Housing Crisis Deepens: Rent Freeze To Cost Corporations €3 Billion
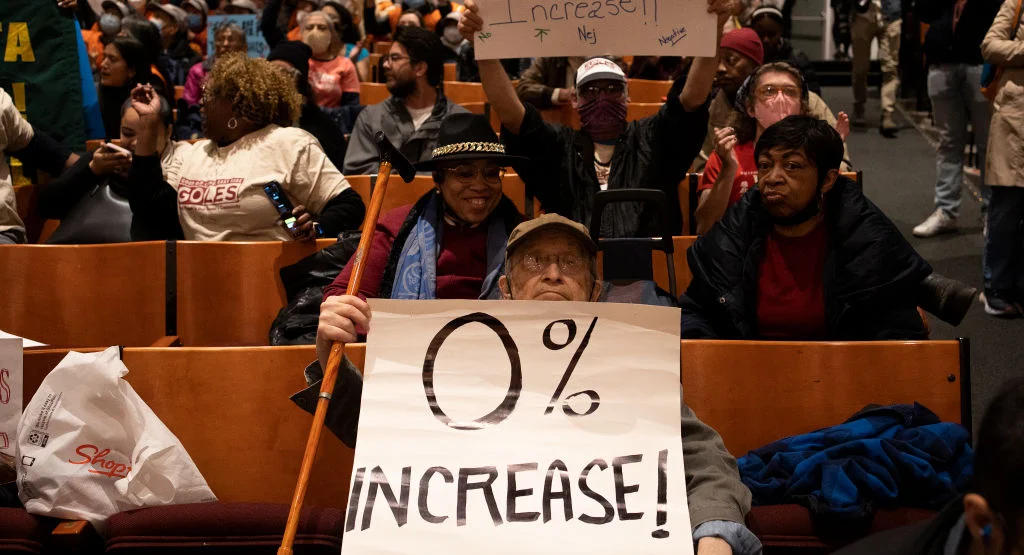
Table of Contents
The Economic Impact of a Rent Freeze on Corporations
A rent freeze costing corporations €3 billion is a substantial blow to the rental sector. This figure represents a collective loss across numerous property companies, calculated by estimating the difference between current rental income and the income they would receive under a frozen rent system. Several factors influence this calculation, including:
- The size of the rental portfolio: Larger corporations with extensive holdings will absorb a more significant financial impact.
- Location of properties: Rent freezes might disproportionately affect corporations owning properties in high-demand urban areas with already high rental costs.
- Existing lease agreements: The impact will depend on the number of properties with existing leases that are unaffected by a freeze.
This financial strain could have severe consequences:
- Reduced profitability: Lower rental income directly impacts corporate profitability and shareholder returns.
- Decreased investment: Corporations might postpone or cancel investments in property maintenance, renovations, and new construction, leading to a deterioration of the housing stock.
- Potential responses: Corporations might respond by selling off properties, focusing on higher-yield investments, or attempting to recoup losses by increasing rents in areas not subject to the freeze. This could create further inequities within the rental market.
The Social Impact of Rent Freezes: Relief for Tenants?
While a rent freeze offers immediate relief to tenants by reducing housing costs and improving affordability, its social impact is complex and not without drawbacks.
Benefits:
- Increased financial stability: Lower rent payments free up household income for essential expenses like food, healthcare, and education.
- Improved quality of life: Reduced financial stress leads to better overall well-being for tenants.
- Protection for vulnerable populations: Low-income families and students are particularly vulnerable to rising rents; a freeze offers a crucial safety net.
Drawbacks:
- Reduced maintenance incentives: Landlords might be less inclined to invest in necessary repairs and maintenance if rental income is capped, leading to deteriorating property conditions.
- Potential for black markets: Rent freezes can create a black market for rental properties, driving up prices illegally and exploiting vulnerable tenants.
- Scarcity of rental units: Reduced profitability might discourage new construction, leading to a further tightening of the rental market supply.
Alternative Solutions to the Housing Crisis
Rent freezes, while offering short-term relief, are not a sustainable long-term solution. Alternative strategies need to be considered to address the root causes of the housing crisis:
- Government subsidies: Direct financial assistance to low-income households can help them afford rental payments, reducing the strain on individuals and families.
- Increased affordable housing construction: Public and private sector collaboration is vital to build more affordable housing units, increasing supply and reducing market pressure.
- Rent control regulations: Well-designed rent control measures can limit rent increases without completely freezing them, offering a more balanced approach.
- Public-private partnerships: Collaboration between governments and private developers can leverage both public funds and private expertise to address the housing shortage effectively.
The Long-Term Sustainability of Rent Freezes
Rent freezes create market distortions and unintended consequences. While they provide temporary relief, they disrupt the natural forces of supply and demand. This can lead to:
- Reduced investment in the rental sector: Long-term, the lack of financial incentives can stifle new development and renovations.
