New CNIL Guidelines On AI: A Practical Guide For Compliance

Table of Contents
Understanding the Scope of the New CNIL Guidelines on AI
The CNIL's guidelines on AI aim to ensure the ethical and lawful use of artificial intelligence while upholding fundamental rights. They apply to a broad range of AI systems, impacting various sectors. This isn't limited to large corporations; even small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) utilizing AI must comply.
The guidelines cover various AI systems, including:
- Image recognition: Systems used for facial recognition, object detection, and image analysis.
- Natural language processing (NLP): Systems involved in chatbots, sentiment analysis, and machine translation.
- Predictive analytics: Systems used for risk assessment, fraud detection, and personalized recommendations.
- Decision-making systems: AI used to automate decisions impacting individuals (e.g., loan applications, hiring processes).
Key concepts central to the CNIL's approach include:
- Algorithmic transparency: Understanding how an AI system arrives at its decisions.
- Data bias: Addressing potential unfairness or discrimination embedded in the data used to train AI models.
- Accountability: Establishing clear lines of responsibility for the actions of AI systems.
The CNIL's focus is firmly on protecting fundamental rights, primarily:
- Privacy: Ensuring the responsible collection, processing, and storage of personal data used in AI systems.
- Non-discrimination: Preventing AI systems from perpetuating or exacerbating existing societal biases.
Bullet Points:
- Specific examples: An e-commerce website using AI for personalized recommendations, a bank employing AI for fraud detection, a hospital using AI for medical diagnosis support.
- Key legal terms: Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA), algorithmic transparency, accountability, data minimization, purpose limitation.
- Links to relevant CNIL publications: [Insert links to relevant CNIL publications here].
Key Requirements for Compliance with CNIL AI Regulations
Compliance with the CNIL's AI guidelines necessitates a proactive approach to data protection. Organizations must adhere to several key obligations:
-
Data protection by design and by default: Integrating data protection principles from the outset of AI system design and implementation. This means minimizing data collection, ensuring data security, and prioritizing privacy-enhancing technologies.
-
Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIAs): Conducting DPIAs for high-risk AI systems to identify and mitigate potential risks to individuals' rights and freedoms. This involves a thorough analysis of the data processing, potential risks, and proposed mitigation measures.
-
Algorithmic transparency and explainability: Providing clear and understandable information about how AI systems operate, particularly for those decisions significantly impacting individuals. This may involve documentation, explanations, and potentially even providing access to relevant data.
-
Bias mitigation: Actively identifying, assessing, and mitigating potential biases in AI systems. This requires careful data selection, algorithm design, and ongoing monitoring.
Bullet Points:
- Step-by-step guide to conducting a DPIA for AI systems: [Insert link to a DPIA template or guide here].
- Checklist of compliance measures: [Insert link to a compliance checklist here].
- Examples of best practices for algorithmic transparency: Using readily understandable language to explain AI decision-making processes, creating visual representations of how the AI works.
- Methods for identifying and mitigating bias: Utilizing diverse datasets, employing fairness-aware algorithms, and implementing ongoing monitoring mechanisms.
Practical Steps for Implementing CNIL Compliance in Your AI Systems
Achieving CNIL compliance requires a structured and comprehensive approach. Here are some actionable steps:
- Implement robust data governance: Establish clear data management policies and procedures, including data security measures, access controls, and data retention policies.
- Document the AI system lifecycle: Maintain meticulous records of the AI system's development, deployment, and operation, including data sources, algorithms, and decision-making processes.
- Establish a process for handling complaints: Develop a clear mechanism for receiving and addressing complaints related to the use of AI systems.
- Implement ongoing monitoring and evaluation: Regularly assess the performance and impact of AI systems, identifying and addressing any issues concerning compliance or fairness.
Bullet Points:
- Examples of tools and technologies that aid in compliance: Privacy-enhancing technologies (PETs), data anonymization tools, AI explainability platforms.
- Templates for documentation and reporting: [Insert links to templates here].
- Best practices for stakeholder communication and engagement: Regular communication with employees, clients, and other stakeholders to ensure transparency and build trust.
- Links to relevant resources and support: [Insert links to relevant resources here].
The Role of Data Protection Officers (DPOs) in CNIL AI Compliance
DPOs play a crucial role in ensuring CNIL compliance for AI systems. Their responsibilities include:
- Advising on data protection implications of AI systems.
- Monitoring compliance with data protection regulations.
- Conducting DPIAs for high-risk AI systems.
- Acting as a point of contact for data protection authorities.
DPOs involved with AI require specific skills and expertise:
- A strong understanding of AI technologies and their implications.
- Expertise in data protection law and regulations.
- Experience in risk assessment and management.
