Elevated Uncertainty: The Growing Risks Of Inflation And Job Losses

Table of Contents
Understanding the Inflationary Spiral
High inflation erodes purchasing power, impacting everyone from individuals to large corporations. Let's examine its root causes and devastating consequences.
Causes of Current Inflation
Several factors contribute to the current inflationary pressures:
- Supply chain disruptions: Global logistics bottlenecks and shortages of raw materials, exacerbated by geopolitical events and the lingering effects of the pandemic, have driven up production costs. This is particularly evident in sectors reliant on international trade and complex supply chains.
- Increased energy prices: Soaring oil, gas, and electricity prices significantly increase production and transportation costs, feeding into higher prices for consumer goods and services. The energy crisis has become a major driver of global inflation.
- Demand-pull inflation: Pent-up demand following pandemic lockdowns, coupled with increased government spending and stimulus packages in some regions, has led to a surge in consumer spending, outpacing supply and driving prices upward. This imbalance between supply and demand is a key factor in inflationary pressure.
- Monetary policy: Decisions made by central banks regarding interest rates and money supply can significantly influence inflation. While monetary tightening aims to curb inflation, it can also lead to economic slowdowns.
- Government spending and stimulus packages: While intended to boost economies, substantial government spending can contribute to inflationary pressures if not carefully managed. The scale and timing of such interventions are crucial.
Consequences of High Inflation
The consequences of sustained high inflation are far-reaching:
- Reduced purchasing power: Consumers find their money buys less, impacting their standard of living and forcing them to cut back on spending. This can trigger a deflationary spiral.
- Increased cost of living: The rising prices of essential goods and services, like food and housing, disproportionately affect low-income households, potentially leading to social unrest. This cost of living crisis is a significant societal concern.
- Erosion of savings and investment returns: Inflation diminishes the real value of savings and investment returns, reducing the financial security of individuals and eroding long-term wealth.
- Damage to business profitability and investment: Higher costs of production and materials reduce profit margins, discouraging investment and potentially leading to business closures.
- Increased borrowing costs: Higher interest rates, a common response to inflation, increase the cost of borrowing for businesses and individuals, further dampening economic activity.
The Looming Threat of Job Losses
The inflationary spiral is closely linked to the risk of increased job losses. Understanding the interplay between these two factors is critical.
Inflation's Impact on Employment
High inflation forces businesses to make difficult choices:
- Businesses forced to cut costs: Decreased profitability due to rising costs often leads to layoffs and reduced hiring. Companies strive to maintain margins in a challenging environment.
- Reduced consumer spending: As purchasing power declines, consumer spending falls, reducing demand for goods and services and forcing businesses to downsize.
- Increased automation: To mitigate rising labor costs, businesses may accelerate the adoption of automation technologies, potentially displacing workers.
- Sectors particularly vulnerable: Industries like manufacturing and hospitality, often with lower profit margins, are particularly susceptible to job losses during inflationary periods.
Other Factors Contributing to Job Losses
Beyond inflation, other factors contribute to job market instability:
- Economic slowdown or recession: A significant economic contraction often leads to widespread job losses across various sectors.
- Technological advancements and automation: Technological progress, while beneficial in the long run, can lead to displacement of workers in certain industries.
- Geopolitical instability and international trade conflicts: Global events can disrupt supply chains, reduce investment, and lead to job losses.
- Shifting consumer preferences and demand: Changes in consumer behavior and demand can lead to restructuring within industries, resulting in job losses in some areas and job creation in others.
Mitigating the Risks of Inflation and Job Losses
Addressing the elevated uncertainty requires a multi-pronged approach involving government policies and proactive strategies by individuals and businesses.
Government Policies and Interventions
Governments play a crucial role in mitigating the risks:
- Fiscal policies: Carefully designed fiscal policies can help manage inflation and stimulate economic growth by addressing supply chain issues and supporting struggling industries.
- Monetary policies: Central banks can use monetary policies, such as adjusting interest rates, to control inflation while minimizing negative impacts on employment.
- Social safety nets: Robust social safety nets, including unemployment benefits and social assistance programs, are crucial to support individuals and families affected by job losses.
