Exclusive: The Fight Against California's Electric Vehicle Mandate
Table of Contents
Economic Concerns Fueling the Opposition to California's EV Mandate
The economic implications of California's EV mandate are a major source of opposition. The rapid shift towards electric vehicles poses significant challenges to the automotive industry and raises concerns about consumer affordability.
Impact on the Automotive Industry
The transition to EVs threatens to disrupt the traditional automotive industry, leading to potential job losses.
- Job displacement: The manufacturing of internal combustion engines (ICE) requires a different skillset than EV production. This shift could lead to significant job losses in factories and related industries unless sufficient retraining and reskilling programs are implemented. Analysts predict thousands of jobs could be at risk in the short term, particularly in areas heavily reliant on the traditional auto industry. The “California EV mandate cost” to the workforce is a major point of contention.
- Financial strain on smaller manufacturers: Smaller auto manufacturers lack the resources to invest heavily in EV technology, putting them at a competitive disadvantage and potentially forcing some out of business. The financial burden of adapting to the new regulations is disproportionately impacting smaller players, highlighting an economic inequality within the industry.
- Increased vehicle prices: The cost of developing and producing EVs is currently higher than for gasoline-powered vehicles. This results in higher prices for consumers, making EVs less accessible, especially for low- and middle-income families. Studies suggest that the average price of EVs could be significantly higher than gasoline cars for several more years, exacerbating the “California EV mandate consumer impact.”
Consumer Affordability and Accessibility
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles remains a significant barrier to wider adoption.
- High purchase price: EVs generally have a higher sticker price than comparable gasoline cars, placing them out of reach for many consumers.
- Limited availability: The supply of EVs is still limited, resulting in longer wait times and potentially higher prices due to increased demand.
- Charging infrastructure: A lack of widespread and reliable charging infrastructure, particularly in underserved communities, adds another layer of complexity and concern regarding EV accessibility. “Charging infrastructure” development needs to keep pace with EV adoption to ensure equitable access.
- Range anxiety: Concerns about the driving range of EVs and the time it takes to recharge them compared to refuelling a gasoline car remain significant obstacles.
Environmental Concerns and the Counterarguments to the EV Mandate
While the intention behind California's EV mandate is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, some argue that the policy's environmental impact is not as straightforward as it seems.
Electricity Generation and Emissions
The environmental benefit of EVs depends heavily on the source of electricity used to charge them.
- Carbon footprint of electricity: If a significant portion of California's electricity is still generated from fossil fuels (natural gas, coal), the emissions associated with charging EVs could offset some of the environmental benefits.
- Renewable energy dependence: The success of the EV mandate relies on a robust and expanding renewable energy sector to power the vehicles. A transition to a fully renewable energy grid is crucial for mitigating emissions. The “California power grid” needs major upgrades to support the increased energy demand from a large number of EVs.
- Life-cycle emissions: A comprehensive analysis of the entire life cycle of EVs, from battery production to end-of-life recycling, is needed to accurately assess their overall environmental impact compared to gasoline vehicles.
Rare Earth Minerals and Environmental Impact
The extraction and processing of rare earth minerals used in EV batteries raise serious environmental concerns.
- Mining impacts: The mining of these minerals can cause significant environmental damage, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Ethical sourcing: Ensuring the ethical sourcing and responsible mining of these materials is crucial to minimizing the negative environmental and social consequences of EV battery production.
- Sustainable EV production: Investing in research and development of more sustainable battery technologies and recycling processes is essential to mitigate the environmental impact of EV production.
Political and Legal Challenges to California's EV Mandate
California's EV mandate faces significant political and legal hurdles.
Legal Battles and Lobbying Efforts
The mandate has attracted significant legal challenges from automakers and other stakeholders.
- Lawsuits and legal challenges: Several lawsuits have been filed against the mandate, alleging it is overly ambitious, economically unfeasible, or exceeds the state's authority. The “California EV mandate lawsuit” landscape is complex and ever-evolving.
- Intense lobbying: Powerful lobbying efforts from various interest groups, including automakers, oil companies, and labor unions, are working to influence the policy's implementation and future. The “political opposition” to the mandate is significant and well-funded.
Federal Regulations and State Preemption
The conflict between California's mandate and potential federal regulations poses a significant challenge.
- Federal preemption: The federal government could potentially preempt California's regulations, arguing that it interferes with national standards. The “Federal EV standards” could supersede state-level regulations, impacting the enforceability of the mandate.
- State vs. federal authority: The legal battle over state versus federal authority in setting vehicle emission standards is a key aspect of the ongoing fight against the mandate.
Conclusion: The Future of California's Electric Vehicle Mandate – A Call to Action
California's electric vehicle mandate is a complex and controversial policy. While proponents emphasize its environmental benefits and the need for a transition to cleaner transportation, opponents raise serious concerns about its economic feasibility, consumer affordability, and potential environmental downsides. The ongoing legal battles and intense lobbying reflect the deep divisions surrounding this policy. The “California EV mandate future” is uncertain, and the outcome will significantly impact the automotive industry, consumers, and the environment.
To stay informed about this crucial debate, we encourage you to research California's electric vehicle mandate further. Contact your representatives to share your views, and consider joining relevant advocacy groups to participate in the ongoing conversation about electric vehicle policy and the future of zero-emission vehicle adoption. Your voice matters in shaping the future of transportation.

