Low Interest Rates And The Canadian Housing Market: A Comprehensive Look
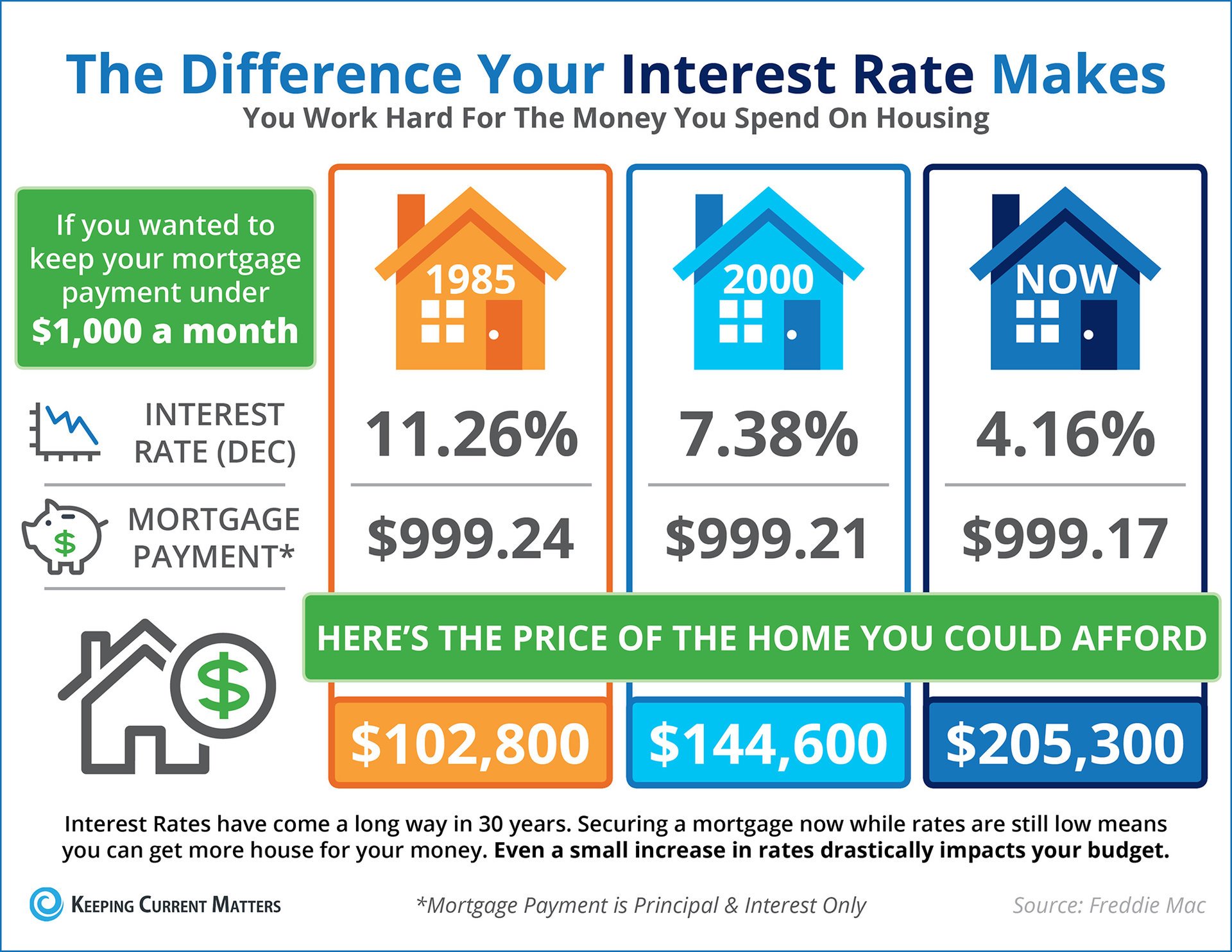
Table of Contents
The Impact of Low Interest Rates on Housing Affordability
Lower interest rates significantly influence housing affordability, primarily by reducing monthly mortgage payments. This increased purchasing power can make homeownership more accessible to a wider range of buyers.
Increased Purchasing Power
Lower interest rates translate directly into lower monthly mortgage payments. Consider this example: a $500,000 mortgage at a 5% interest rate will have significantly higher monthly payments than the same mortgage at a 3% interest rate. This difference can be substantial, making a previously unaffordable home suddenly within reach.
- Example 1: A 25-year mortgage of $500,000 at 5% interest results in a monthly payment of approximately $2,800.
- Example 2: The same mortgage at 3% interest reduces the monthly payment to approximately $2,100 – a difference of $700 per month.
This significant reduction in monthly costs makes a considerable difference for first-time homebuyers, often the most price-sensitive segment of the market.
Increased Demand and Price Inflation
The increased affordability spurred by low interest rates drives higher demand. This surge in demand, when coupled with a relatively fixed supply of housing, inevitably leads to price inflation. The result? Higher home prices.
