Mitigating Urban Heat In India: Exploring Advanced Construction Materials

Table of Contents
Understanding the Urban Heat Island Effect in India
Causes and Consequences
The Urban Heat Island (UHI) effect describes the phenomenon where urban areas experience significantly higher temperatures than surrounding rural areas. In Indian cities, this effect is amplified by several factors, leading to dangerously high temperatures, increased energy consumption for cooling, and serious health risks.
- Increased concrete and asphalt: The prevalence of dark-colored, heat-absorbing materials traps solar radiation, raising ambient temperatures.
- Reduced green spaces: The lack of vegetation reduces evapotranspiration, a natural cooling process.
- Lack of ventilation: Densely packed buildings hinder air circulation, trapping heat.
- Pollution: Airborne pollutants absorb and re-emit solar radiation, contributing to higher temperatures.
The consequences are severe. Heat-related illnesses, including heatstroke and dehydration, are on the rise, contributing significantly to mortality rates, especially among vulnerable populations. Studies show a direct correlation between increasing UHI intensity and heat-related deaths in major Indian cities.
The Need for Sustainable Solutions
Addressing the UHI effect in Indian cities is paramount. Sustainable building practices are no longer a luxury but a necessity to create livable and healthy urban environments. The transition to sustainable construction offers multiple benefits:
- Reduced carbon footprint: Sustainable materials and practices minimize greenhouse gas emissions throughout the building lifecycle.
- Improved energy efficiency: Buildings designed for thermal comfort require less energy for heating and cooling.
- Enhanced public health: Reducing UHI intensity directly improves public health outcomes by mitigating heat-related illnesses.
- Creating more livable cities: Sustainable buildings contribute to a more comfortable and enjoyable urban environment.
Advanced Construction Materials for Heat Mitigation
Cool Roofs
Cool roof technology plays a crucial role in mitigating urban heat. Cool roofs are designed with high solar reflectance index (SRI) and low thermal emittance, reflecting sunlight and reducing heat absorption.
- Reflective paints and coatings: These significantly reduce surface temperatures.
- Cool tiles: Certain tile materials, like those with lighter colors and reflective properties, offer improved thermal performance.
- Government initiatives: Several Indian states are promoting cool roof adoption through subsidies and awareness campaigns. These incentives are vital for wider acceptance.
Thermal Mass Materials
Materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete and brick, can effectively regulate indoor temperatures by absorbing heat during the day and releasing it slowly at night.
- Optimizing thermal mass: Proper insulation, strategic placement of thermal mass elements within building design, and utilizing materials with superior thermal properties are essential for maximizing effectiveness.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs): These advanced materials absorb and release large amounts of heat during phase transitions, providing superior temperature regulation. Their application is increasing in India's construction sector.
Insulating Materials
Efficient insulation is crucial for minimizing heat transfer through building envelopes. Various materials offer superior insulation properties.
- Aerogel: Known for its exceptional insulating capacity.
- Fiberglass and cellulose: Cost-effective and widely available insulation options.
- Reducing energy consumption: Proper insulation drastically reduces the reliance on air conditioning, leading to substantial energy savings and lower carbon emissions.
Green Building Materials
Utilizing eco-friendly and locally sourced materials reduces the environmental impact of construction while supporting local economies.
- Bamboo: A rapidly renewable resource with good thermal properties.
- Rammed earth: A traditional technique offering excellent thermal mass and insulation.
- Recycled materials: Incorporating recycled content reduces waste and lowers the embodied carbon in building materials. This is a growing trend in eco-conscious construction in India.
Policy and Implementation Challenges
Regulatory Framework
The current building codes and regulations in India need significant improvements to effectively address thermal performance.
- Gaps in regulations: Many codes lack stringent requirements for thermal performance, hindering the widespread adoption of advanced materials.
- Policy changes: Introducing stricter building codes focused on thermal comfort and incorporating incentives for sustainable construction practices is crucial.
Cost and Availability
The initial cost of advanced construction materials can be a barrier to their widespread adoption.
- Initial cost vs. long-term savings: While the upfront investment may be higher, the long-term savings in energy consumption and maintenance more than compensate.
- Improving affordability: Government subsidies, tax incentives, and promoting local manufacturing of these materials can improve affordability.
Awareness and Training
Educating architects, builders, and policymakers is crucial for successful implementation.
- Workshops and training programs: Providing practical training on the use of advanced materials and sustainable construction techniques is essential.
- Awareness campaigns: Raising public awareness about the benefits of sustainable building practices can drive demand for these materials.
- Technology transfer: Facilitating technology transfer and knowledge sharing can accelerate the adoption of advanced construction materials.
