New COVID-19 Variant: Global Case Surge, WHO Confirms
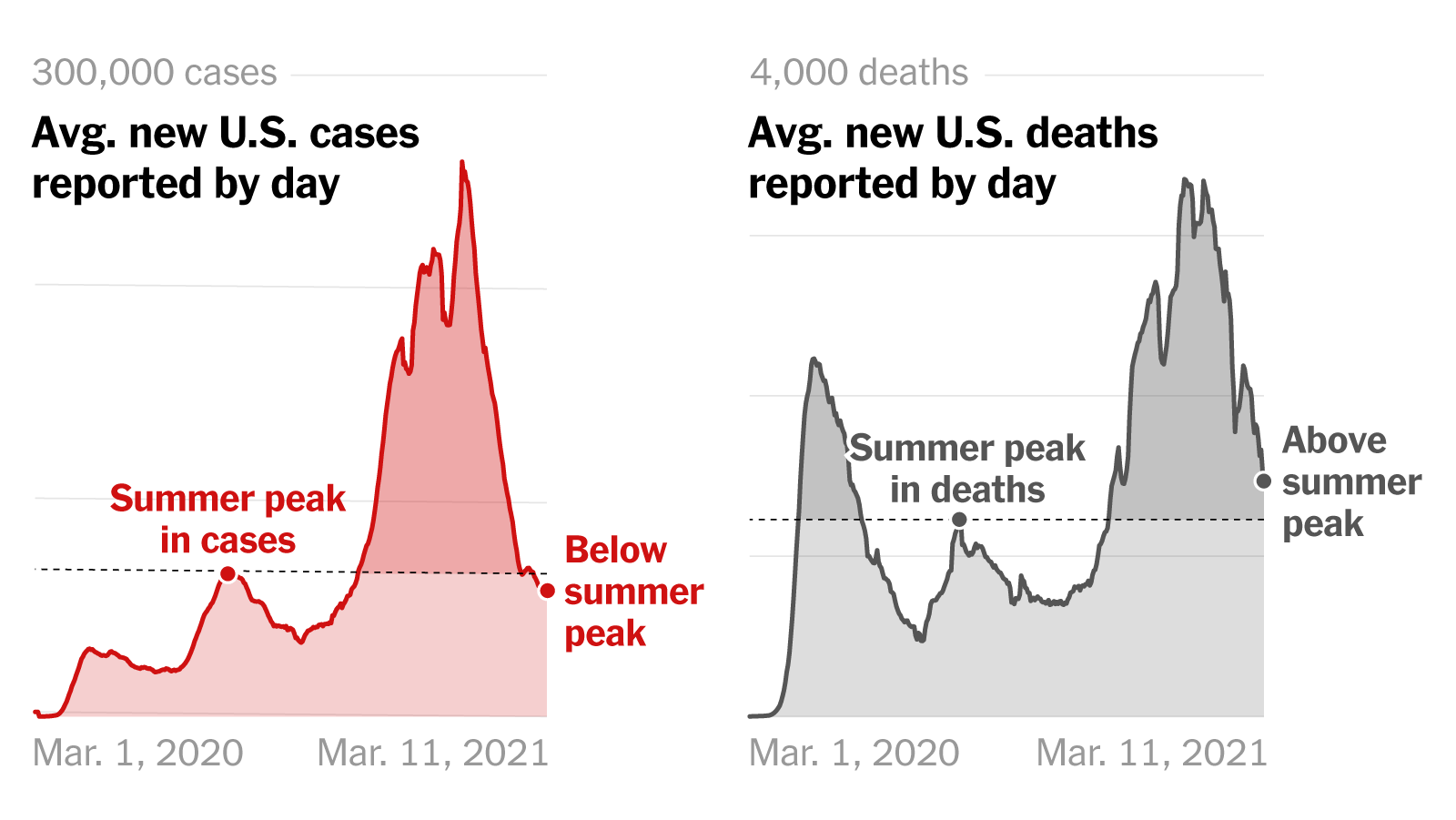
Table of Contents
Understanding the New COVID-19 Variant
Variant Identification and Origins
While the specific designation may evolve (e.g., using Greek letters or numerical designations), let's refer to this new variant as "Variant X" for clarity. Initial detection of Variant X appears to have been in [Insert Location of Initial Detection], although the precise origin remains under investigation. Early genomic sequencing suggests several key mutations compared to previous variants, including [Insert specific mutations if known, e.g., spike protein mutations]. Further research is underway to fully understand its genetic relationship to earlier variants like Delta and Omicron, and to determine the factors contributing to its emergence and rapid spread.
- Mutations: [List known mutations and their potential impacts on transmissibility, severity, and vaccine efficacy].
- Evolutionary Lineage: [Discuss any known links to previous variants, explaining how Variant X might have evolved].
- Ongoing Research: [Mention ongoing studies and collaborations aimed at understanding Variant X's characteristics].
