Enhancing Resilience And Sustainable Development In Least Developed Countries
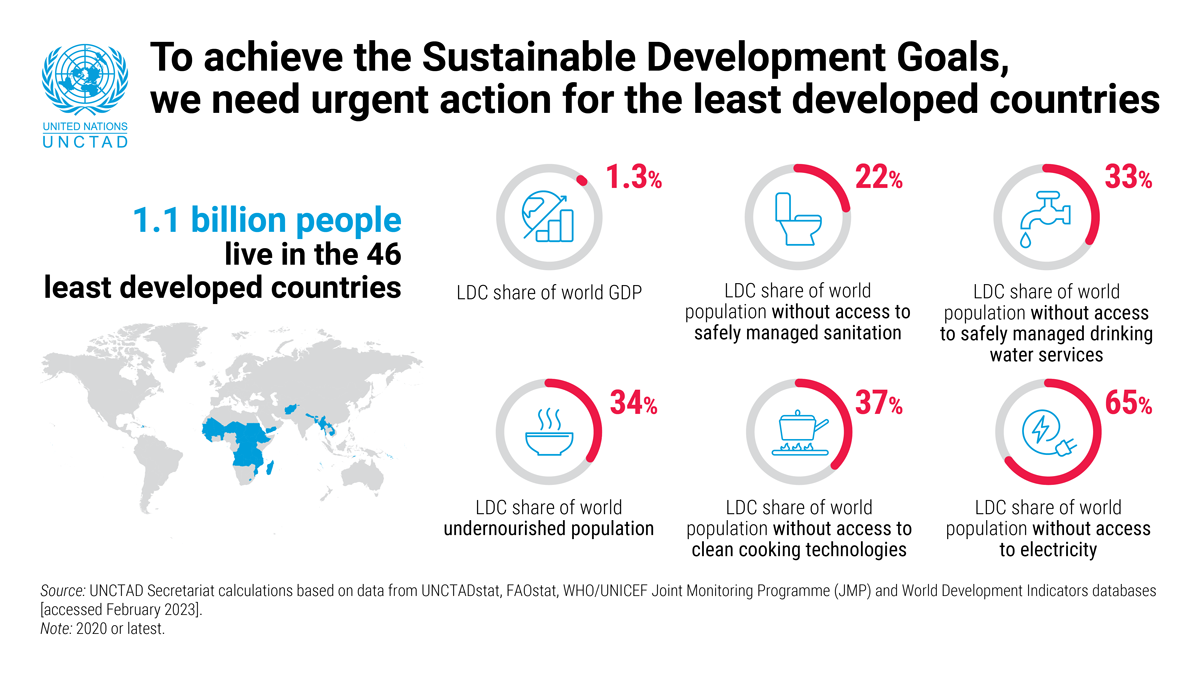
Table of Contents
Strengthening Institutional Capacity for Resilience
Effective governance is the bedrock of resilience. Without strong, accountable institutions, efforts to build resilience and achieve sustainable development are severely hampered.
Good Governance and Transparency
Transparent and accountable governance structures are crucial for fostering resilience. Corruption diverts resources away from essential services, weakens public trust, and undermines development efforts. Conversely, good governance promotes equitable resource allocation, fosters public participation, and strengthens the rule of law.
- Examples of good governance initiatives: Implementing open budgeting systems, strengthening anti-corruption agencies, promoting independent judiciaries.
- The role of civil society: Empowering civil society organizations to monitor government activities and hold officials accountable.
- Combating corruption: Implementing robust anti-corruption legislation and strengthening law enforcement mechanisms.
- Promoting participatory decision-making: Involving communities in planning and implementing development projects to ensure their needs are addressed. This participatory development approach increases ownership and effectiveness.
Keywords: Good governance, transparency, accountability, anti-corruption, participatory development.
Investing in Human Capital
Investing in human capital – education, healthcare, and skills development – is paramount for building individual and community resilience. A healthy, educated population is better equipped to cope with shocks and adapt to change.
- Investing in education for girls: Educated girls are more likely to participate in the workforce, earn higher incomes, and contribute to economic growth.
- Improving healthcare access: Improved healthcare reduces vulnerability to disease outbreaks and other health crises, enhancing community resilience.
- Vocational training programs: Equipping individuals with marketable skills enhances their employment prospects and reduces poverty.
- Promoting entrepreneurship: Fostering entrepreneurship creates new jobs, stimulates innovation, and promotes economic diversification.
Keywords: Human capital, education, healthcare, skills development, entrepreneurship.
Promoting Economic Diversification and Sustainable Growth
Economic diversification and sustainable growth are critical for enhancing resilience in LDCs. Over-reliance on a few sectors makes these countries vulnerable to global price fluctuations and other external shocks.
Sustainable Agriculture and Food Security
Sustainable agriculture practices are crucial for enhancing food security and building resilience to climate change. Climate-smart agriculture techniques can help farmers adapt to changing weather patterns and ensure food production despite increasing climate variability.
- Climate-resilient crops: Promoting the cultivation of drought-resistant and pest-resistant crops.
- Drought-resistant techniques: Implementing water harvesting and conservation techniques to reduce reliance on rain-fed agriculture.
- Fair trade initiatives: Ensuring fair prices for farmers' produce and improving market access.
