New COVID-19 Wave: Hong Kong And Singapore's Cases Explode – What Does It Mean For India?
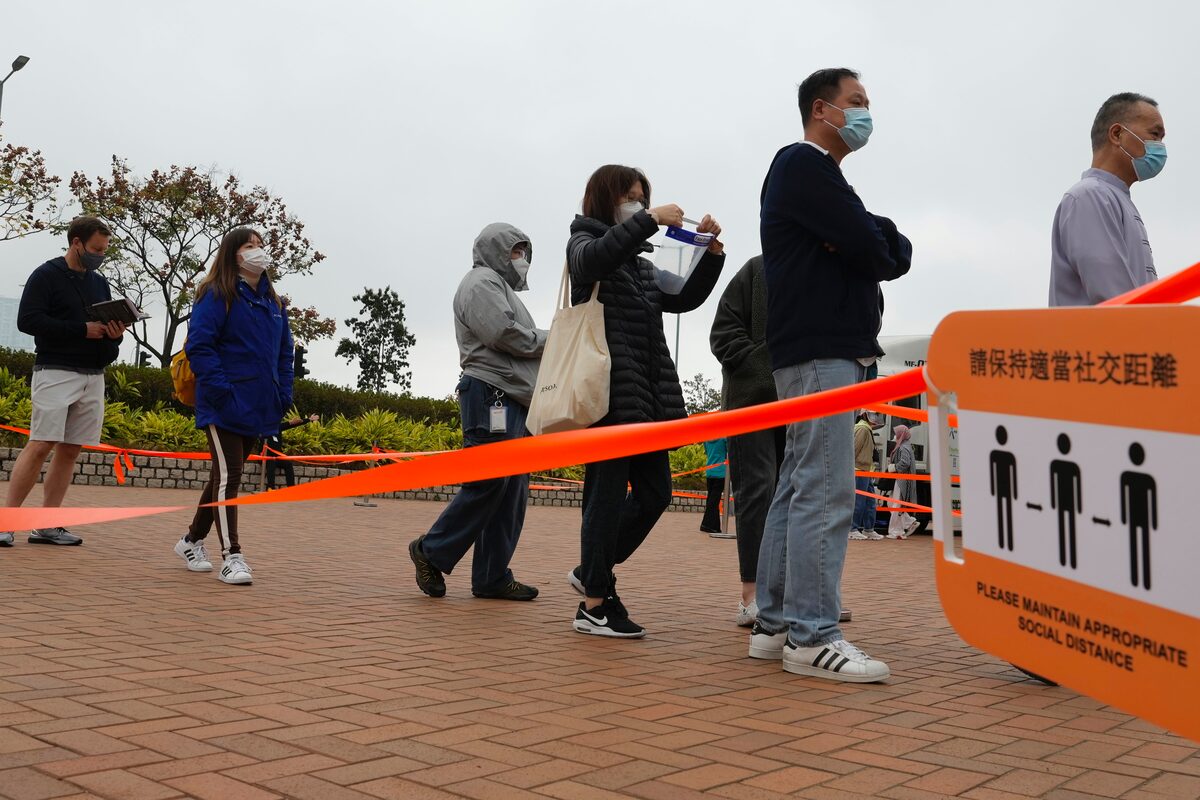

Table of Contents
The Hong Kong Situation: A Deep Dive
Factors Contributing to the Surge in Hong Kong:
The recent surge in Hong Kong can be attributed to a confluence of factors:
-
Relaxation of COVID-19 restrictions: The easing of social distancing measures and travel restrictions contributed to increased social interaction and viral transmission. The swift return to pre-pandemic normalcy proved insufficiently cautious given the ongoing global threat of new variants.
-
Emergence of new variants: The emergence of new, highly transmissible COVID-19 variants, potentially evading existing immunity, fueled the rapid spread of the virus. While specific variant dominance might vary, the ability of these variants to outpace prior immune responses is a significant concern.
-
Waning immunity from previous infections/vaccinations: Over time, immunity from prior infections or vaccinations wanes, leaving individuals susceptible to reinfection. This effect is amplified by the emergence of new variants capable of evading previously acquired immunity.
-
Low vaccination rates in specific age groups: Lower vaccination rates among certain demographic groups created pockets of vulnerability within the population, facilitating easier viral transmission. Addressing vaccine hesitancy and ensuring equitable access to vaccination are crucial aspects of pandemic management.
-
Increased social interaction and travel: Increased social gatherings, indoor activities, and international travel all increased opportunities for virus transmission and the potential introduction of new variants. The interconnected nature of global travel highlights the vulnerability of individual countries to outbreaks elsewhere.
-
Specific Statistics (Illustrative): (Note: Replace these with actual data from reliable sources at the time of publication) Hong Kong experienced a daily case increase of X% in [time period], with hospitalization rates reaching Y% and mortality rates at Z%.
Hong Kong's Response and Lessons Learned:
Hong Kong initially implemented a strict "zero-COVID" strategy, but later shifted to a more relaxed approach. The effectiveness of their response remains a subject of debate. Key lessons include:
- The importance of a robust and adaptable public health infrastructure capable of quickly responding to surges in cases.
