Justice Department's Decision To End School Desegregation Order: Implications And Future Of Desegregation

Table of Contents
Immediate Implications of the Decision
The immediate impact of the Justice Department's decision to end these desegregation orders is multifaceted and potentially devastating for affected school districts. The legal ramifications are far-reaching, potentially creating a ripple effect across the nation. The most concerning implication is the heightened risk of re-segregation, reversing decades of progress toward racial integration in education.
-
Increased racial disparities in school resources: With the oversight of desegregation orders removed, there's a greater chance that already existing resource disparities between predominantly minority and majority-white schools will worsen. This could exacerbate inequalities in teacher quality, curriculum offerings, and access to advanced programs.
-
Challenges to existing desegregation plans: School districts that relied on these orders for guidance and legal protection in maintaining integration efforts now face uncertainty and potential legal challenges to their existing plans. This uncertainty could lead to dismantling of carefully constructed programs designed to ensure diversity.
-
Potential legal challenges to the Justice Department’s decision: The decision is likely to face legal challenges from various groups arguing that it violates the constitutional rights of students and undermines the progress made in achieving racial equality in education. These legal battles could drag on for years.
-
Impact on students' educational opportunities: The ultimate victims of re-segregation are the students themselves. Increased segregation limits access to quality education, perpetuates achievement gaps, and hinders social and economic mobility for minority students.
Long-Term Effects on School Diversity
The long-term effects of ending these desegregation orders extend beyond the immediate legal and logistical challenges. The potential for a significant shift towards re-segregation poses profound societal consequences.
-
Reduced interracial interaction and understanding: Segregated schools limit opportunities for students from different racial backgrounds to interact, learn from one another, and develop understanding and empathy. This lack of interaction can perpetuate harmful stereotypes and prejudices.
-
Perpetuation of socioeconomic inequalities: School segregation often mirrors socioeconomic segregation. Ending desegregation orders risks exacerbating existing inequalities by concentrating students from low-income families in under-resourced schools, hindering their educational advancement and limiting their life chances.
-
Impact on the future workforce diversity: A less diverse education system can lead to a less diverse workforce, hindering innovation and economic growth. Companies and organizations benefit from the creativity and diverse perspectives that come from a diverse employee base, fostered through integrated educational experiences.
-
Long-term effects on social mobility: School segregation can significantly limit social mobility for students from minority and low-income backgrounds. Access to quality education is a crucial factor in breaking cycles of poverty and achieving upward mobility.
The Role of the Justice Department in Promoting School Integration
The Justice Department has historically played a crucial role in enforcing school desegregation through litigation and oversight. However, the current administration's approach represents a significant shift in the Department’s priorities.
-
Shift in enforcement priorities: The decision to end these desegregation orders reflects a shift in the Department's enforcement priorities, potentially signaling a reduced commitment to addressing school segregation.
-
Impact on other civil rights enforcement: This shift could have broader implications for other civil rights enforcement efforts, sending a message that the federal government is less committed to protecting the rights of minority communities.
-
Future litigation related to school segregation: The decision is likely to spark renewed litigation regarding school segregation, potentially leading to a wave of new lawsuits challenging discriminatory school practices.
-
Role of other federal agencies: Other federal agencies, such as the Department of Education, will need to play a more active role in promoting school integration in the absence of strong Justice Department enforcement.
Alternative Strategies for Achieving School Desegregation
While the Justice Department's decision presents challenges, it also necessitates a renewed focus on exploring alternative strategies for achieving racial balance in schools.
-
Magnet schools and school choice programs: These programs can attract students from diverse backgrounds to schools across district lines, potentially fostering integration. However, careful design and implementation are essential to avoid exacerbating existing inequalities.
-
Busing and transportation initiatives: Busing, while controversial, remains a powerful tool for achieving school integration, particularly in geographically segregated communities. However, effective busing plans require careful consideration of logistical challenges and community concerns.
-
Housing policies and urban planning: Addressing residential segregation is crucial for achieving school integration. Policies that promote affordable housing and integrated communities can create a foundation for more integrated schools.