- Improving infrastructure for market access: Investing in rural infrastructure such as roads, storage facilities, and transportation networks to facilitate access to markets.
Keywords: Sustainable agriculture, food security, climate-smart agriculture, climate resilience, market access.
Developing a Robust Private Sector
A vibrant private sector is essential for creating jobs, generating economic growth, and attracting foreign direct investment (FDI). Supporting small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) is crucial for fostering inclusive growth and boosting economic resilience.
- Access to finance: Providing SMEs with access to credit and other financial services.
- Business incubators: Creating business incubators and innovation hubs to support entrepreneurship.
- Skills development programs for entrepreneurs: Providing entrepreneurs with training in business management, marketing, and finance.
- Incentives for FDI: Implementing policies that attract FDI and encourage investment in productive sectors.
Keywords: Private sector development, SMEs, entrepreneurship, foreign direct investment, access to finance.
Building Climate Resilience and Adapting to Climate Change
Climate change poses a significant threat to LDCs, exacerbating existing vulnerabilities and hindering development progress. Building climate resilience is therefore crucial for sustainable development.
Investing in Climate Change Adaptation Measures
Investing in adaptation measures is crucial for reducing the vulnerability of LDCs to the impacts of climate change. This includes developing early warning systems for extreme weather events and building climate-resilient infrastructure.
- Early warning systems: Developing and implementing early warning systems for droughts, floods, and other climate-related hazards.
- Drought-resistant infrastructure: Investing in drought-resistant infrastructure such as water storage facilities and irrigation systems.
- Climate-resilient agriculture: Promoting climate-resilient agriculture practices to ensure food security.
- Disaster risk reduction: Implementing disaster risk reduction strategies to minimize the impact of climate-related disasters.
Keywords: Climate change adaptation, climate resilience, disaster risk reduction, early warning systems.
Promoting Sustainable Resource Management
Sustainable resource management is essential for ensuring the long-term viability of LDCs' economies and ecosystems. This involves responsible management of natural resources such as water, land, and forests.
- Sustainable forestry practices: Implementing sustainable forestry practices to prevent deforestation and promote reforestation.
- Water conservation techniques: Implementing water conservation techniques to improve water security.
- Land management strategies: Implementing sustainable land management strategies to prevent land degradation.
- Protecting biodiversity: Protecting biodiversity to maintain ecosystem services and enhance resilience.
Keywords: Sustainable resource management, water conservation, land management, biodiversity conservation.
Conclusion
Enhancing resilience and sustainable development in Least Developed Countries requires a multi-faceted approach that addresses institutional capacity, economic diversification, and climate change adaptation. Strengthening governance, investing in human capital, promoting sustainable agriculture, developing a robust private sector, and building climate resilience are all interconnected and crucial for achieving sustainable development goals in these vulnerable nations. The key takeaways emphasize the importance of holistic and integrated strategies to build more resilient and prosperous communities. Learn more about how you can support resilience and sustainable development in Least Developed Countries. Find resources and opportunities to make a difference today by exploring initiatives from organizations like the UN, World Bank, and various NGOs working on the ground. Let's work together to build a more sustainable and resilient future for LDCs.

Featured Posts
-
 100 000 Zl Odszkodowania Panstwowa Spolka Przeciwko Onetowi
May 07, 2025
100 000 Zl Odszkodowania Panstwowa Spolka Przeciwko Onetowi
May 07, 2025 -
 Zaufanie Polakow Najnowszy Ranking Ib Ri S Dla Onetu
May 07, 2025
Zaufanie Polakow Najnowszy Ranking Ib Ri S Dla Onetu
May 07, 2025 -
 Golden State Warriors Win Kuminga Back Curry And Kerr Hit Milestones
May 07, 2025
Golden State Warriors Win Kuminga Back Curry And Kerr Hit Milestones
May 07, 2025 -
 Going From March Madness To Trademarks Madness Protecting Your Brand During The Tournament
May 07, 2025
Going From March Madness To Trademarks Madness Protecting Your Brand During The Tournament
May 07, 2025 -
 And Kara 100
May 07, 2025
And Kara 100
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Kripto Para Yatirimcilari Icin Kripto Lider Riskler Ve Firsatlar
May 08, 2025
Kripto Para Yatirimcilari Icin Kripto Lider Riskler Ve Firsatlar
May 08, 2025 -
 Kripto Lider In Basarisinin Sirri Teknoloji Ekip Ve Vizyon
May 08, 2025
Kripto Lider In Basarisinin Sirri Teknoloji Ekip Ve Vizyon
May 08, 2025 -
 Kripto Lider Gelecegin Kripto Para Projesi Mi Analiz Ve Degerlendirme
May 08, 2025
Kripto Lider Gelecegin Kripto Para Projesi Mi Analiz Ve Degerlendirme
May 08, 2025 -
 Kripto Lider Nedir Ve Neden Herkes Bundan Bahsediyor
May 08, 2025
Kripto Lider Nedir Ve Neden Herkes Bundan Bahsediyor
May 08, 2025 -
 Kripto Para Piyasasinda Kripto Lider In Hizli Yuekselisi Detayli Inceleme
May 08, 2025
Kripto Para Piyasasinda Kripto Lider In Hizli Yuekselisi Detayli Inceleme
May 08, 2025
