New Research: Elevated ADHD Diagnosis Rates Among Adults With Autism And Intellectual Disabilities
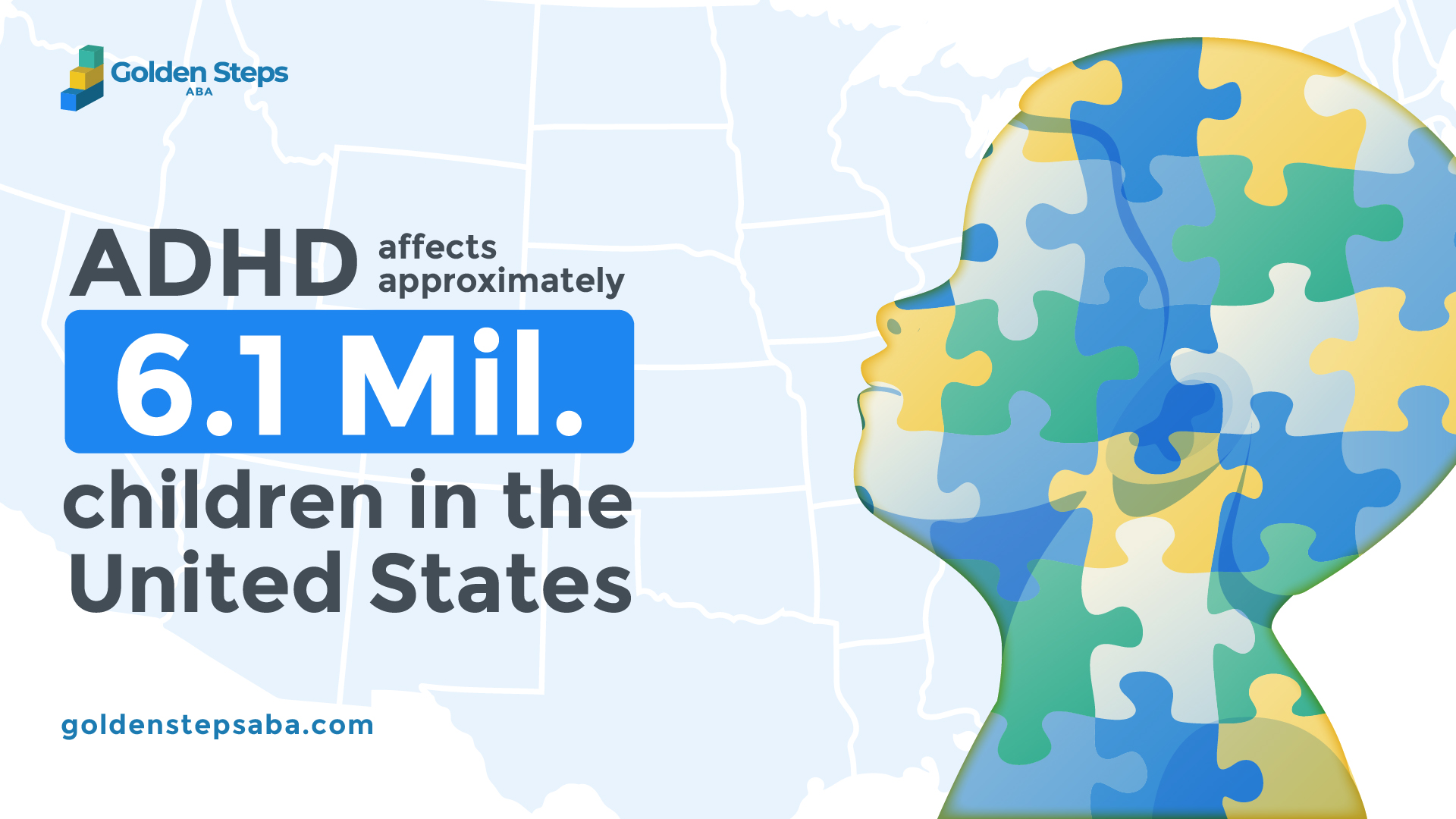
Table of Contents
The Complex Relationship Between Autism, Intellectual Disabilities, and ADHD
The co-occurrence of autism, intellectual disabilities, and ADHD presents significant diagnostic challenges due to overlapping symptoms. Accurate assessment requires careful consideration of the unique characteristics of each condition.
