Growing Number Of Unrelated Measles Cases In Texas
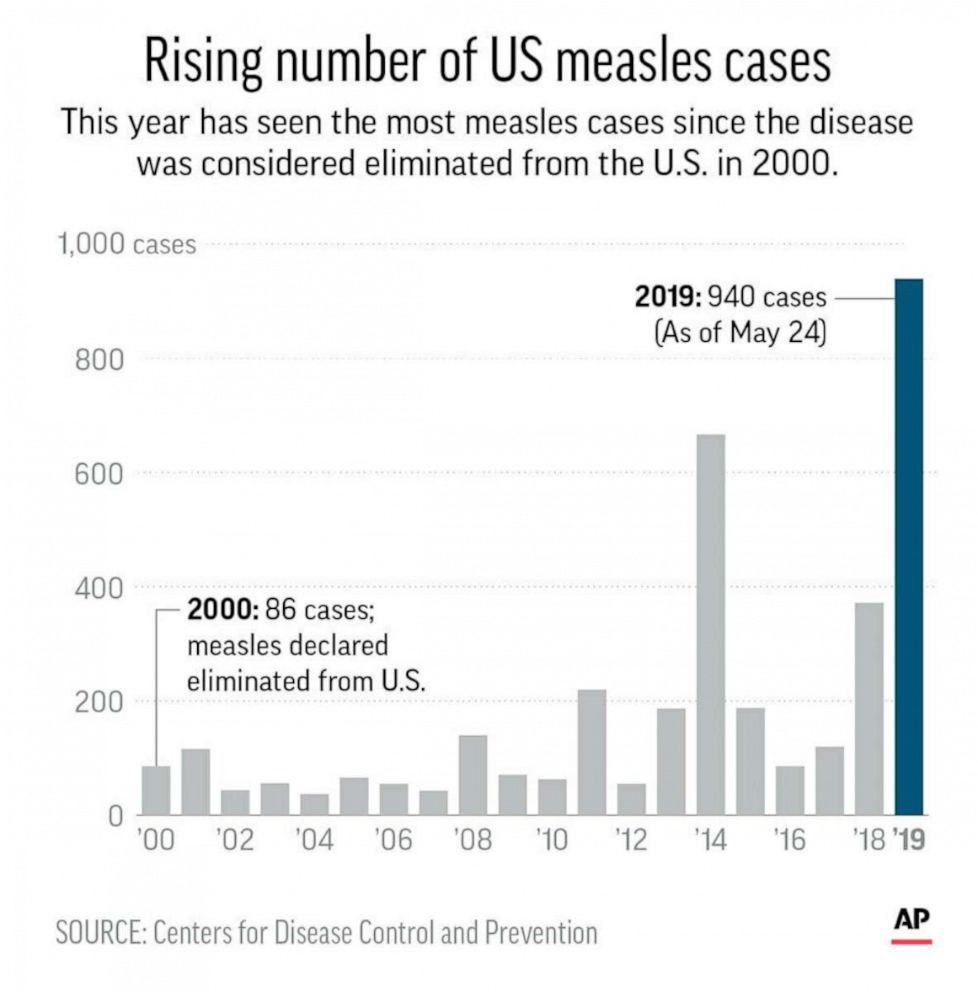
Table of Contents
Geographic Distribution of Unrelated Measles Cases in Texas
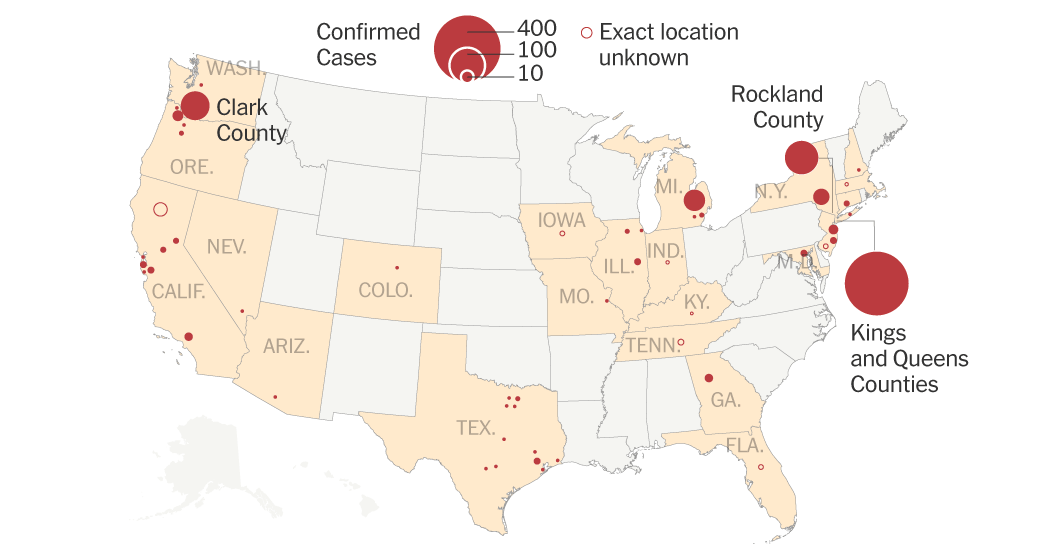
Understanding the spatial spread of measles is critical to controlling the outbreak. Mapping the outbreaks reveals a complex picture of the spread of measles across the state.
Mapping the Outbreaks
While precise, real-time data fluctuates, initial reports and data from the Texas Department of State Health Services (DSHS) show a concerning pattern of unrelated measles cases scattered across Texas. A comprehensive map (if available and legally permissible to reproduce) would visually illustrate this distribution. For instance, we might see clusters in specific counties or cities, suggesting localized outbreaks, while others demonstrate cases seemingly appearing independently.