- Investment in infrastructure and job creation programs: Investing in infrastructure projects and job creation initiatives can stimulate economic growth and create new employment opportunities.
Individual and Business Strategies
Individuals and businesses need to adapt to the changing economic landscape:
- Diversification of investments and savings: Diversifying investments across different asset classes can help mitigate the impact of inflation and market volatility.
- Budgeting and financial planning: Careful budgeting and financial planning are essential to manage rising costs and prepare for potential job losses.
- Upskilling and reskilling: Continuously upgrading skills and acquiring new ones is crucial to remain competitive in a changing job market.
- Improved business efficiency and cost management: Businesses need to enhance efficiency and carefully manage costs to maintain profitability in a challenging environment.
- Exploring alternative revenue streams and business models: Identifying and developing new revenue streams and adapting business models can improve resilience against economic shocks.
Conclusion:
The current economic climate presents significant challenges due to the elevated uncertainty created by the combined threats of inflation and job losses. Understanding the interconnected nature of these risks is crucial for both individuals and businesses. By proactively implementing strategies to manage expenses, adapt to changing economic conditions, and advocate for effective government policies, we can navigate this period of uncertainty and mitigate its impact. Stay informed about economic trends and actively seek resources and support to understand and manage the risks associated with elevated uncertainty caused by inflation and the potential for job losses. Don't let elevated uncertainty control your future; take proactive steps today to secure your financial well-being.

