus, allowing for timely intervention and preventing further transmission.
- Importance of public health education campaigns: Public health campaigns play a vital role in raising awareness about measles, its symptoms, and the importance of vaccination. These campaigns are crucial in encouraging vaccination uptake and promoting preventive measures.
Improved Access to Healthcare and Vaccination Programs
Ensuring equitable access to healthcare services, particularly in underserved communities, is crucial for boosting vaccination rates. Various government programs and non-profit organizations actively work to overcome barriers to vaccination, making vaccines readily available to all.
- Examples of successful vaccination outreach programs: Mobile vaccination clinics, community-based immunization drives, and partnerships with community leaders have proven effective in reaching underserved populations.
- Government initiatives aimed at increasing vaccination access: Government funding for vaccination programs and initiatives to improve access to healthcare facilities have played a vital role in boosting vaccination rates.
- Role of community health centers in improving vaccination rates: Community health centers provide vital services, including vaccination, to underserved communities, significantly contributing to improved vaccination coverage.
Global Efforts and Reduced Importation of Measles
Global vaccination efforts have significantly reduced measles transmission worldwide. This global decline in measles cases minimizes the risk of imported cases into the United States. International collaborations play a critical role in disease control, sharing best practices and coordinating responses to outbreaks.
- Global measles eradication initiatives: The World Health Organization (WHO) leads global efforts to eradicate measles, working with countries worldwide to improve vaccination coverage and strengthen surveillance systems.
- Impact of international travel restrictions during outbreaks: Temporary travel restrictions during outbreaks help contain the spread of the virus, preventing the importation of cases.
- Collaboration between global health organizations: International collaboration among organizations such as the WHO, CDC, and UNICEF is crucial in sharing knowledge, resources, and expertise to combat measles globally.
Maintaining the Decline in Measles Cases in the United States
The decline in measles cases in the US is a testament to the success of sustained vaccination efforts, improved public health infrastructure, and global cooperation. To maintain this progress and prevent future outbreaks, continued high vaccination rates are essential to sustain herd immunity. This requires ongoing commitment to vaccination programs, addressing vaccine hesitancy, and ensuring equitable access to healthcare for all.
Continue to protect yourself and your community by staying up-to-date on your measles vaccinations and supporting public health efforts to combat this preventable disease. Learn more about measles prevention and vaccination today! [Link to CDC website]

Featured Posts
-
 Cts Eventim Q1 Figures Show Growth In Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Q1 Figures Show Growth In Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025 -
 The Post Roe Reality Over The Counter Birth Control And Its Implications
May 30, 2025
The Post Roe Reality Over The Counter Birth Control And Its Implications
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Lanza Venue Virtual Mira Tu Asiento Antes De Comprar
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Lanza Venue Virtual Mira Tu Asiento Antes De Comprar
May 30, 2025 -
 Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 16 3
May 30, 2025
Plires Programma Tileorasis Gia Tin Kyriaki 16 3
May 30, 2025 -
 Reasons For The Lack Of Excessive Heat Warnings In Weather Reports
May 30, 2025
Reasons For The Lack Of Excessive Heat Warnings In Weather Reports
May 30, 2025