Ensuring Ongoing CNIL Compliance for Your AI Initiatives
Complying with the CNIL's guidelines on AI is not a one-time task but an ongoing process requiring continuous monitoring, evaluation, and adaptation. Proactive compliance minimizes the risk of penalties and builds trust with stakeholders. Ethical and responsible AI development provides long-term benefits, enhancing your reputation and fostering customer confidence.
Ensure your organization stays ahead of the curve with our comprehensive guide to CNIL compliance for AI systems. Download our free checklist to help you navigate the complexities of new CNIL AI guidelines. [Insert link to checklist/guide here]

Featured Posts
-
 Informations Cles Du Document Amf Seb S A Cp 2025 E1021792
Apr 30, 2025
Informations Cles Du Document Amf Seb S A Cp 2025 E1021792
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Schneider Electric Consecutive Worlds Most Sustainable Corporation Award
Apr 30, 2025
Schneider Electric Consecutive Worlds Most Sustainable Corporation Award
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Blue Ivy And Rumi Carters Stylish Super Bowl Appearance
Apr 30, 2025
Blue Ivy And Rumi Carters Stylish Super Bowl Appearance
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Ru Pauls Drag Race Season 17 Episode 6 Preview Things Get Fishy
Apr 30, 2025
Ru Pauls Drag Race Season 17 Episode 6 Preview Things Get Fishy
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Yate Recycling Centre Incident Air Ambulance On Scene
Apr 30, 2025
Yate Recycling Centre Incident Air Ambulance On Scene
Apr 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Channing Tatum Moves On Romance With Inka Williams After Zoe Kravitz Split
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatum Moves On Romance With Inka Williams After Zoe Kravitz Split
Apr 30, 2025 -