Overlapping Symptoms and Diagnostic Challenges
Differentiating between ADHD symptoms and those related to autism or intellectual disabilities can be exceptionally difficult. Many behaviors associated with ADHD, such as inattentiveness, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, also manifest in individuals with autism or intellectual disabilities, leading to misdiagnosis or delayed diagnosis.
- Difficulty focusing: A common symptom in all three conditions, making it hard to determine the primary cause.
- Impulsivity: Can manifest as interrupting conversations, acting without thinking, or difficulty with self-regulation, making it difficult to attribute to a specific disorder.
- Social communication challenges: Present in both autism and ADHD, albeit often expressed differently, further complicating diagnosis.
Prevalence Rates and Statistical Significance
New research indicates a substantially higher prevalence of ADHD among adults with both autism and intellectual disabilities compared to the general population. While specific percentages vary depending on the study and methodology, many studies consistently show a significantly elevated rate. One recent study (cite specific study if possible, including journal, authors, and year) of [sample size] adults with ASD and ID found that [percentage]% also met the criteria for ADHD. This study employed [describe methodology, e.g., standardized diagnostic interviews, behavioral rating scales] to enhance the reliability of its findings.
- Key Statistic 1: [Insert specific statistic from research, e.g., "A threefold increase in ADHD diagnoses was observed in the study group."]
- Key Statistic 2: [Insert another statistic, e.g., "Individuals with both ASD and ID were significantly more likely to exhibit inattentive-type ADHD."]
- Study Methodology: [Briefly describe the methodology used, for example, "The study utilized DSM-5 criteria for diagnosis and included a diverse sample representing varying levels of intellectual disability."]
Impact on Functional Outcomes
The comorbidity of ADHD, autism, and intellectual disabilities can significantly impact daily functioning across multiple life domains. Individuals may experience increased challenges in areas like:
- Employment: Difficulty maintaining focus, following instructions, and managing time can hinder job performance and career advancement.
- Relationships: Impulsivity, social communication difficulties, and emotional dysregulation can strain interpersonal relationships.
- Independent living: Challenges with organization, planning, and self-care can impact an individual’s ability to live independently.
- Academic/Vocational Success: Difficulties with attention and organization can significantly impact academic performance and vocational training.
Improved Diagnostic Approaches and Assessment Tools
Accurate diagnosis and effective intervention require a multi-faceted approach that accounts for the complex interplay of symptoms.
The Need for Comprehensive Evaluations
Relying solely on behavioral observations or self-report measures is insufficient for diagnosing ADHD in individuals with autism and intellectual disabilities. Comprehensive evaluations are crucial.
- Structured clinical interviews: These tools provide a standardized approach to gathering information about symptoms and functional impairment.
- Behavioral rating scales: Completed by parents, caregivers, teachers, or the individual themselves, these scales assess the frequency and severity of ADHD symptoms.
- Neuropsychological testing: Can help to rule out other conditions and to assess cognitive abilities that might influence ADHD symptoms.
Addressing Diagnostic Bias
Diagnostic bias can significantly affect the accuracy of ADHD diagnoses in this population. Clinicians must receive specific training to recognize the subtle nuances of ADHD symptoms in the context of autism and intellectual disabilities.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Assessments must be culturally sensitive and account for individual differences in symptom presentation.
- Minimizing Stereotyping: Clinicians must avoid stereotyping individuals based on their diagnoses and must consider the full range of individual presentations.
- Collaboration with other Professionals: Working closely with professionals familiar with ASD and ID is essential for accurate diagnosis.
