Inside Our ADHD Minds: A Guide For Individuals And Families

Table of Contents
Understanding the ADHD Brain: Neurological Differences and Symptoms
Neurological Basis of ADHD
The ADHD brain differs neurobiologically from neurotypical brains. Research points to imbalances in key neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine, which play crucial roles in attention, focus, and impulse control. Understanding these neurological differences is key to comprehending the challenges faced by individuals with ADHD.
- Dopamine: This neurotransmitter is essential for motivation, reward processing, and focus. In ADHD, dopamine pathways may be less efficient, leading to difficulties with attention and motivation.
- Norepinephrine: This neurotransmitter regulates alertness, arousal, and attention. Imbalances can contribute to inattention, distractibility, and difficulties with task completion.
While the exact neurological basis of ADHD is still being researched, some studies have identified potential structural differences in certain brain regions, although these findings are not universally consistent across all studies.
Recognizing ADHD Symptoms in Adults and Children
ADHD symptoms vary greatly between individuals and across age groups. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for early diagnosis and intervention.
Key Symptoms of Inattention:
- Difficulty sustaining attention in tasks or play.
- Appears not to listen when spoken to directly.
- Difficulty organizing tasks and activities.
- Avoids, dislikes, or is reluctant to engage in tasks that require sustained mental effort.
- Often loses things necessary for tasks or activities (e.g., school materials, pencils, books, tools).
- Is often easily distracted by extraneous stimuli.
- Is often forgetful in daily activities.
Key Symptoms of Hyperactivity/Impulsivity:
- Fidgets with hands or feet or squirms in seat.
- Leaves seat in classroom or in other situations in which remaining seated is expected.
- Runs about or climbs excessively in situations in which it is inappropriate (in adolescents or adults, may be limited to subjective feelings of restlessness).
- Has difficulty playing or engaging in leisure activities quietly.
- Is often "on the go" or acts as if "driven by a motor."
- Talks excessively.
- Blurts out answers before questions have been completed.
- Has difficulty waiting turn.
- Interrupts or intrudes on others (e.g., butts into conversations or games).
ADHD in Adults vs. Children: While child ADHD is often characterized by hyperactivity, adult ADHD may present primarily with inattention and difficulty with organization and time management. Symptoms may also shift and change over time.
The Challenges of Living with ADHD: Daily Life and Relationships
Academic and Professional Challenges
ADHD significantly impacts academic and professional success. Difficulties with executive function, a set of cognitive skills that control behavior, are central to these challenges.
Examples of Challenges:
- Procrastination and difficulty prioritizing tasks.
- Struggles with organization and time management.
- Difficulty with planning and completing complex projects.
- Forgetfulness and missed deadlines.
Strategies for Overcoming Challenges:
- Time-blocking: Scheduling specific times for tasks.
- Task breakdown: Breaking down large tasks into smaller, more manageable steps.
- Utilizing technology: Employing calendar apps, reminder systems, and organizational tools.
Social and Emotional Impacts of ADHD
ADHD can also significantly impact social interactions, self-esteem, and emotional regulation.
Difficulties:
- Impulsivity in social situations leading to misunderstandings or hurt feelings.
- Difficulty with emotional control, leading to outbursts or emotional dysregulation.
- Challenges with maintaining relationships due to inconsistent behavior or difficulty understanding social cues.
Co-occurring Conditions: Individuals with ADHD often experience co-occurring conditions such as anxiety and depression, which can further complicate their lives and require additional support.
Effective Strategies for Managing ADHD: Treatment and Support
Treatment Options for ADHD
A holistic approach to ADHD treatment is often most effective. This usually involves a combination of medication and therapy.
Medication:
- Stimulant medications (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamine) increase dopamine and norepinephrine levels in the brain, improving focus and attention.
- Non-stimulant medications (e.g., atomoxetine) work through different mechanisms to address ADHD symptoms.
Therapy:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
- Behavioral therapy focuses on teaching coping mechanisms and strategies for managing impulsivity and hyperactivity.
Support Systems and Resources
Building a strong support system is vital for managing ADHD. Many resources are available for individuals and families.
Support and Resources:
- CHADD (Children and Adults with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder): A leading organization providing information, support, and advocacy for individuals with ADHD and their families.
- Online forums and communities: Connecting with others who understand the challenges of living with ADHD can provide valuable support and shared experiences. (Note: always exercise caution and discretion when using online resources).
Conclusion
Understanding the complexities of ADHD is the first step towards effective management and a better quality of life. This guide has explored the neurological underpinnings of ADHD, the challenges it presents, and strategies for coping and thriving. By implementing the suggested strategies and seeking support, individuals and families can navigate the complexities of ADHD and build a more fulfilling life. Remember, learning more about ADHD and accessing the right support is key to managing this condition successfully. Continue your journey towards understanding ADHD by exploring additional resources and seeking professional guidance.