-
Community-based initiatives for integration: Local initiatives and community involvement are essential for fostering school integration. Parent groups, community organizations, and school leaders can work together to create welcoming and inclusive school environments.
Conclusion: The Future of School Desegregation – A Call to Action
The Justice Department's decision to end certain school desegregation orders has significant implications for the future of racial equality and educational equity in the United States. While this decision presents considerable challenges, it also creates an opportunity to re-evaluate existing strategies and develop new approaches to achieving meaningful school integration. The potential for increased segregation, the exacerbation of existing inequalities, and the weakening of federal commitment to desegregation are serious concerns. However, the fight for school desegregation is far from over. We must continue to advocate for policies that promote racial equality and educational opportunities for all students. The pursuit of school integration requires a renewed commitment from all stakeholders—federal agencies, local school districts, community organizations, and individuals—to ensure that every child has access to a quality education regardless of race or socioeconomic status. Let us work together to create truly integrated schools that foster a more just and equitable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Doctor Who Actor Backlash Proves The Shows Relevance
May 03, 2025
Doctor Who Actor Backlash Proves The Shows Relevance
May 03, 2025 -
 Chinese Naval Activity Off Sydney What Does It Mean For Australia
May 03, 2025
Chinese Naval Activity Off Sydney What Does It Mean For Australia
May 03, 2025 -
 Le Role De Macron Dans Le Choix Du Prochain Pape Enquete A Rome
May 03, 2025
Le Role De Macron Dans Le Choix Du Prochain Pape Enquete A Rome
May 03, 2025 -
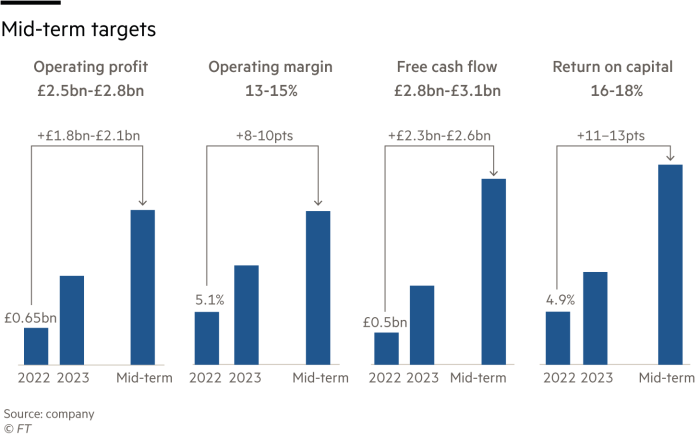 Rolls Royce 2025 Targets Remain Unchanged Amidst Tariff Concerns
May 03, 2025
Rolls Royce 2025 Targets Remain Unchanged Amidst Tariff Concerns
May 03, 2025 -
 Check Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Winning Numbers
May 03, 2025
Check Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Winning Numbers
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Is Rupert Lowe The Right Leader To Replace Nigel Farage In Reform
May 04, 2025
Is Rupert Lowe The Right Leader To Replace Nigel Farage In Reform
May 04, 2025 -
 Reform Party Leadership Should Farage Step Aside For Rupert Lowe
May 04, 2025
Reform Party Leadership Should Farage Step Aside For Rupert Lowe
May 04, 2025 -
 Largest Heat Pump System In Europe A Collaboration Between Innomotics Eneco And Johnson Controls
May 04, 2025
Largest Heat Pump System In Europe A Collaboration Between Innomotics Eneco And Johnson Controls
May 04, 2025 -
 Stockage D Energie Eneco Inaugure Un Parc De Batteries Geant A Au Roeulx
May 04, 2025
Stockage D Energie Eneco Inaugure Un Parc De Batteries Geant A Au Roeulx
May 04, 2025 -
 Record Breaking Heat Pump System Launched By Innomotics Eneco And Johnson Controls
May 04, 2025
Record Breaking Heat Pump System Launched By Innomotics Eneco And Johnson Controls
May 04, 2025