- Specific counties or cities experiencing significant outbreaks: [Insert specific county/city examples with case numbers if available and verifiable. Avoid naming specific individuals due to privacy concerns].
- Differences in case numbers between urban and rural areas: Analyzing whether urban centers or rural communities are disproportionately affected is crucial for targeted interventions. [Insert data or observations if available and verifiable. Cite sources].
- Potential links to travel or community events: Investigating whether recent travel or large gatherings (religious events, festivals, etc.) could have facilitated the spread is important for understanding transmission pathways. [Insert examples if available and verifiable].
Factors Contributing to the Rise in Unrelated Measles Cases
Several intertwined factors contribute to the alarming rise in unrelated measles infections across Texas.
Low Vaccination Rates
A significant correlation exists between low vaccination rates and the increased number of measles cases. Measles is a highly contagious disease, and achieving herd immunity requires high vaccination coverage.
- Statistics on vaccination rates in Texas: [Insert relevant statistics on vaccination rates across different age groups and regions in Texas. Cite the source of this data].
- Discussion of vaccine hesitancy and misinformation: Vaccine hesitancy, fueled by misinformation spread through social media and other channels, significantly impacts vaccination uptake. Addressing these concerns through evidence-based communication is crucial.
- Potential impact of vaccine exemptions: The availability of non-medical exemptions for vaccination contributes to lower overall vaccination rates, increasing the risk of outbreaks. [Cite relevant laws and regulations].
Weakened Herd Immunity
Low vaccination rates directly lead to weakened herd immunity, making entire communities more vulnerable to outbreaks.
- Definition and explanation of herd immunity: Herd immunity is a form of indirect protection from infectious diseases where a sufficient proportion of the population is immune, limiting the spread of the disease to those who aren't.
- Consequences of weakened herd immunity on vulnerable populations: Weakened herd immunity disproportionately affects vulnerable populations such as infants too young to be vaccinated, individuals with compromised immune systems, and those with medical contraindications to vaccination.
Public Health Response and Prevention Strategies
Combating the growing number of unrelated measles cases requires a multi-pronged approach involving public health agencies and community engagement.
Role of Public Health Agencies
Texas health authorities are playing a crucial role in controlling the measles outbreak.
- Contact tracing efforts: Identifying and monitoring contacts of infected individuals is essential to prevent further spread.
- Public health announcements and campaigns: Public awareness campaigns are crucial in communicating the risks of measles and encouraging vaccination.
- Availability of vaccines and testing: Ensuring easy access to measles vaccines and diagnostic testing is vital.
Community Awareness Campaigns
Community engagement is paramount to successful measles prevention.
- Educational initiatives targeting parents and communities: Educational initiatives targeting parents and communities are crucial to address vaccine hesitancy and promote vaccination uptake.
- Collaboration with healthcare providers and community leaders: Collaboration with healthcare providers and trusted community leaders is essential to build trust and disseminate accurate information.
Conclusion
The growing number of unrelated measles cases in Texas presents a serious public health challenge. Low vaccination rates, fueled by vaccine hesitancy and misinformation, have led to weakened herd immunity, resulting in widespread outbreaks across the state. The effective response requires coordinated efforts from public health agencies, healthcare providers, and communities. To combat the growing number of unrelated measles cases in Texas, it is crucial for everyone eligible to get vaccinated and to encourage others to do the same. Protect yourself and your community – learn more about measles prevention and vaccination in Texas today! Visit your doctor or the Texas Department of State Health Services website for more information and to find vaccination locations near you.

Featured Posts
-
 Mad By Sparks Album Review And Track By Track Breakdown
May 30, 2025
Mad By Sparks Album Review And Track By Track Breakdown
May 30, 2025 -
 Measles Outbreak Expands Six New Cases Confirmed In Kansas
May 30, 2025
Measles Outbreak Expands Six New Cases Confirmed In Kansas
May 30, 2025 -
 Sjekkliste For Bading Temperatur Vaer Og Sikkerhet
May 30, 2025
Sjekkliste For Bading Temperatur Vaer Og Sikkerhet
May 30, 2025 -
 Servicio Militar De Bts Previsiones Para Su Regreso A La Musica
May 30, 2025
Servicio Militar De Bts Previsiones Para Su Regreso A La Musica
May 30, 2025 -
 Cyberpunk 2 Development Challenges And Opportunities For Cd Projekt Red
May 30, 2025
Cyberpunk 2 Development Challenges And Opportunities For Cd Projekt Red
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Elon Musks Awkward Saudi Encounter With Donald Trump
May 31, 2025
Elon Musks Awkward Saudi Encounter With Donald Trump
May 31, 2025 -
 Trumps Changing Stance On Musk Cnn Data Chief Explains
May 31, 2025
Trumps Changing Stance On Musk Cnn Data Chief Explains
May 31, 2025 -
 Madrid Atp 1000 Girons Victory Over Berrettini
May 31, 2025
Madrid Atp 1000 Girons Victory Over Berrettini
May 31, 2025 -
 Munich Tennis Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Bmw Open Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025
Munich Tennis Zverev Battles Griekspoor In Bmw Open Quarter Finals
May 31, 2025 -
 Zverev Vs Griekspoor Bmw Open 2025 Quarter Final Highlights
May 31, 2025
Zverev Vs Griekspoor Bmw Open 2025 Quarter Final Highlights
May 31, 2025
