Investigation Into Persistent Toxic Chemicals In Buildings Following Ohio Train Derailment
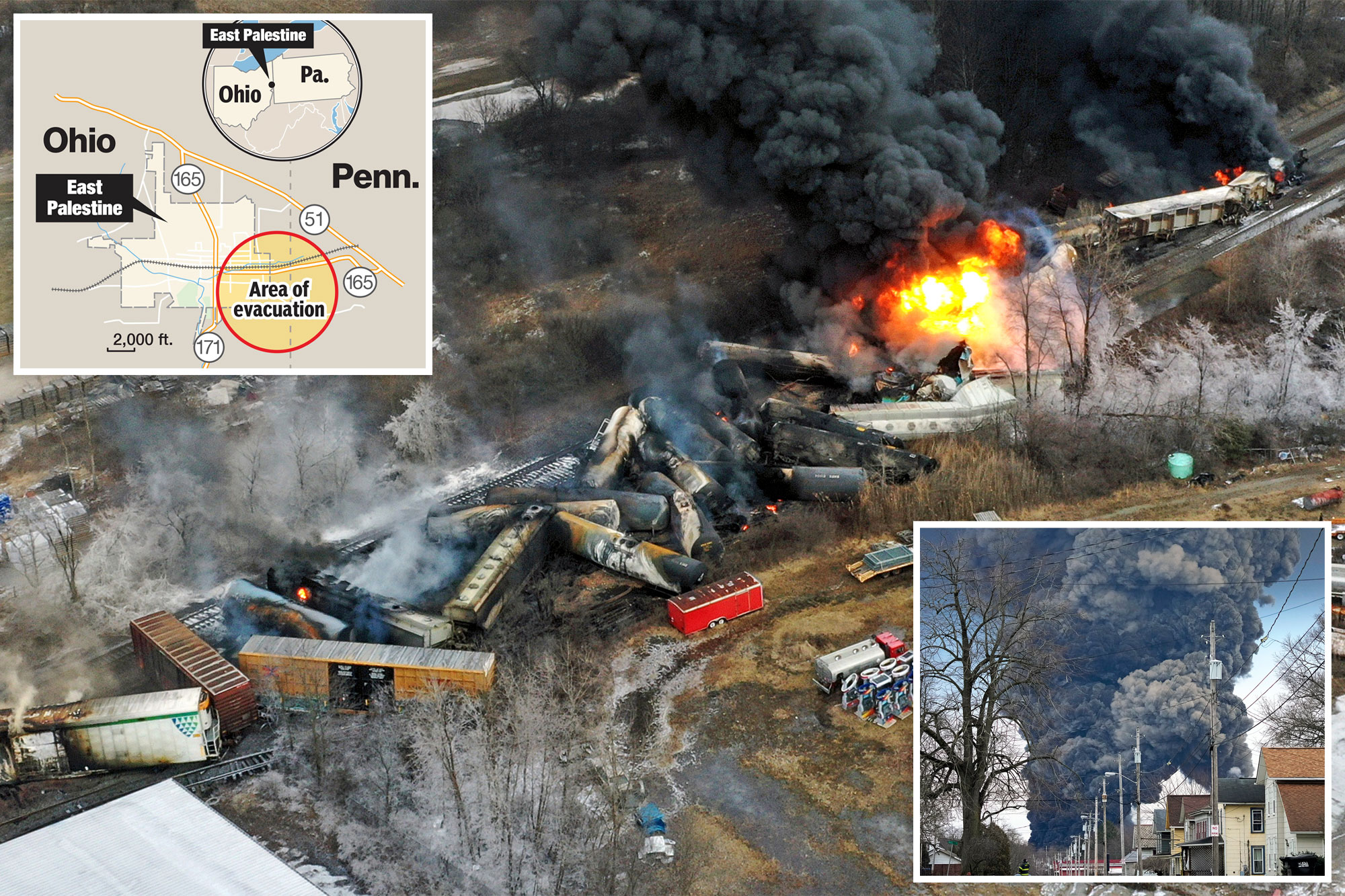

Table of Contents
Types of Persistent Toxic Chemicals Released
The Ohio train derailment involved the release of several hazardous materials, many of which are classified as persistent organic pollutants (POPs). These chemicals persist in the environment for extended periods, accumulating in living organisms and posing significant long-term health risks. Key chemicals of concern include:
- Vinyl chloride: A known carcinogen linked to liver cancer, brain cancer, and lymphoma. It is volatile and can easily infiltrate buildings through air infiltration.
- Butyl acrylate: An irritant that can cause respiratory problems, skin irritation, and eye damage. Its persistence in building materials is a concern.
- Other chemicals: The exact composition of the released materials is still under investigation, but other potentially persistent pollutants may be present, requiring comprehensive testing.
These chemicals' persistence is due to their resistance to breakdown in the environment, meaning they can remain in the soil, water, and air for months or even years, leading to continued exposure risks. [Link to relevant EPA report on chemical persistence]. [Link to scientific study on health impacts of vinyl chloride].
Pathways of Building Contamination
Several pathways facilitated the entry of toxic chemicals into buildings near the derailment site:
- Air Infiltration: Volatile organic compounds (VOCs), such as vinyl chloride, can easily enter buildings through cracks, windows, and ventilation systems. Weather patterns, such as wind direction and precipitation, significantly influence the extent of air contamination.
