Heatwave Deaths In England Reach 311: A Public Health Crisis?

Table of Contents
H2: The Severity of the Heatwave and its Impact on Vulnerable Populations
The intensity and duration of the recent heatwave in England were significant, with prolonged periods of exceptionally high temperatures exceeding previously recorded levels. This extreme heat had a disproportionate impact on vulnerable groups, exacerbating existing health conditions and leading to increased heat stress and heatstroke. These vulnerable populations include:
- The Elderly: Older individuals are particularly susceptible to heat-related illnesses due to decreased thermoregulation and often pre-existing health conditions. Many elderly individuals live alone and may be less likely to seek help during heatwaves.
- Infants and Young Children: Their bodies are less efficient at regulating temperature, making them highly vulnerable to heatstroke.
- Individuals with Underlying Health Conditions: People with cardiovascular, respiratory, or renal diseases are at significantly increased risk of heat-related complications.
- The Socially Isolated: Those living alone, with limited social contact, or lacking access to adequate cooling facilities are more prone to experiencing the severe effects of extreme heat.
Statistics on deaths within these vulnerable groups during the heatwave are crucial for understanding the impact and for targeting future preventative measures. While precise figures may take time to collate, early data strongly suggests a higher mortality rate within these specific populations. The physiological effects of extreme heat, ranging from heat exhaustion to life-threatening heatstroke, are well documented and require effective preventative strategies. Excess deaths, beyond what would be normally expected for this time of year, serve as a powerful indicator of the heatwave's impact.
H2: Failures in Public Health Preparedness and Response
The effectiveness of existing heatwave action plans and warning systems in England needs careful scrutiny following this tragedy. While the UK has a heatwave plan in place, questions remain about its implementation and reach. Shortcomings may include:
- Inadequate Communication Strategies: Did warnings reach all vulnerable populations effectively? Clear, accessible, and multilingual communication is vital, especially for those who might not regularly access mainstream media.
- Insufficient Healthcare Capacity: Were healthcare services adequately equipped to handle the surge in heat-related illnesses? Hospitals may have experienced increased admissions and strain on resources.
- Uneven Resource Allocation: Were resources—such as cooling centers and support services—sufficiently allocated and distributed to areas most affected by the heatwave? Effective resource allocation requires proactive planning and accurate prediction of areas most at risk.
- Early Warning Systems: Could improvements be made to early warning systems to provide more accurate and timely forecasts, giving communities more time to prepare?
H2: Long-Term Strategies for Mitigation and Prevention
The increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves, undeniably linked to climate change, demand long-term strategies for mitigation and prevention. This requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Climate Change Adaptation: Investing in climate change adaptation is crucial to reduce the overall impact of extreme weather events.
- Urban Planning: Improving urban planning to mitigate the urban heat island effect (where cities are significantly hotter than surrounding areas) is essential. This includes increasing green spaces, using reflective materials in construction, and promoting sustainable urban design.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Sustained public awareness campaigns must educate the public about heatwave safety, emphasizing the risks to vulnerable populations and providing practical advice on staying safe during extreme heat.
- Community Support Networks: Strengthening community support networks can ensure that vulnerable individuals receive the necessary assistance and support during heatwaves. This includes checking on elderly neighbors and providing access to cooling centers.
- Infrastructure Improvements: Investing in infrastructure improvements, such as better cooling systems in public buildings and improved public transport, is vital to enhance resilience to extreme heat.
Conclusion:
The 311 heatwave deaths in England underscore a critical need for significant improvements in public health preparedness and response to extreme heat events. Failures in communication, resource allocation, and targeted support for vulnerable populations contributed to this tragic toll. The increasing frequency and intensity of heatwaves, driven by climate change, demand urgent and comprehensive action. Addressing heatwave deaths in England requires a multi-faceted approach. We need immediate improvements in heatwave action plans, enhanced communication strategies, and increased support for vulnerable populations. Investing in climate change adaptation measures and improving public awareness is crucial to reducing the devastating impact of future heatwaves. Let's work together to prevent future heatwave deaths in England and build a more resilient and prepared nation. We must act now to mitigate the risks associated with heatwave mortality and prevent further tragedies caused by extreme heat.