Featured Posts
-
 Byd A Evropa Role Managementu A Hybridnich Vozidel V Budovani Znacky
May 13, 2025
Byd A Evropa Role Managementu A Hybridnich Vozidel V Budovani Znacky
May 13, 2025 -
 Landman Season 2 Sam Elliott Cast In New Role Report Confirmed
May 13, 2025
Landman Season 2 Sam Elliott Cast In New Role Report Confirmed
May 13, 2025 -
 Nhl Draft Lottery 2025 New York Islanders Get 1 San Jose Sharks 2 Chicago Blackhawks 3
May 13, 2025
Nhl Draft Lottery 2025 New York Islanders Get 1 San Jose Sharks 2 Chicago Blackhawks 3
May 13, 2025 -
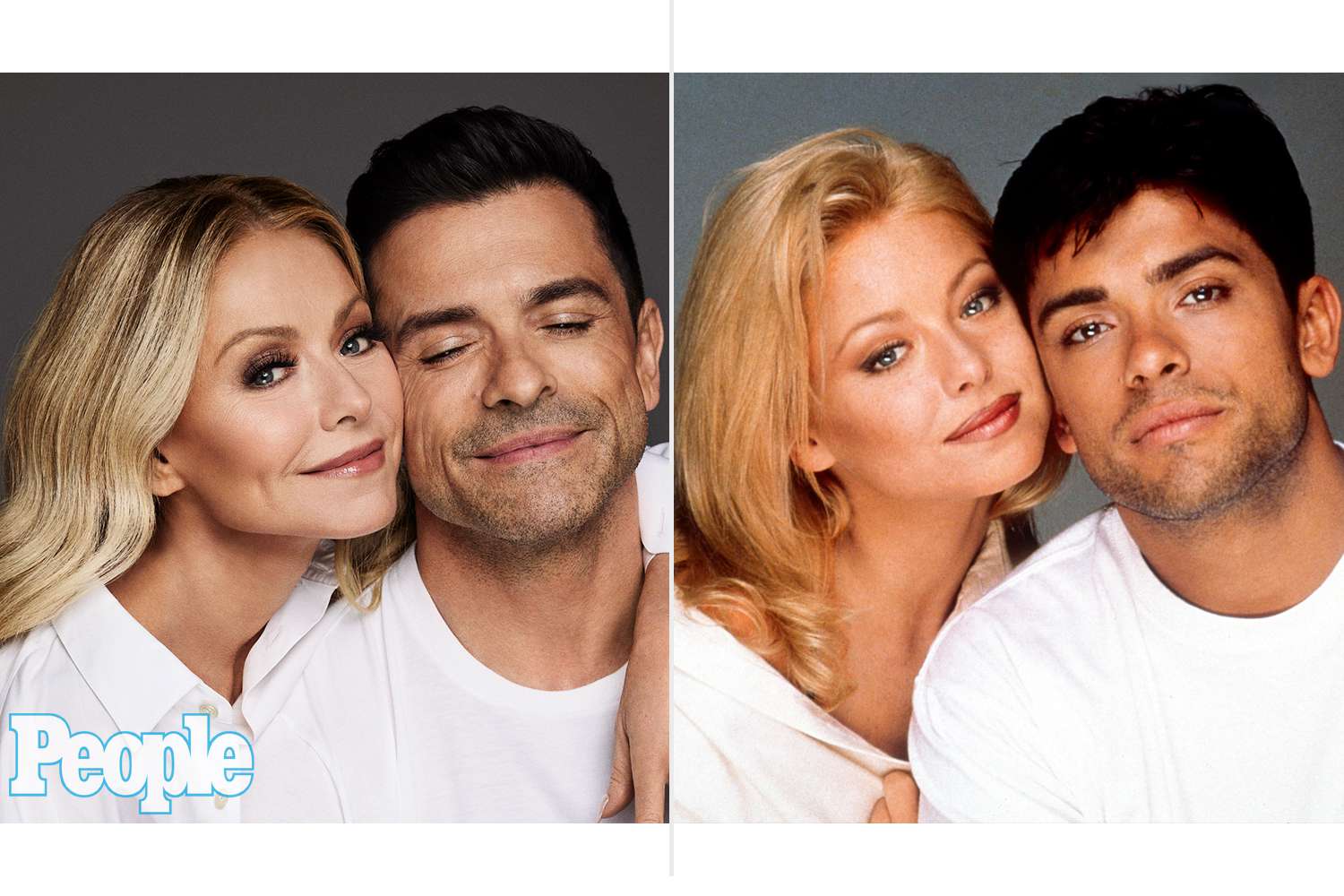 New Live Studio Setup Kelly Ripa And Mark Consuelos Temporary Space And Fan Feedback
May 13, 2025
New Live Studio Setup Kelly Ripa And Mark Consuelos Temporary Space And Fan Feedback
May 13, 2025 -
 Nba Draft Lottery How The System Works
May 13, 2025
Nba Draft Lottery How The System Works
May 13, 2025
