FTC's Defense Strategy Takes Center Stage In Meta Monopoly Case
Table of Contents
The FTC's Core Argument: Stifling Competition
The FTC's central argument rests on the assertion that Meta has engaged in anti-competitive practices to maintain its dominance in the social media and digital advertising sectors. This argument is built upon two key pillars: evidence of anti-competitive acquisitions and a refutation of Meta's "network effects" defense.
Evidence of Anti-Competitive Acquisitions
The FTC cites several acquisitions as key evidence of Meta's anti-competitive behavior. These include:
-
Instagram (2012): The FTC argues that acquiring Instagram, a burgeoning competitor, prevented it from becoming a significant threat to Facebook's market share. This prevented the emergence of a true alternative social media platform and stifled innovation. Internal Meta communications, if presented as evidence, could significantly bolster this claim.
-
WhatsApp (2014): Similarly, the acquisition of WhatsApp, a popular messaging app, is presented by the FTC as a move to eliminate a potential competitor and consolidate Meta's control over communication channels. The FTC likely points to the potential for WhatsApp to have developed into a significant social media platform in its own right.
The FTC aims to demonstrate that these acquisitions weren’t simply about growth but were strategic moves to neutralize emerging threats and cement Meta’s monopolistic position. Expert testimony will likely be crucial in establishing this causal link, detailing the competitive landscape that would have existed had these acquisitions not occurred.
Meta's Network Effects Argument and the FTC's Counter
Meta's defense likely centers on the argument that its size and market share are a natural outcome of "network effects"—the phenomenon where a product or service becomes more valuable as more people use it. However, the FTC counters this by arguing that while network effects play a role, Meta’s actions actively prevented the development of competitive alternatives. The FTC aims to show that Meta’s actions went beyond simply leveraging network effects; they were deliberately anti-competitive, creating an unlevel playing field and eliminating potential competitors. The FTC will likely introduce economic modeling to demonstrate that Meta’s growth trajectory is inconsistent with a purely organic, network-effect-driven model.
Key Challenges Faced by the FTC
Despite the compelling nature of its arguments, the FTC faces significant hurdles in proving its case. Two key challenges stand out: the burden of proof and the definition of the relevant market.
The Burden of Proof: A High Bar
The FTC bears the significant burden of proving that Meta engaged in anti-competitive behavior and that this behavior caused harm to consumers. This requires demonstrating not just that Meta acted in ways that could potentially harm competition but that these actions actually did cause harm. Establishing causation—proving a direct link between Meta's actions and a reduction in competition—is a complex and challenging task. The FTC must meticulously present evidence to overcome this challenge.
Defining the Relevant Market: A Crucial Determination
The definition of the "relevant market" is crucial. The FTC must convincingly define the market in which Meta operates to establish its monopolistic position. Is it the social networking market, the digital advertising market, or a broader combination? Meta will likely argue for a broader market definition to dilute the perception of its market dominance, making it harder for the FTC to demonstrate monopolistic power. The court’s decision on this definition will significantly impact the outcome of the case.
The Role of Data and Evidence in the FTC's Strategy
The FTC's strategy relies heavily on the presentation of compelling data and evidence. This includes internal Meta documents and expert testimony supported by economic modeling.
Internal Meta Documents: A Treasure Trove of Evidence
Internal Meta documents, including emails, memos, and strategic planning documents, could provide crucial insights into Meta's intentions and actions. These documents could contain evidence supporting the FTC’s claims of anti-competitive behavior. However, the FTC must overcome legal hurdles to gain access and use these documents effectively as evidence, navigating potential issues of privilege and relevance.
Expert Testimony and Economic Modeling: Quantifying Anti-Competitive Effects
Expert witnesses will play a crucial role in presenting economic analysis and modeling to demonstrate the anti-competitive effects of Meta's actions. This involves creating and presenting models that show how Meta's behavior has distorted the market, reduced competition, and potentially harmed consumers. The credibility and robustness of these economic models will significantly influence the court's decision.
Potential Outcomes and Implications
The outcome of the FTC's case against Meta will have far-reaching implications, impacting future tech regulation and global competition.
Structural Remedies vs. Behavioral Remedies: Shaping Meta's Future
If the FTC prevails, the court could order various remedies. These could range from structural remedies, such as forcing Meta to divest itself of Instagram or WhatsApp, to behavioral remedies, such as imposing restrictions on Meta's future acquisition activities. The chosen remedy will significantly shape Meta's future operations and market presence.