- Housing shortages: Limited investment leads to fewer rental units, further increasing competition and potentially driving up prices in unregulated areas.
- Decreased property values: A rent freeze can negatively impact the value of rental properties, potentially impacting those who rely on their property for retirement income.
Conclusion: Navigating the Housing Crisis through Effective Policy
The €3 billion cost of a rent freeze to corporations highlights the significant economic implications of this policy. While offering temporary relief to tenants, it risks creating a range of social and economic problems in the long term. The housing crisis demands comprehensive solutions that address both the immediate needs of tenants and the sustainability of the rental market. Exploring and implementing a combination of alternative strategies, such as government subsidies, increased affordable housing construction, and effective rent control regulations, offers a more robust and enduring approach. We urge readers to engage in the ongoing discussion surrounding affordable housing and advocate for well-researched and effective policies. Further research into sustainable housing policies is crucial for finding long-term solutions to the housing crisis. Let's work together to create truly affordable housing for all.
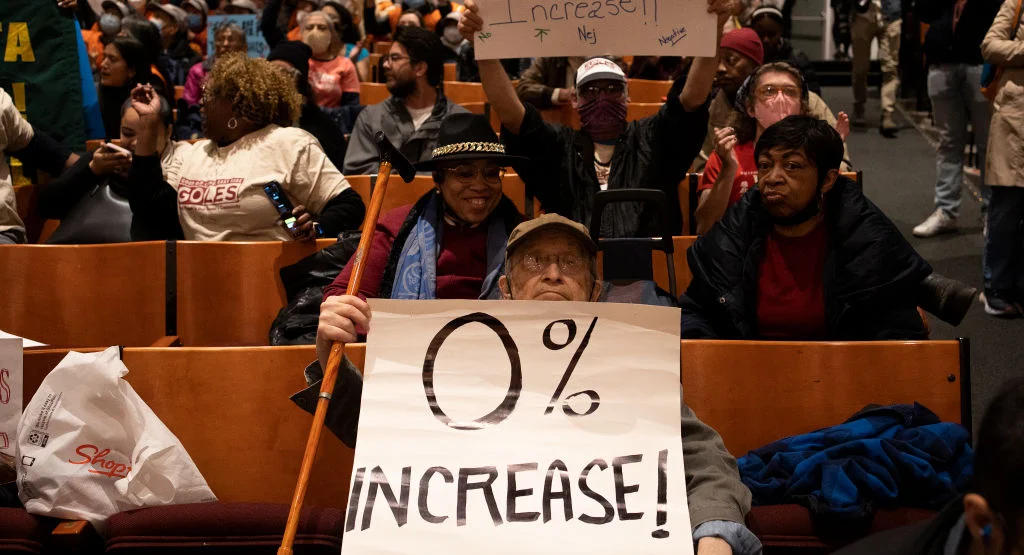
Featured Posts
-
 Leeds United Transfer News England Star Set For Elland Road
May 28, 2025
Leeds United Transfer News England Star Set For Elland Road
May 28, 2025 -
 Retrospective Padres Vs Cubs Series
May 28, 2025
Retrospective Padres Vs Cubs Series
May 28, 2025 -
 Kasatlantas Baru Polresta Balikpapan Akp Djauhari Jadi Imam Sholat Subuh
May 28, 2025
Kasatlantas Baru Polresta Balikpapan Akp Djauhari Jadi Imam Sholat Subuh
May 28, 2025 -
 National Media Ranks Padres Lower In Updated Mlb Power Rankings
May 28, 2025
National Media Ranks Padres Lower In Updated Mlb Power Rankings
May 28, 2025 -
 Man United In Race For Lyon Starlet Rayan Cherki
May 28, 2025
Man United In Race For Lyon Starlet Rayan Cherki
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Ukraine Conflict Fact Checking Trumps Two Week Resolution Claim
May 30, 2025
Ukraine Conflict Fact Checking Trumps Two Week Resolution Claim
May 30, 2025 -
 Understanding Trumps Repeated Two Week Prediction On Ukraine
May 30, 2025
Understanding Trumps Repeated Two Week Prediction On Ukraine
May 30, 2025 -
 Assessing The Accuracy Of Trumps Two Week Ukraine Resolution Claim
May 30, 2025
Assessing The Accuracy Of Trumps Two Week Ukraine Resolution Claim
May 30, 2025 -
 Trumps Ukraine Peace Prediction A Consistent Two Week Timeline
May 30, 2025
Trumps Ukraine Peace Prediction A Consistent Two Week Timeline
May 30, 2025 -
 Analyzing Trumps Consistent Two Weeks To Resolution Claim On Ukraine
May 30, 2025
Analyzing Trumps Consistent Two Weeks To Resolution Claim On Ukraine
May 30, 2025