Featured Posts
-
 Cts Eventim Q1 Figures Show Growth In Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025
Cts Eventim Q1 Figures Show Growth In Revenue And Adjusted Ebitda
May 30, 2025 -
 Bath Hosts World Premiere Of New Hitchcock Musical
May 30, 2025
Bath Hosts World Premiere Of New Hitchcock Musical
May 30, 2025 -
 Foraging For Parsnips A Country Diary Of Roastable Root Vegetables
May 30, 2025
Foraging For Parsnips A Country Diary Of Roastable Root Vegetables
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster Mejorando La Experiencia Del Usuario
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Se Integra Con Ticketmaster Mejorando La Experiencia Del Usuario
May 30, 2025 -
 Rasakan Sensasi Baru Tiga Jet Ski Premium Kawasaki Resmi Di Pasaran Indonesia
May 30, 2025
Rasakan Sensasi Baru Tiga Jet Ski Premium Kawasaki Resmi Di Pasaran Indonesia
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Impact Of Canadian Wildfires On Minnesotas Air Quality
May 31, 2025
Impact Of Canadian Wildfires On Minnesotas Air Quality
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Wildfires A Public Health Threat To Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires A Public Health Threat To Minnesota
May 31, 2025 -
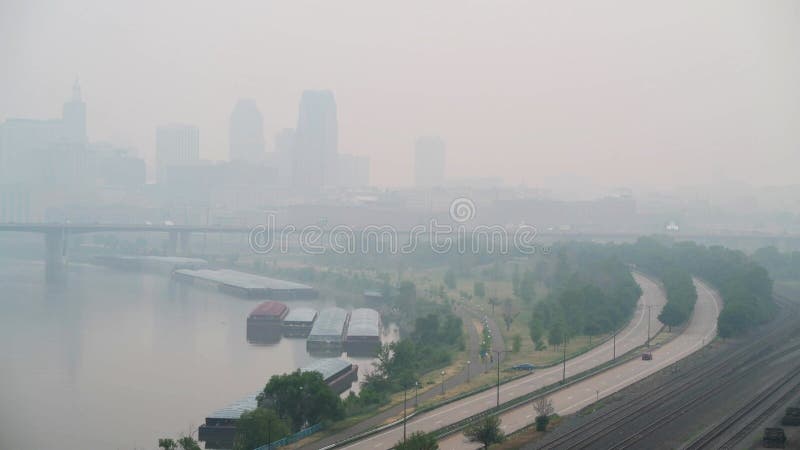 Minnesota Suffers From Degraded Air Quality Canadian Wildfires To Blame
May 31, 2025
Minnesota Suffers From Degraded Air Quality Canadian Wildfires To Blame
May 31, 2025 -
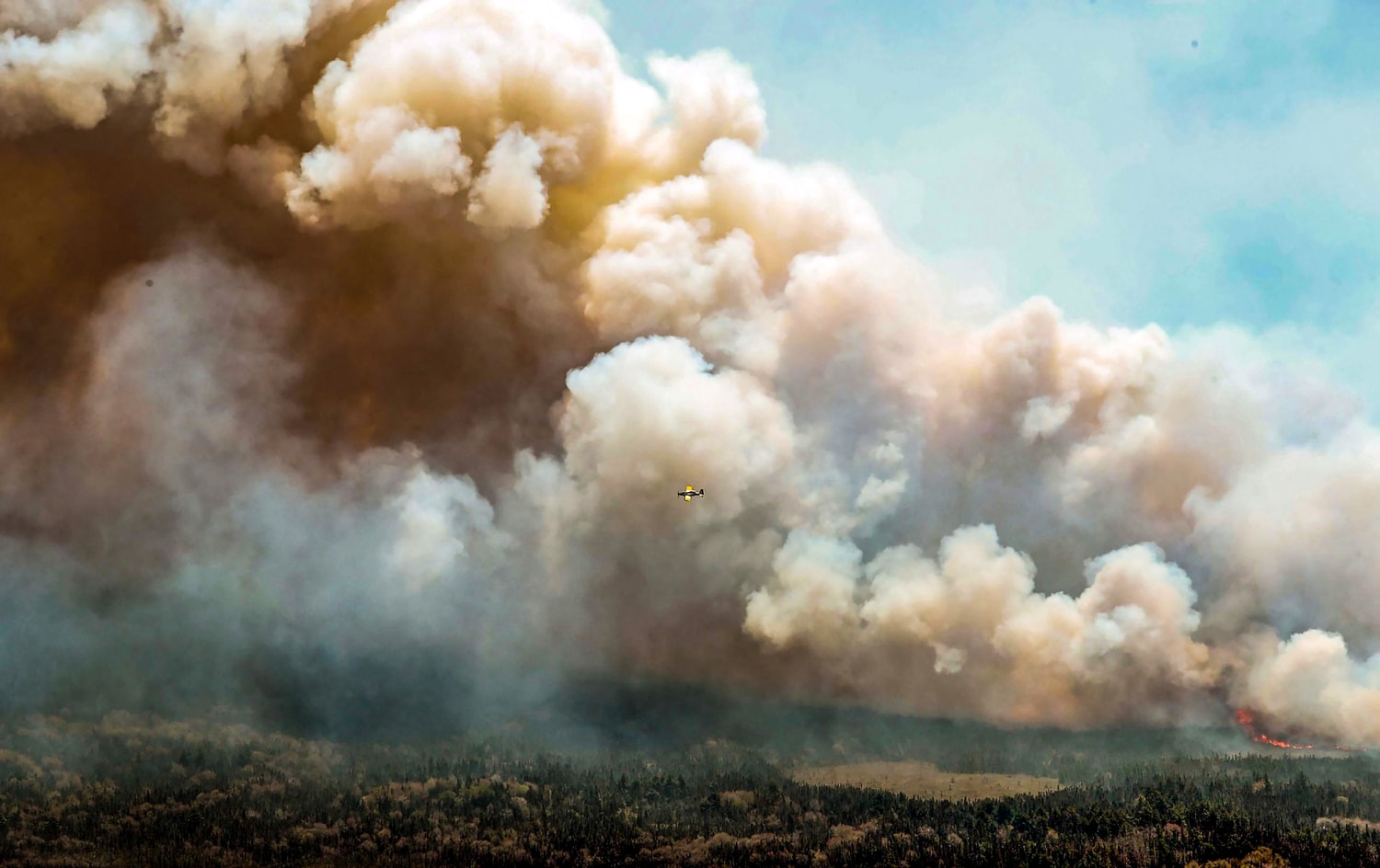 Poor Air Quality In Minnesota Due To Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025
Poor Air Quality In Minnesota Due To Canadian Wildfires
May 31, 2025 -
 Canadian Wildfires Send Dangerous Smoke To Minnesota
May 31, 2025
Canadian Wildfires Send Dangerous Smoke To Minnesota
May 31, 2025