Impact on Future Tech Regulation: Setting a Precedent
The outcome of this case will set a precedent for future antitrust enforcement against Big Tech companies. A successful FTC case could embolden regulators worldwide to take a more aggressive stance against potentially anti-competitive behavior by dominant tech firms. Conversely, a loss could embolden large tech companies to engage in practices that might harm competition.
Global Implications: A Ripple Effect Across Borders
This case's implications extend beyond the United States. The outcome will influence antitrust enforcement efforts in other jurisdictions and shape the global regulatory landscape for tech companies. International bodies and other countries’ regulators will closely watch the decision and its rationale, shaping their own approaches to antitrust enforcement in the digital sector.
Conclusion
The FTC's defense strategy in the Meta monopoly case is a critical battle in the fight for fair competition in the digital market. The success of the FTC's strategy will determine not only Meta's future but also set a precedent for future antitrust enforcement against large technology companies. The evidence, legal arguments, and the court's decision will profoundly impact the future of digital markets. Stay informed about developments in this landmark case and understand the implications of the FTC's actions on the future of competition. Follow future articles for further updates on this vital FTC vs. Meta monopoly case.

Featured Posts
-
 King Day 2024 Celebration Plans Vs Abolition Debate
May 18, 2025
King Day 2024 Celebration Plans Vs Abolition Debate
May 18, 2025 -
 Netherlands Majority Opposes Eus Response To Trump Import Tariffs
May 18, 2025
Netherlands Majority Opposes Eus Response To Trump Import Tariffs
May 18, 2025 -
 9 11 Netflix Docuseries Shows Mans Terrifying Realization He Was On Fire
May 18, 2025
9 11 Netflix Docuseries Shows Mans Terrifying Realization He Was On Fire
May 18, 2025 -
 The Burning Tower A 9 11 Survivors Story Netflix Documentary
May 18, 2025
The Burning Tower A 9 11 Survivors Story Netflix Documentary
May 18, 2025 -
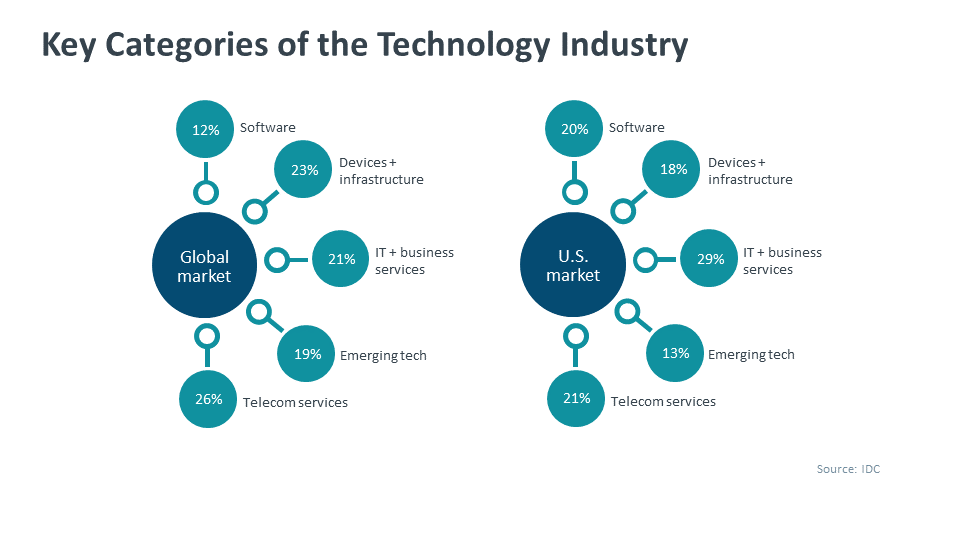 The Countrys New Business Landscape Key Growth Areas Revealed
May 18, 2025
The Countrys New Business Landscape Key Growth Areas Revealed
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Analyzing Michael Confortos Performance Overcoming Early Spring Challenges
May 18, 2025
Analyzing Michael Confortos Performance Overcoming Early Spring Challenges
May 18, 2025 -
 Michael Confortos Hot Streak Continues In Dodgers Victory Over Mariners
May 18, 2025
Michael Confortos Hot Streak Continues In Dodgers Victory Over Mariners
May 18, 2025 -
 Amanda Bynes Only Fans Debut Strict Rules And New Chapter
May 18, 2025
Amanda Bynes Only Fans Debut Strict Rules And New Chapter
May 18, 2025 -
 Confortos Spring Training Slump How He Bounced Back
May 18, 2025
Confortos Spring Training Slump How He Bounced Back
May 18, 2025 -
 Michael Confortos Early Season Struggles A Look At His Overcoming Them
May 18, 2025
Michael Confortos Early Season Struggles A Look At His Overcoming Them
May 18, 2025
