New Report Highlights Dangerous Climate Whiplash Impacts On Global Cities
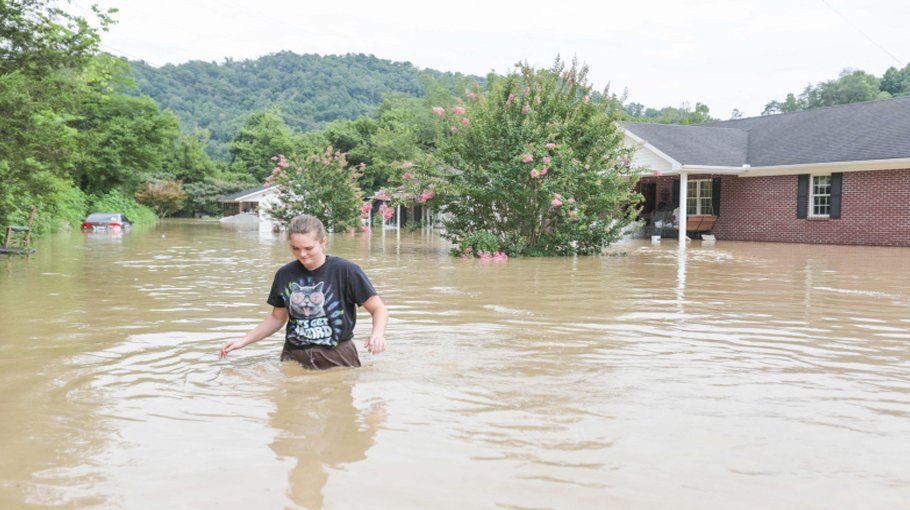

Table of Contents
Understanding Climate Whiplash and its Urban Impacts
Defining Climate Whiplash
Climate whiplash refers to the rapid and unpredictable oscillations between extreme weather events. Instead of a gradual shift in climate patterns, we see sudden and dramatic transitions. For example, a city might experience a prolonged drought, followed immediately by torrential rainfall and flooding – a jarring and destructive sequence. These events are not simply isolated incidents; they are interconnected, demonstrating the complex and volatile nature of our changing climate.
- Defining Climate Whiplash Concisely: Climate whiplash is the rapid succession of contrasting extreme weather events, such as drought followed by flood, or heatwave followed by intense cold.
- Scientific Mechanisms: Climate change intensifies weather patterns, leading to more frequent and intense extreme events. Changes in atmospheric circulation, jet stream behavior, and ocean currents contribute to this instability.
- Amplified Urban Effects: Urban areas, with their heat island effect (where cities are significantly warmer than surrounding areas) and limited green spaces, experience amplified impacts of climate whiplash. Concrete surfaces absorb and retain heat, exacerbating heatwaves, while inadequate drainage systems worsen flooding.
Case Studies: Cities Facing the Brunt of Climate Whiplash
City A: London, UK
London, a city known for its moderate climate, is increasingly vulnerable to climate whiplash. In recent years, London has experienced periods of intense heat followed by unusually heavy rainfall, leading to significant flooding in low-lying areas and disruptions to transport systems. The 2021 heatwave, followed by heavy summer downpours, caused widespread disruption and significant economic losses.
- Specific Events: Intense heatwaves, flash floods, and periods of extreme dryness.
- Quantifiable Impacts: Millions of pounds in economic losses, disruptions to transport, and damage to infrastructure.
- Governmental Responses: Investment in improved drainage systems and early warning systems for extreme weather events.
City B: Mumbai, India
Mumbai, a coastal megacity, faces a different set of challenges. The city's vulnerability to monsoons is compounded by rising sea levels and extreme temperature fluctuations, leading to devastating flooding and severe heat stress. The city's dense population and limited infrastructure make it particularly susceptible to the impacts of climate whiplash.
- Specific Events: Intense monsoonal rainfall leading to severe flooding, followed by periods of extreme heat.
- Quantifiable Impacts: Significant loss of life, widespread displacement, and substantial damage to infrastructure and property.
- Governmental Responses: Efforts to improve drainage infrastructure and create early warning systems, alongside initiatives to promote green spaces and urban resilience.