Conclusion
Mitigating urban heat in India requires a multi-pronged approach, and the adoption of advanced construction materials is a critical component. By leveraging cool roofs, thermal mass materials, efficient insulation, and green building solutions, we can create more sustainable and resilient cities. Overcoming challenges related to policy, cost, and awareness is essential for widespread implementation. Investing in research, development, and education surrounding advanced construction materials in India is crucial for ensuring a cooler, healthier, and more comfortable future for all. Let's work together to build a more sustainable urban environment by embracing innovative advanced construction materials and strategies.

Featured Posts
-
 Atp Madrid Draper Through To First Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025
Atp Madrid Draper Through To First Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025 -
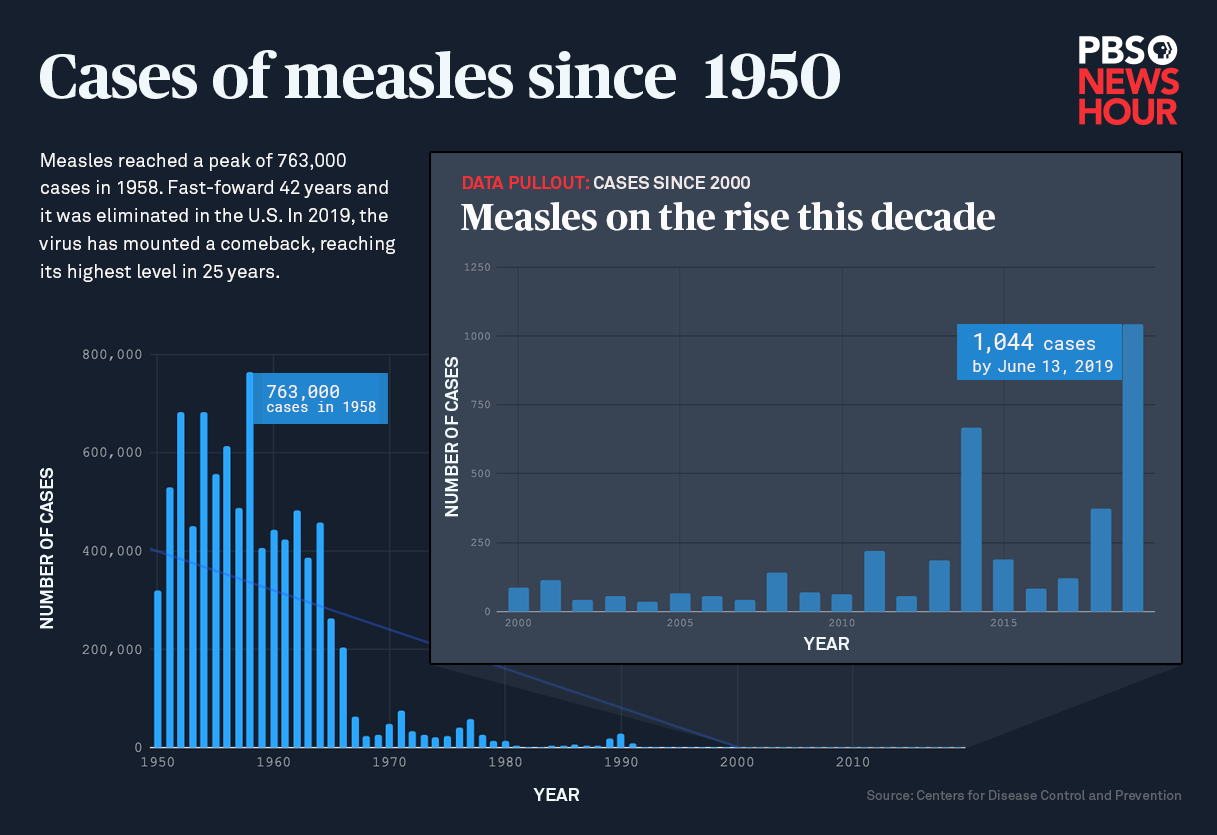 Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025
Measles Cases In The Us A Slowdown Explained
May 30, 2025 -
 Gilermo Del Toro Perviy Treyler Filma Frankenshteyn Viydet V Etu Subbotu
May 30, 2025
Gilermo Del Toro Perviy Treyler Filma Frankenshteyn Viydet V Etu Subbotu
May 30, 2025 -
 Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Integracion Para Una Compra De Entradas Optimizada
May 30, 2025
Setlist Fm Y Ticketmaster Integracion Para Una Compra De Entradas Optimizada
May 30, 2025 -
 Kg Motors And The Mibot A New Era For Japanese Electric Vehicles
May 30, 2025
Kg Motors And The Mibot A New Era For Japanese Electric Vehicles
May 30, 2025