- Statistic 1: Between 2015 and 2021, periods of low interest rates coincided with a sharp increase in Canadian home prices in many major cities.
- Statistic 2: The average price of a home in Toronto increased by X% during the same period. (Replace X with actual data)
This escalating demand fueled by low-interest rates can create a housing bubble, where prices are inflated beyond their intrinsic value, making the market vulnerable to a sudden correction.
Accessibility for Different Income Groups
While low interest rates boost affordability, their impact varies across different income groups. Higher-income earners benefit disproportionately, as their increased purchasing power is amplified by lower borrowing costs. Lower-income earners, however, may still struggle to afford a down payment, even with lower monthly payments.
- Data Point 1: Affordability for those earning less than $60,000 annually remained largely unchanged despite low interest rates, according to recent studies.
- Data Point 2: Government initiatives like the First-Time Home Buyers' Incentive aim to mitigate this disparity by providing financial assistance.
The Role of the Bank of Canada in Interest Rate Adjustments
The Bank of Canada plays a pivotal role in shaping the Canadian housing market through its monetary policy, which includes adjusting interest rates.
Monetary Policy and its Influence
The Bank of Canada's primary mandate is to maintain price stability and full employment. Interest rates are a crucial tool for achieving these goals. By raising interest rates, the Bank aims to curb inflation by reducing borrowing and spending. Conversely, lowering interest rates stimulates economic activity.
- Point 1: Higher interest rates increase borrowing costs, cooling down the economy and reducing inflationary pressures.
- Point 2: Lower interest rates make borrowing cheaper, encouraging spending and investment, thus stimulating economic growth.
Predicting Future Interest Rate Movements
Predicting future interest rate movements is challenging and crucial for understanding the future of the Canadian housing market. The Bank of Canada's decisions are influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including inflation, employment rates, economic growth, and global economic conditions.
- Factor 1: Inflationary pressures exert significant influence on the Bank of Canada's decisions. High inflation often leads to interest rate hikes.
- Factor 2: The unemployment rate also plays a role, with low unemployment often leading to interest rate increases to cool down the economy and prevent overheating.
Risks and Challenges Associated with Low Interest Rates
While low interest rates can boost affordability and economic activity, they also carry inherent risks.
Increased Household Debt
Low interest rates often lead to increased borrowing and a rise in household debt. Easily accessible mortgages can tempt individuals to borrow more than they can comfortably repay, increasing their financial vulnerability.
- Statistic 1: Canadian household debt-to-income ratios have risen significantly in recent years, raising concerns about potential financial instability.
- Statistic 2: A significant portion of this increased debt is attributable to mortgages.
Speculative Investing
Low interest rates can also encourage speculative investing in the housing market. With borrowing costs low, individuals may be tempted to purchase properties not for residential use but as investment vehicles, potentially driving up prices further and increasing market instability.
- Example 1: Investors purchasing multiple properties solely for rental income contribute to increased demand and price inflation.
- Example 2: "Flipping" properties, buying and quickly reselling for profit, becomes more attractive with low interest rates and increased demand.
Impact on Rental Markets
Low interest rates also impact the rental market. As homeownership becomes more accessible, the demand for rental properties may decrease, potentially stabilizing or even lowering rental prices. However, this effect can be countered by increased demand from those who cannot afford to purchase a home.
- Rental Market Trend 1: In some areas, rental prices have remained high despite low interest rates due to limited rental supply.
- Rental Market Trend 2: In other areas, increased homeownership has led to a decrease in rental demand and thus lower rental prices.
Conclusion
The relationship between low interest rates and the Canadian housing market is intricate and multifaceted. While lower rates increase affordability and stimulate economic activity, they also present risks such as increased household debt and speculative investment. Understanding these complexities is crucial for navigating the market effectively. The impact of interest rate fluctuations on the Canadian real estate market is ongoing and dynamic, influenced by various economic and social factors. Understanding the impact of low interest rates on the Canadian housing market is crucial for informed decision-making. Stay updated on economic trends and consult with financial professionals before making significant housing investments.

Featured Posts
-
 Landman Season 2 Casting Update Demi Moores Role Resolved Fan Concerns
May 13, 2025
Landman Season 2 Casting Update Demi Moores Role Resolved Fan Concerns
May 13, 2025 -
 Cassie And Alex Fine First Red Carpet Appearance Since Pregnancy Announcement
May 13, 2025
Cassie And Alex Fine First Red Carpet Appearance Since Pregnancy Announcement
May 13, 2025 -
 Flushed Away Characters Plot And Lasting Impact
May 13, 2025
Flushed Away Characters Plot And Lasting Impact
May 13, 2025 -
 Gibraltar The Lingering Brexit Dispute
May 13, 2025
Gibraltar The Lingering Brexit Dispute
May 13, 2025 -
 Dispute Erupts Gov Abbotts Warning Vs Epic City Developers Claims
May 13, 2025
Dispute Erupts Gov Abbotts Warning Vs Epic City Developers Claims
May 13, 2025
