Household Wariness Hampering China's Consumer-Led Growth Strategy
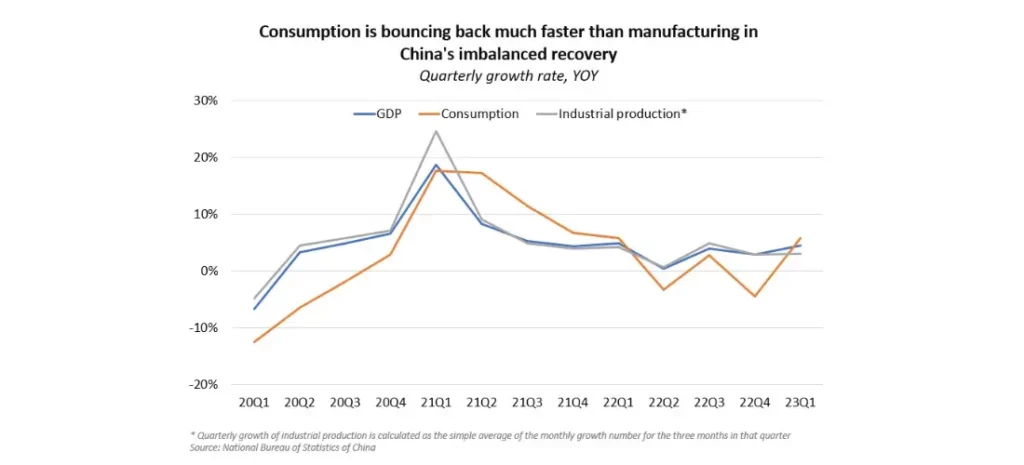
Table of Contents
China's ambitious plan for consumer-led economic growth is facing a significant headwind: widespread household wariness. After years of uncertainty, from the pandemic to the ongoing property market woes and geopolitical tensions, Chinese consumers are tightening their purse strings, significantly impacting the nation's economic trajectory. This cautiousness, characterized by reduced consumer spending, poses a considerable challenge to the government's economic goals and has global implications. This article explores the key factors contributing to this wariness and its implications for China's future.
The Impact of Reduced Consumer Spending on China's GDP
Consumer spending is a cornerstone of China's GDP, historically contributing a substantial percentage to its overall economic growth. However, recent data reveals a concerning slowdown in consumer spending, directly impacting the nation's economic performance. This reduced consumer confidence translates into tangible consequences across various sectors.
- Decreased retail sales figures: Official statistics reveal a consistent decline in retail sales growth compared to previous years, indicating a significant reduction in consumer purchasing power and willingness to spend.
- Impact on various sectors: The slowdown is felt acutely across various sectors. The automotive industry, a major indicator of consumer confidence, has experienced a noticeable slump in sales. Similarly, the luxury goods market and the tourism sector are feeling the pinch, with reduced demand impacting revenue and growth.
- Comparison with previous years' growth rates: Comparing the current growth rates with those of previous years paints a clear picture of the deceleration in consumer spending. The sharp contrast highlights the severity of the issue and its potential long-term consequences.
- Analysis of the GDP contribution decline due to reduced consumer confidence: Economists are increasingly analyzing the direct correlation between the decline in consumer confidence and the decrease in China's GDP growth. This analysis underscores the critical role of consumer spending in driving economic expansion.
Key Factors Driving Household Wariness in China
Several interconnected factors contribute to the prevalent household wariness in China. These range from lingering pandemic effects to the ongoing real estate crisis and broader economic uncertainties.
- Lingering effects of the pandemic on consumer confidence: The COVID-19 pandemic, with its prolonged lockdowns and economic disruptions, significantly impacted consumer confidence. The uncertainty surrounding health risks and future economic prospects continues to influence spending habits.
- Impact of the real estate crisis and its ripple effects on household wealth: The ongoing real estate crisis, characterized by defaults by major developers and falling property values, has severely eroded household wealth. This has led to increased financial anxieties and reduced willingness to spend.
- Role of unemployment and income insecurity: Rising unemployment and income insecurity are further contributing to household wariness. Concerns about job security and future earnings are prompting consumers to prioritize saving over spending.
Bullet points summarizing contributing factors:
- Concerns about job security and future income.
- Debt burdens from mortgages and other loans exacerbated by the real estate crisis.
- Uncertainty surrounding government policies and regulations.
- Geopolitical uncertainties and their impact on the economy.
- Rising inflation and cost of living, eroding purchasing power.