- The need for continuous monitoring of new variants and their impact on existing immunity.
- The crucial role of vaccination in mitigating severe illness and death, combined with targeted public health campaigns addressing vaccine hesitancy.
- The delicate balance between economic recovery and public health safety necessitates careful, data-driven decision-making regarding restriction levels.
These lessons are directly applicable to India's pandemic preparedness, emphasizing the need for ongoing surveillance and flexible strategies.
Singapore's Experience: A Comparative Analysis
Singapore's Surge: Similar Trends, Different Outcomes?
Singapore, while also experiencing a surge, demonstrated a different trajectory compared to Hong Kong. Both countries saw increases driven by new variants and waning immunity, but Singapore's robust healthcare system and proactive public health measures led to comparatively lower hospitalization and mortality rates. This highlights the crucial role of effective healthcare infrastructure and strategic interventions.
- Comparative Statistics (Illustrative): (Note: Replace these with actual data from reliable sources at the time of publication) Comparing peak daily case numbers, hospitalization rates, and mortality rates in Hong Kong versus Singapore reveals significant differences, highlighting the impact of varying public health responses.
Singapore's Strategies and Their Applicability to India:
Singapore's success stemmed from several key strategies:
- Early and widespread testing: Aggressive testing and contact tracing enabled quick identification and isolation of infected individuals, preventing widespread transmission.
- High vaccination rates: A high vaccination rate among the population provided a significant level of protection against severe illness and death.
- Targeted and adaptable restrictions: Targeted restrictions were implemented and adjusted based on real-time data and the evolving situation.
While directly replicating Singapore's approach in India might be challenging due to scale and infrastructure differences, adapting key elements like targeted testing and bolstering vaccination campaigns remains crucial.
Implications for India: Preparedness and Response
Vulnerabilities and Potential Risks in India:
India's unique epidemiological context presents specific vulnerabilities:
-
Vast population and diverse healthcare infrastructure: The sheer size of India's population and variations in healthcare infrastructure across regions pose challenges to effective response.
-
Existing health challenges: Pre-existing health issues within the population could exacerbate the impact of a COVID-19 surge.
-
Potential for overwhelmed healthcare systems: A sudden influx of severe cases could overwhelm the healthcare system in certain areas.
-
Vaccine coverage gaps: Uneven vaccine coverage across different populations necessitates focused campaigns to reach under-vaccinated communities.
-
Specific Concerns: (Illustrative examples): Capacity limitations in ICU beds, potential shortages of medical supplies, variations in testing capacity across states, and varying degrees of vaccination compliance.
Strategies for Mitigation and Prevention in India:
To mitigate the risks, India needs:
-
Strengthening public health infrastructure: Investing in healthcare infrastructure, particularly in rural and underserved areas, is critical.
-
Improved surveillance and testing systems: Enhanced surveillance systems to detect new variants early and ensure robust testing capacity are crucial.
-
Sustained and equitable vaccination campaigns: Continuing vaccination campaigns with a focus on reaching unvaccinated populations and providing booster shots are vital.
-
Public health awareness and compliance: Public awareness campaigns and community engagement are essential for maintaining compliance with public health guidelines.
-
Preventive Measures: * (Examples)* Promoting mask-wearing in crowded areas, encouraging hand hygiene, maintaining social distancing in high-risk settings, and promoting responsible behaviour during travel.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 surges in Hong Kong and Singapore offer valuable, albeit concerning, insights into the ongoing pandemic's potential. The differing outcomes highlight the crucial role of effective public health measures, robust healthcare infrastructure, and proactive responses in controlling outbreaks. India, given its unique vulnerabilities, must learn from these experiences and prioritize strengthening its public health system, improving its surveillance capacity, and ensuring widespread vaccination coverage to mitigate the potential impact of a future COVID-19 wave. Stay informed about the evolving COVID-19 situation, consult reliable sources for up-to-date information on this new COVID-19 wave and its implications for India, and practice responsible behaviors to prevent a potential surge. Vigilance and proactive measures are crucial in preventing a significant new COVID-19 outbreak in India.

Featured Posts
-
 Thursday March 27 2025 5 Key Things You Need To Know
May 31, 2025
Thursday March 27 2025 5 Key Things You Need To Know
May 31, 2025 -
 Watch Canelo Vs Golovkin Live Stream Results And Play By Play Commentary
May 31, 2025
Watch Canelo Vs Golovkin Live Stream Results And Play By Play Commentary
May 31, 2025 -
 Iconic Rock Bands Glastonbury Return A Life Or Death Decision
May 31, 2025
Iconic Rock Bands Glastonbury Return A Life Or Death Decision
May 31, 2025 -
 Northeast Ohio Election Day Weather Showers Expected
May 31, 2025
Northeast Ohio Election Day Weather Showers Expected
May 31, 2025 -
 Sanofi Kauft Autoimmun Medikament Fuer Bis Zu 1 9 Milliarden Us Dollar
May 31, 2025
Sanofi Kauft Autoimmun Medikament Fuer Bis Zu 1 9 Milliarden Us Dollar
May 31, 2025