Featured Posts
-
 Beyond The Baseline Unveiling The Challenges Faced By Players Competing Against French Favorites At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025
Beyond The Baseline Unveiling The Challenges Faced By Players Competing Against French Favorites At Roland Garros
May 30, 2025 -
 3 Billion Loan Cancellation Trump Administrations Impact On Sunnova Energy
May 30, 2025
3 Billion Loan Cancellation Trump Administrations Impact On Sunnova Energy
May 30, 2025 -
 Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Preparacion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025
Ticketmaster Y Setlist Fm La Guia Definitiva Para La Preparacion De Conciertos
May 30, 2025 -
 Astratyjyt Dwytshh Bnk Aljdydt Ltezyz Hdwrh Balimarat
May 30, 2025
Astratyjyt Dwytshh Bnk Aljdydt Ltezyz Hdwrh Balimarat
May 30, 2025 -
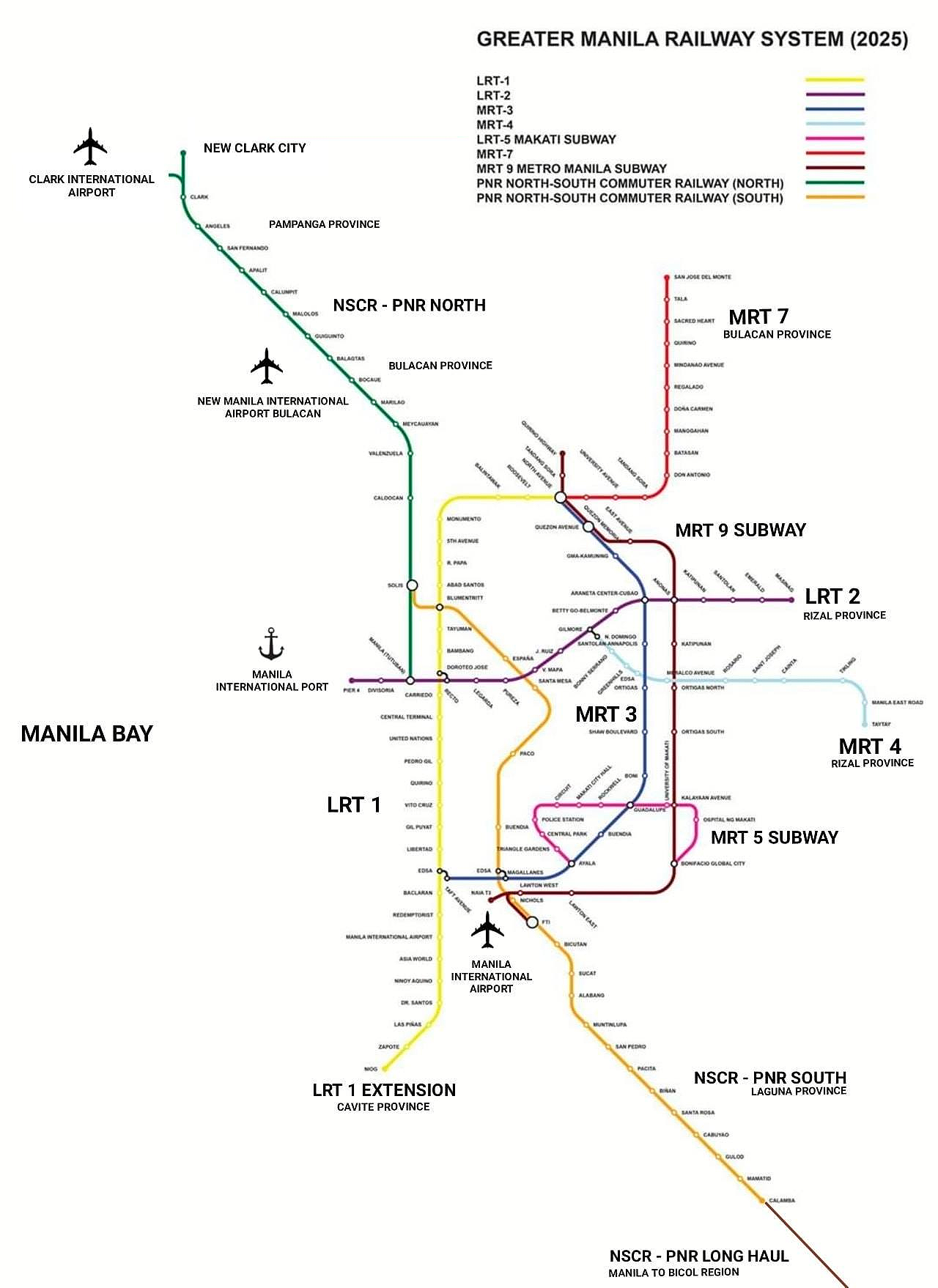 The Future Of Manila Bay Threats And Opportunities For Continued Vitality
May 30, 2025
The Future Of Manila Bay Threats And Opportunities For Continued Vitality
May 30, 2025