Government Initiatives to Boost Consumer Confidence and Spending
The Chinese government has implemented various initiatives to stimulate consumer spending and bolster economic growth. These range from fiscal measures to policy adjustments aimed at addressing specific concerns.
- Tax cuts and subsidies: The government has introduced tax cuts and subsidies to incentivize consumption and boost consumer demand, particularly in key sectors.
- Infrastructure investments to create jobs: Significant infrastructure investments aim to create employment opportunities and alleviate unemployment concerns, indirectly boosting consumer confidence.
- Measures to support small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs): Supporting SMEs, which are crucial for job creation, is a key component of the government's strategy.
- Promotional campaigns to encourage consumption: The government is employing various promotional campaigns to encourage spending and stimulate demand, though their effectiveness is debated.
- Policies aimed at stabilizing the real estate market: Addressing the real estate crisis through policy adjustments is considered crucial for restoring consumer confidence and preventing further negative impacts.
The effectiveness of these policies, however, remains a subject of ongoing debate and analysis. Challenges include the complexity of the economic situation, the scale of the problems, and the potential for unintended consequences.
Long-Term Implications of Household Wariness for China's Economic Growth
Sustained low consumer spending carries significant long-term risks for China's economic growth. The consequences extend beyond immediate economic indicators, posing challenges to the nation's long-term development trajectory.
- Potential for deflationary pressures: Prolonged weak demand can lead to deflationary pressures, further hindering economic activity and investment.
- Impact on foreign investment: A slowdown in consumer spending can negatively impact foreign investment confidence, potentially leading to capital flight.
- Challenges to achieving sustainable economic development: Household wariness threatens the government's goals for sustainable economic development, emphasizing the need for structural reforms and addressing underlying economic vulnerabilities.
- Social and political implications of economic stagnation: Economic stagnation can have far-reaching social and political implications, including increased social unrest and political instability.
Conclusion: Addressing Household Wariness for a Stronger Chinese Economy
Household wariness poses a formidable challenge to China's ambitious goal of consumer-led economic growth. The interplay of the lingering pandemic effects, the real estate crisis, and broader economic uncertainties has dampened consumer confidence, leading to reduced spending and impacting GDP growth. While the government is actively implementing measures to boost consumer confidence, their long-term effectiveness remains uncertain. The ongoing uncertainty underscores the need for proactive, comprehensive strategies that directly address household concerns and foster a more robust and resilient consumer market. Understanding the multifaceted nature of household wariness is crucial for navigating China's evolving economic landscape. Further research and analysis are necessary to develop effective solutions to stimulate consumer spending and secure China's future economic prosperity. Stay informed on the latest developments regarding household wariness and its impact on China's consumer-led growth strategy.

Featured Posts
-
 Prediksi Skor Bali United Vs Dewa United Head To Head And Susunan Pemain
May 28, 2025
Prediksi Skor Bali United Vs Dewa United Head To Head And Susunan Pemain
May 28, 2025 -
 Liverpool Eyeing Cherki Summer Transfer On The Cards
May 28, 2025
Liverpool Eyeing Cherki Summer Transfer On The Cards
May 28, 2025 -
 Most Violent Pirate Crews In One Piece A Ranking Of Ruthless Buccaneers
May 28, 2025
Most Violent Pirate Crews In One Piece A Ranking Of Ruthless Buccaneers
May 28, 2025 -
 Historical Find 13th Century Construction At Binnenhof
May 28, 2025
Historical Find 13th Century Construction At Binnenhof
May 28, 2025 -
 Mundial De Atletismo Nanjing 2023 La Seleccion Espanola Confirmada
May 28, 2025
Mundial De Atletismo Nanjing 2023 La Seleccion Espanola Confirmada
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Del Toros Pick The Best Realized World In Gaming
May 30, 2025
Del Toros Pick The Best Realized World In Gaming
May 30, 2025 -
 Guillermo Del Toro Names Top Video Game World A Fully Realized Vision
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro Names Top Video Game World A Fully Realized Vision
May 30, 2025 -
 Guillermo Del Toro Praises Popular Shooters World Building
May 30, 2025
Guillermo Del Toro Praises Popular Shooters World Building
May 30, 2025 -
 Global Investment Opportunities In Saudi Arabia A Deutsche Bank Perspective
May 30, 2025
Global Investment Opportunities In Saudi Arabia A Deutsche Bank Perspective
May 30, 2025 -
 L Ere Moderne De La Deutsche Bank Un Recit Complexe De Hauts Et De Bas
May 30, 2025
L Ere Moderne De La Deutsche Bank Un Recit Complexe De Hauts Et De Bas
May 30, 2025