Featured Posts
-
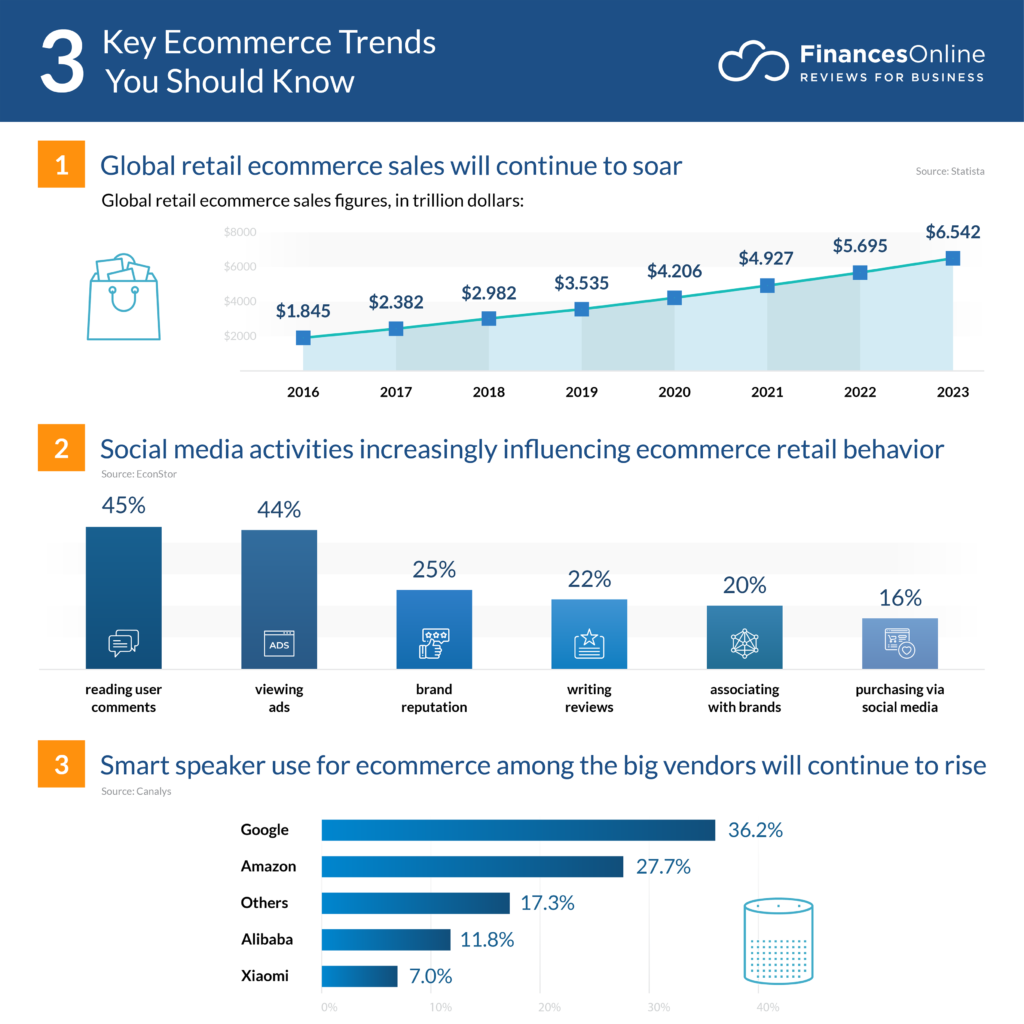 The Rise Of Mobile Marketing In E Commerce Trends And Predictions
May 19, 2025
The Rise Of Mobile Marketing In E Commerce Trends And Predictions
May 19, 2025 -
 The Future Of Transportation Waymo And Ubers Autonomous Ride Services In Austin
May 19, 2025
The Future Of Transportation Waymo And Ubers Autonomous Ride Services In Austin
May 19, 2025 -
 L Tzoymis Kai I Enallaktiki Toy Gia To Kypriako O Dromos Toy Kateynasmoy
May 19, 2025
L Tzoymis Kai I Enallaktiki Toy Gia To Kypriako O Dromos Toy Kateynasmoy
May 19, 2025 -
 Saturday Night Live Is A Fan Favorite Leaving
May 19, 2025
Saturday Night Live Is A Fan Favorite Leaving
May 19, 2025 -
 Militarizacion Del Cne Reacciones Y Consecuencias De La Intervencion
May 19, 2025
Militarizacion Del Cne Reacciones Y Consecuencias De La Intervencion
May 19, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 I A Stasi Xairetismon Sta Ierosolyma Istoria Simasia Kai Paradoseis
May 19, 2025
I A Stasi Xairetismon Sta Ierosolyma Istoria Simasia Kai Paradoseis
May 19, 2025 -
 Mnimi Payloy Pyrino Paroysia Toy Beroias Panteleimonos
May 19, 2025
Mnimi Payloy Pyrino Paroysia Toy Beroias Panteleimonos
May 19, 2025 -
 I Klironomia Toy Samoy Eysevioy Pisti Ekklisia Kai Xristianiki Zoi
May 19, 2025
I Klironomia Toy Samoy Eysevioy Pisti Ekklisia Kai Xristianiki Zoi
May 19, 2025 -
 I A Stasi Ton Xairetismon Sta Ierosolyma Odigos Gia Toys Proskynites
May 19, 2025
I A Stasi Ton Xairetismon Sta Ierosolyma Odigos Gia Toys Proskynites
May 19, 2025 -
 Samoy Eysevios I Prosklisi Stin Ekklisia Kai I Zoi Toy Xristianoy
May 19, 2025
Samoy Eysevios I Prosklisi Stin Ekklisia Kai I Zoi Toy Xristianoy
May 19, 2025