The Long-Term Consequences of Climate Whiplash on Urban Infrastructure and Public Health
Infrastructure Vulnerability
Repeated exposure to extreme weather events strains urban infrastructure significantly. Roads and bridges are damaged by flooding, power grids fail during heatwaves or storms, and water systems are overwhelmed. The cumulative effect of climate whiplash leads to costly repairs and long-term disruptions to essential services.
- Infrastructure Failures: Examples include collapsed roads, power outages, and contaminated water supplies.
- Economic Burden: The cost of repairing and replacing damaged infrastructure is substantial, placing a burden on city budgets.
Public Health Impacts
Climate whiplash has severe consequences for public health. Heatwaves lead to heatstroke and other heat-related illnesses, while flooding increases the risk of waterborne diseases. The stress and uncertainty caused by frequent extreme weather events also negatively impact mental health.
- Heat-Related Illnesses: Increased hospital admissions and deaths due to heatstroke and respiratory problems.
- Infectious Diseases: Increased risk of waterborne diseases like cholera and typhoid fever, and vector-borne diseases like dengue fever.
Building Climate Resilience in Global Cities: Mitigation and Adaptation Strategies
Mitigation Strategies
To lessen the severity of climate whiplash, cities must take significant steps to mitigate climate change. This requires a global effort to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy Transition: Switching to renewable energy sources like solar and wind power.
- Energy Efficiency: Improving the energy efficiency of buildings and transportation systems.
Adaptation Strategies
Cities must also adapt to the unavoidable impacts of climate change. This involves developing strategies and infrastructure to better cope with extreme weather events.
- Green Infrastructure: Increasing green spaces and permeable surfaces to manage rainfall and reduce the urban heat island effect.
- Improved Drainage Systems: Investing in more robust drainage systems to handle extreme rainfall.
- Early Warning Systems: Developing and implementing effective early warning systems for extreme weather events.
Addressing the dangers of climate whiplash requires immediate and concerted global action. The information presented highlights the urgent need to both mitigate climate change through emission reductions and adapt to its unavoidable effects by building more resilient cities. Learn more about climate whiplash and support climate-friendly policies, advocate for improved urban planning, and invest in climate-resilient infrastructure. Let's work together to build more resilient cities for a sustainable future.

Featured Posts
-
 Late Match Jitters Fail To Halt Sinners Paris Run
May 28, 2025
Late Match Jitters Fail To Halt Sinners Paris Run
May 28, 2025 -
 Pop Star Lorde Makes Surprise Guest Appearance At Dedicated Fan Night
May 28, 2025
Pop Star Lorde Makes Surprise Guest Appearance At Dedicated Fan Night
May 28, 2025 -
 Pacers Vs Bulls March 10th Where To Watch And Live Stream Details
May 28, 2025
Pacers Vs Bulls March 10th Where To Watch And Live Stream Details
May 28, 2025 -
 Angels Defeat Dodgers In Thrilling Freeway Series Matchup
May 28, 2025
Angels Defeat Dodgers In Thrilling Freeway Series Matchup
May 28, 2025 -
 Todays Mlb Game Brewers Vs Diamondbacks Predictions Betting Odds And Analysis
May 28, 2025
Todays Mlb Game Brewers Vs Diamondbacks Predictions Betting Odds And Analysis
May 28, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Bayern Muenih Augsburg Maci Canli Yayin Bilgileri Ve Izleme Secenekleri
May 30, 2025
Bayern Muenih Augsburg Maci Canli Yayin Bilgileri Ve Izleme Secenekleri
May 30, 2025 -
 Augsburg Bayern Muenih Macini Canli Olarak Izlemenin En Iyi Yollari
May 30, 2025
Augsburg Bayern Muenih Macini Canli Olarak Izlemenin En Iyi Yollari
May 30, 2025 -
 Fca Augsburg Neuer Torwart Garteig Kommt Von Ingolstadt
May 30, 2025
Fca Augsburg Neuer Torwart Garteig Kommt Von Ingolstadt
May 30, 2025 -
 Reporte Caida De Ticketmaster El 8 De Abril Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025
Reporte Caida De Ticketmaster El 8 De Abril Grupo Milenio
May 30, 2025 -
 Augsburg Bayern Muenih Maci Canli Izle Hangi Kanalda Ve Nereden
May 30, 2025
Augsburg Bayern Muenih Maci Canli Izle Hangi Kanalda Ve Nereden
May 30, 2025