- Water Contamination: Surface water and groundwater contamination can lead to the leaching of chemicals into building water supplies. This pathway may be more significant for buildings with private wells.
- Soil Migration: Chemicals deposited in the soil can migrate into building foundations and potentially into indoor air through cracks or basement seepage. This is particularly concerning for older buildings with less effective foundation sealing.
The proximity of a building to the derailment site, its age and construction materials, and the effectiveness of its ventilation and filtration systems all affect the level of contamination. [Include a diagram illustrating these pathways].
Methods for Detecting and Measuring Contamination
Accurate detection and measurement of persistent toxic chemicals in buildings are critical for assessing health risks and implementing appropriate remediation strategies. Several methods are employed:
- Air Sampling: Air samples are collected using specialized equipment and analyzed for the presence of VOCs and other airborne pollutants. Passive sampling techniques and active air pumps are used depending on the suspected contaminants.
- Water Sampling: Water samples from wells, municipal supplies, and building plumbing are analyzed to identify any dissolved or suspended contaminants.
- Soil Testing: Soil samples are collected around buildings to determine the level of chemical contamination in the surrounding environment. This helps in evaluating the potential for soil migration.
Accredited laboratories using EPA-approved methods should conduct all testing to ensure the reliability and validity of results. [Link to information on accredited laboratories and testing standards]. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each method is crucial for selecting the most appropriate approach.
Health Risks Associated with Exposure
Exposure to the persistent toxic chemicals released during the derailment poses significant health risks, including:
- Vinyl Chloride: Increased risk of liver cancer, brain cancer, lymphoma, and other cancers.
- Butyl Acrylate: Respiratory irritation, skin and eye irritation, and potential for allergic reactions.
Children, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing respiratory or cardiovascular conditions are particularly vulnerable to these health risks. Long-term exposure can result in chronic health problems. [Link to relevant CDC health information]. [Link to resources on vulnerable populations].
Remediation Strategies and Building Safety
Remediation strategies focus on removing or mitigating the contamination in affected buildings:
- Air Purification: High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration systems and other air purification technologies can help remove airborne contaminants.
- Water Treatment: Water treatment systems, including activated carbon filtration, can remove dissolved chemicals from drinking water supplies.
- Soil Remediation: Soil excavation and replacement or in-situ remediation techniques may be necessary to remove contamination from the soil around buildings.
Following safety protocols during remediation is vital to protect workers and residents. Building owners and residents should follow guidelines provided by environmental health authorities. [Link to resources on remediation techniques and safety protocols].
Conclusion
The Ohio train derailment has raised significant concerns about the presence of persistent toxic chemicals in nearby buildings, posing substantial health risks to residents. This investigation highlights the various types of persistent pollutants released, the pathways of contamination, the available testing methods, associated health risks, and the remediation strategies needed. Understanding the potential impact of persistent toxic chemicals is crucial for ensuring long-term health and safety following the Ohio train derailment. If you live near the derailment site or have concerns about your indoor air quality, it is crucial to conduct testing for persistent toxic chemicals. Contact your local health department or an accredited environmental testing laboratory to learn more about testing and remediation options. Don't hesitate to take proactive steps to protect your family's health and safety.

Featured Posts
-
 Nueve Meses Despues Belinda Bencic Reclama El Titulo De Campeona
Apr 27, 2025
Nueve Meses Despues Belinda Bencic Reclama El Titulo De Campeona
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Ramiro Helmeyer And The Pursuit Of Barcelona Success
Apr 27, 2025
Ramiro Helmeyer And The Pursuit Of Barcelona Success
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Impresionante Eliminacion En Indian Wells Fin Del Sueno Para La Favorita
Apr 27, 2025
Impresionante Eliminacion En Indian Wells Fin Del Sueno Para La Favorita
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Hhss Controversial Choice Anti Vaccine Activist To Examine Debunked Autism Vaccine Claims
Apr 27, 2025
Hhss Controversial Choice Anti Vaccine Activist To Examine Debunked Autism Vaccine Claims
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Bencic Triumphant Abu Dhabi Open Win
Apr 27, 2025
Bencic Triumphant Abu Dhabi Open Win
Apr 27, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Whitecaps Pne Stadium Plan Updates On Negotiations And Timeline
Apr 27, 2025
Whitecaps Pne Stadium Plan Updates On Negotiations And Timeline
Apr 27, 2025 -
 New Vancouver Whitecaps Stadium Pne Fairgrounds A Potential Site
Apr 27, 2025
New Vancouver Whitecaps Stadium Pne Fairgrounds A Potential Site
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Bc Place Alternative Whitecaps Explore Pne Stadium Development
Apr 27, 2025
Bc Place Alternative Whitecaps Explore Pne Stadium Development
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Whitecaps Eyeing New Stadium Pne Fairgrounds Negotiations Underway
Apr 27, 2025
Whitecaps Eyeing New Stadium Pne Fairgrounds Negotiations Underway
Apr 27, 2025 -
 Whitecaps Stadium Talks New Pne Fairgrounds Venue Possible
Apr 27, 2025
Whitecaps Stadium Talks New Pne Fairgrounds Venue Possible
Apr 27, 2025
