India's Economy: The Ripple Effects Of Reciprocal Tariffs
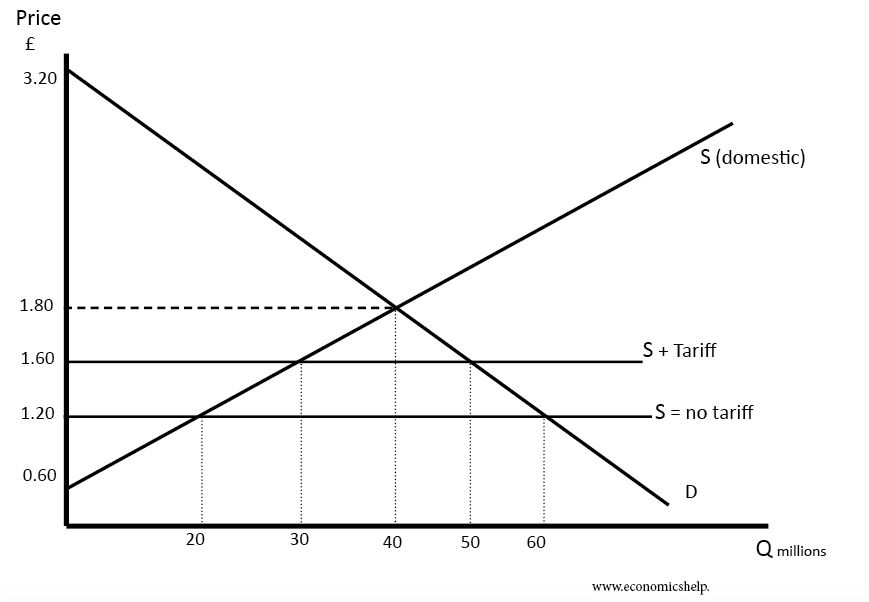
Table of Contents
Understanding Reciprocal Tariffs and Their Mechanism in India
Reciprocal tariffs are taxes imposed on imported goods, often in response to similar tariffs imposed by another country. This tit-for-tat approach can escalate into trade wars, significantly impacting global trade flows. Within the context of India's international trade agreements, reciprocal tariffs disrupt established trade relationships and lead to uncertainty for businesses.
Recent examples include tariff disputes with countries like the US and China, impacting sectors ranging from agriculture and textiles to technology. These actions are governed by the rules and regulations of the World Trade Organization (WTO), which aims to promote fair trade practices. However, navigating WTO regulations regarding retaliatory measures can be complex and often leads to prolonged trade disputes.
- Impact on specific sectors: The agriculture sector, for example, has faced challenges due to tariffs on agricultural exports, while the technology sector has grappled with increased costs on imported components. The textile industry has also been significantly affected by reciprocal tariffs.
- Retaliatory measures: Other countries may retaliate with their own tariffs, further escalating the economic impact and potentially leading to a trade war.
- Bilateral trade agreements: Bilateral trade agreements can play a crucial role in mitigating the negative impacts of reciprocal tariffs by offering preferential access to markets and reducing tariff barriers.
The Impact of Reciprocal Tariffs on India's GDP Growth
Reciprocal tariffs exert a significant influence on India's GDP growth. The immediate impact is often a slowdown in economic activity as import costs rise and export competitiveness decreases. This short-term effect can trigger a ripple effect, affecting investment, consumer spending, and overall economic confidence. The long-term consequences can be more severe, hindering sustainable economic growth and potentially leading to reduced foreign investment. The multiplier effect – where the initial impact on one sector propagates through the economy – exacerbates these challenges.
- Statistical data: Comparing GDP growth rates before and after the implementation of significant reciprocal tariffs reveals a clear negative correlation in many cases.
- Investment and consumer spending: Increased import costs lead to reduced consumer spending power and lower investment in certain sectors.
- Job losses/gains: While some sectors might experience job losses due to reduced competitiveness, others might benefit from increased domestic demand.
Inflationary Pressures and the Cost of Living
Reciprocal tariffs contribute to inflationary pressures by increasing the cost of imported goods. This directly impacts the cost of essential goods and services, affecting consumers across all income groups. However, low-income households are disproportionately affected due to their limited budget and reliance on essential goods.
- Price increases: The price increases vary across product categories, with essential goods like food and fuel experiencing steeper rises.
- Impact on low-income households: The increased cost of living erodes the purchasing power of low-income families, leading to a decrease in their standard of living.
- Government measures: The Indian government often implements measures like subsidies and price controls to mitigate the impact of inflation caused by reciprocal tariffs.
How Indian Businesses Adapt to Reciprocal Tariffs
Indian businesses are employing various strategies to navigate the challenges posed by reciprocal tariffs. These include diversification of supply chains, increased investment in domestic production, and adoption of new technologies. Government support through policy interventions and incentives also plays a vital role in facilitating this adaptation.
- Supply chain diversification: Businesses are exploring alternative sourcing options to reduce reliance on affected import markets.
- Domestic production: Investment in domestic manufacturing capabilities helps reduce dependency on imports and enhances competitiveness.
- Technology adoption: Investing in technology and automation improves efficiency and competitiveness, offsetting the impact of tariffs.
Geopolitical Implications of Reciprocal Tariffs on India's Trade Relations
Reciprocal tariffs significantly impact India's relationships with major trading partners. These trade disputes can lead to trade diversion, where countries shift trade flows to alternative partners, and realignment of global trade relationships. Regional trade agreements, such as the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP), play a crucial role in mitigating these impacts by fostering regional trade cooperation and reducing tariff barriers among participating countries.
- Impact on bilateral agreements: Reciprocal tariffs can strain existing bilateral trade agreements and require renegotiation or adaptation.
- Regional trade cooperation: Regional trade agreements offer opportunities for increased regional trade cooperation and diversification of trade partners.
- Global trade relationships: India's global trade relationships are reshaped as it adapts to the challenges and opportunities presented by reciprocal tariffs.
Conclusion
This article has examined the multifaceted ripple effects of reciprocal tariffs on India's economy. The implementation of reciprocal tariffs poses significant challenges, impacting GDP growth, inflation, and the competitiveness of Indian businesses. Understanding these effects is paramount for both policymakers and businesses. To navigate this complex landscape, continuous monitoring of global trade dynamics and proactive adaptation strategies are essential. By actively engaging with the evolving implications of reciprocal tariffs, India can strive towards a more resilient and robust economy. Further in-depth research and analysis of the long-term effects of reciprocal tariffs on India's economy are crucial for well-informed policymaking and business decision-making.

Featured Posts
-
 Rockies Seek First Win In Eight Games Against Padres
May 15, 2025
Rockies Seek First Win In Eight Games Against Padres
May 15, 2025 -
 Pley Off N Kh L Bobrovskiy Ustanavlivaet Noviy Rekord Pyatiy Sukhar
May 15, 2025
Pley Off N Kh L Bobrovskiy Ustanavlivaet Noviy Rekord Pyatiy Sukhar
May 15, 2025 -
 1 050 V Mware Price Hike At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
May 15, 2025
1 050 V Mware Price Hike At And Ts Concerns Over Broadcoms Acquisition
May 15, 2025 -
 Jalen Brunson Out How The Knicks Depth Steps Up
May 15, 2025
Jalen Brunson Out How The Knicks Depth Steps Up
May 15, 2025 -
 Gsw Campus Incident Individual Apprehended All Clear
May 15, 2025
Gsw Campus Incident Individual Apprehended All Clear
May 15, 2025