Transmission Rate and Severity
Preliminary data indicates that Variant X exhibits a significantly higher transmission rate than previous variants. Early reports suggest a [Insert percentage or multiplier] increase in transmissibility compared to Omicron, for example. This rapid spread is contributing to the observed global case surge. The severity of illness caused by Variant X is currently being assessed. While data is still emerging, initial observations suggest [Insert information on hospitalization rates and mortality compared to previous variants]. It's crucial to monitor these indicators closely as more data becomes available.
- Infection Rates: [Insert data on infection rates if available, differentiating between regions if possible].
- Hospitalization Rates: [Insert data on hospitalization rates, comparing them to previous variants].
- Mortality Rates: [Insert data on mortality rates, highlighting any differences compared to previous variants].
- Symptom Variations: [Mention any observable differences in symptoms compared to previous variants].
Symptoms of the New COVID-19 Variant
While many symptoms overlap with previous COVID-19 variants, some unique characteristics of Variant X may be emerging. Common symptoms include fever, cough, fatigue, and shortness of breath. However, reports are also suggesting [Insert any unique or less common symptoms]. It's important to note that these symptoms can vary in severity and presentation from person to person. If you experience any concerning symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for appropriate testing and advice.
- Common Symptoms: Cough, fever, fatigue, headache, muscle aches, sore throat, loss of taste or smell, shortness of breath.
- Less Common Symptoms: [List less common symptoms reported, if any].
- Severity Variations: [Describe the range of symptom severity observed, from mild to severe cases].
Global Impact and Response
Surge in Global Cases and Geographic Distribution
The new COVID-19 variant is driving a rapid increase in cases globally. [Insert a map or chart illustrating the global distribution of Variant X cases if possible]. Specific regions experiencing particularly significant surges include [List countries or regions with the most significant increases]. The rapid spread underlines the need for a prompt and coordinated international response to prevent further escalation.
- Regional Impact: [Detail the impact of the variant in different geographical areas, highlighting variations in case numbers and severity].
- Case Tracking: [Mention any challenges in tracking cases accurately due to the rapid spread and potential limitations in testing capacity].
WHO Recommendations and Public Health Measures
The WHO is actively monitoring the situation and issuing recommendations to governments and health authorities worldwide. These recommendations emphasize the importance of:
- Vaccination Campaigns: Expanding vaccination coverage globally to protect populations from severe illness and death.
- Testing Strategies: Implementing robust testing strategies to identify and isolate infected individuals to curb transmission.
- Border Controls: Implementing appropriate border control measures where deemed necessary to slow the spread of the variant.
- Public Health Measures: Maintaining effective public health measures, including mask mandates in high-risk settings, social distancing, and improved hygiene practices.
Vaccine Effectiveness and Booster Shots
Current evidence suggests that existing COVID-19 vaccines offer some level of protection against severe illness caused by Variant X, although their efficacy may be reduced compared to previous variants. [Cite relevant studies if available]. Booster shots are highly recommended to enhance immunity and offer increased protection against infection and severe outcomes, especially for vulnerable populations. Research into the development of updated or adapted vaccines that specifically target Variant X is ongoing.
- Vaccine Efficacy Data: [Cite specific data regarding the effectiveness of current vaccines against Variant X].
- Booster Shot Recommendations: [Explain the recommendations for booster shots, including timelines and eligibility].
- New Vaccine Development: [Mention any progress on developing vaccines tailored to address Variant X].
Conclusion
The emergence of this new COVID-19 variant and the resulting global case surge underscore the continuing threat of the pandemic. The WHO's confirmation of the increased transmission rate highlights the urgent need for sustained vigilance and coordinated action. While existing vaccines offer some protection, bolstering vaccination rates globally, ensuring widespread access to testing, and maintaining effective public health measures remain critical to mitigating the impact of this new COVID-19 variant. Stay informed about the latest developments by following the WHO and your local health authorities. Get vaccinated, consider booster shots when eligible, and continue to follow public health guidelines to protect yourself and your community from this concerning new COVID-19 variant. Your vigilance is essential in the fight against this evolving virus.

Featured Posts
-
 Griekspoor Stuns Top Seed Zverev In Indian Wells
May 31, 2025
Griekspoor Stuns Top Seed Zverev In Indian Wells
May 31, 2025 -
 Comida Aragonesa Tradicional Receta Sencilla De 3 Ingredientes
May 31, 2025
Comida Aragonesa Tradicional Receta Sencilla De 3 Ingredientes
May 31, 2025 -
 Guelsen Bubikoglu Ndan Duygu Dolu Tuerker Inanoglu Paylasimi
May 31, 2025
Guelsen Bubikoglu Ndan Duygu Dolu Tuerker Inanoglu Paylasimi
May 31, 2025 -
 Fox Raceway National 2025 Complete Pro Motocross Round 1 Results
May 31, 2025
Fox Raceway National 2025 Complete Pro Motocross Round 1 Results
May 31, 2025 -
 Nigora Bannatynes Sparkling Co Ord Style And Fitness Goals
May 31, 2025
Nigora Bannatynes Sparkling Co Ord Style And Fitness Goals
May 31, 2025