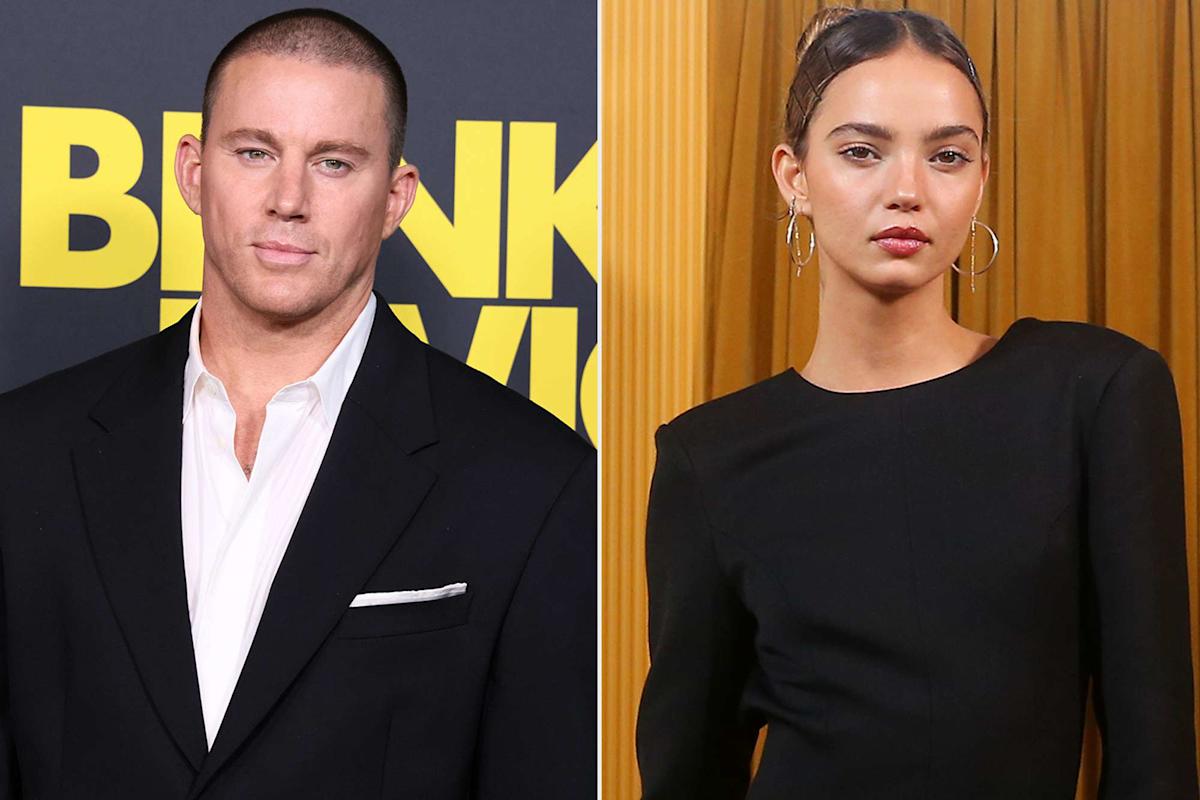 Channing Tatums New Girlfriend Inka Williams And Their Public Display Of Affection
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatums New Girlfriend Inka Williams And Their Public Display Of Affection
Apr 30, 2025 -
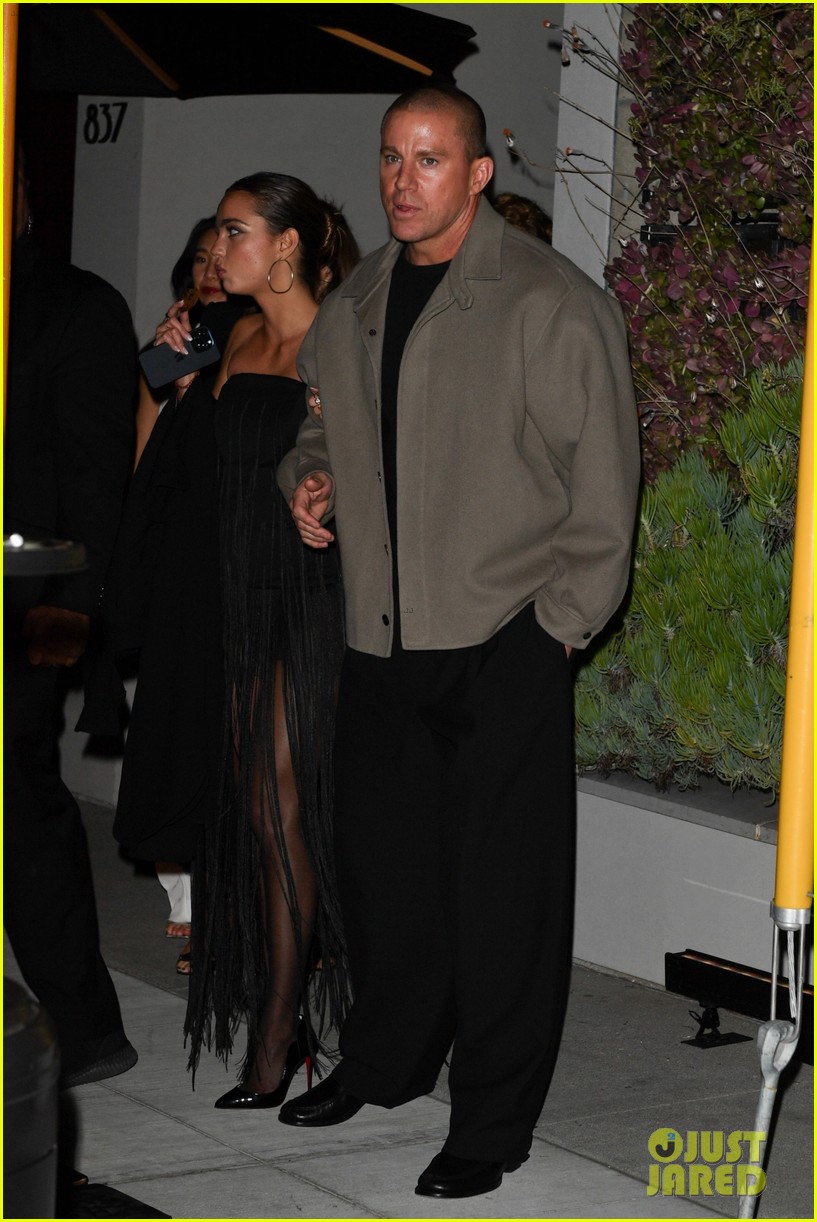 Channing Tatum 44 And Inka Williams 25 New Romance Confirmed
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatum 44 And Inka Williams 25 New Romance Confirmed
Apr 30, 2025 -
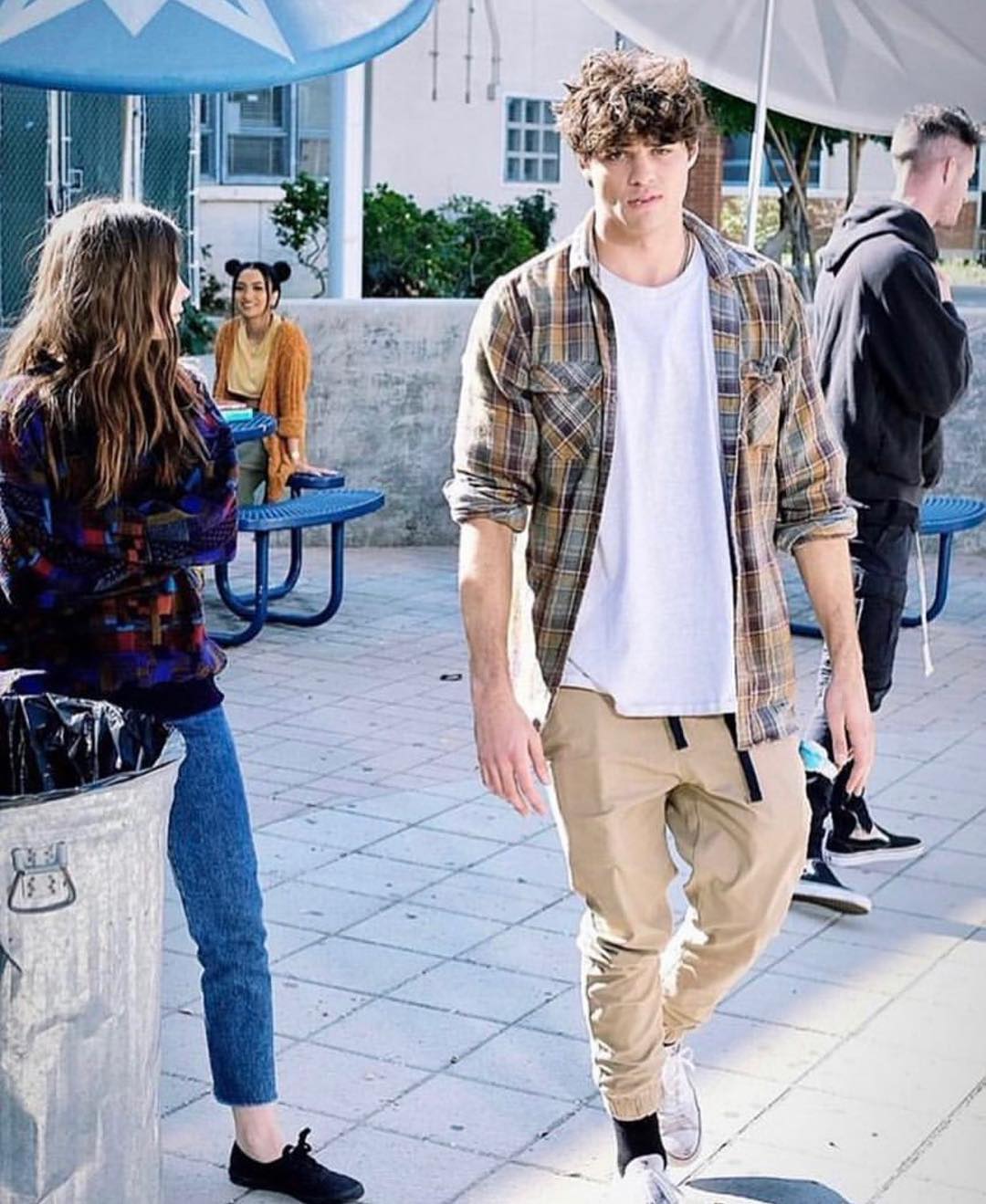 Exploring The Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Dating Speculation
Apr 30, 2025
Exploring The Zoe Kravitz And Noah Centineo Dating Speculation
Apr 30, 2025 -
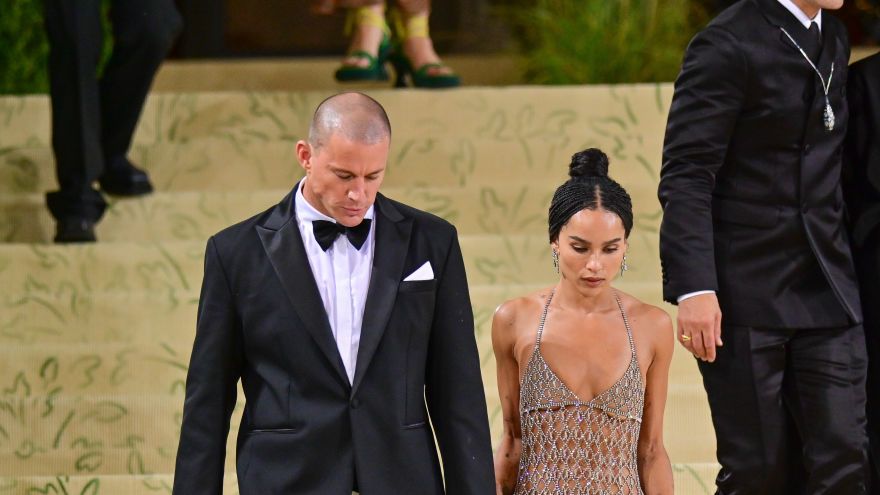 Channing Tatum Dating Australian Model Inka Williams Following Zoe Kravitz Breakup
Apr 30, 2025
Channing Tatum Dating Australian Model Inka Williams Following Zoe Kravitz Breakup
Apr 30, 2025