Implications for Treatment and Intervention
Accurate diagnosis is essential for developing tailored treatment plans that address the unique needs of each individual.
- Behavioral therapy: Strategies like organizational skills training, self-monitoring techniques, and cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) can be highly effective.
- Medication management: Stimulant or non-stimulant medications may be considered in some cases, but should be carefully monitored due to potential interactions with other medications.
- Support Services: Access to support services, such as occupational therapy, speech therapy, and social skills training, is crucial for comprehensive support.
Conclusion
New research underscores the significantly elevated rates of ADHD diagnoses among adults with autism and intellectual disabilities. The overlapping symptoms of these conditions create substantial diagnostic challenges, highlighting the critical need for comprehensive assessment tools and clinician training to mitigate diagnostic bias. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for developing and implementing effective interventions, ultimately improving the quality of life for these individuals. Understanding the elevated rates of ADHD in adults with autism and intellectual disabilities is crucial for providing effective support and interventions. Learn more about accurate diagnosis and treatment options today!

Featured Posts
-
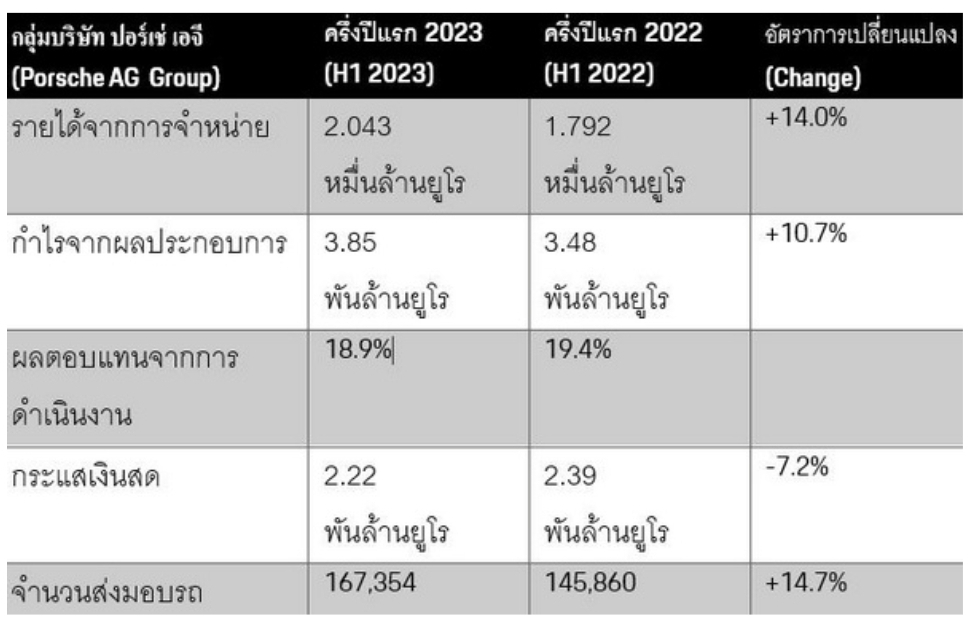 Porsche Ag
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Ag
Apr 29, 2025 -
 We Now Know How Ai Thinks And Its Barely Thinking At All
Apr 29, 2025
We Now Know How Ai Thinks And Its Barely Thinking At All
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Understanding The Russian Militarys Actions And Europes Response
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding The Russian Militarys Actions And Europes Response
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025
Nyt Spelling Bee February 28 2025 Solutions And Spangram
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Porsche Cayenne Ev 2026 Leaked Spy Shots And Speculation
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Cayenne Ev 2026 Leaked Spy Shots And Speculation
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Top Summer Slides 2025 Reviews And Buying Guide
Apr 30, 2025
Top Summer Slides 2025 Reviews And Buying Guide
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Revised Yate Train Services Reaching Bristol And Gloucester
Apr 30, 2025
Revised Yate Train Services Reaching Bristol And Gloucester
Apr 30, 2025 -
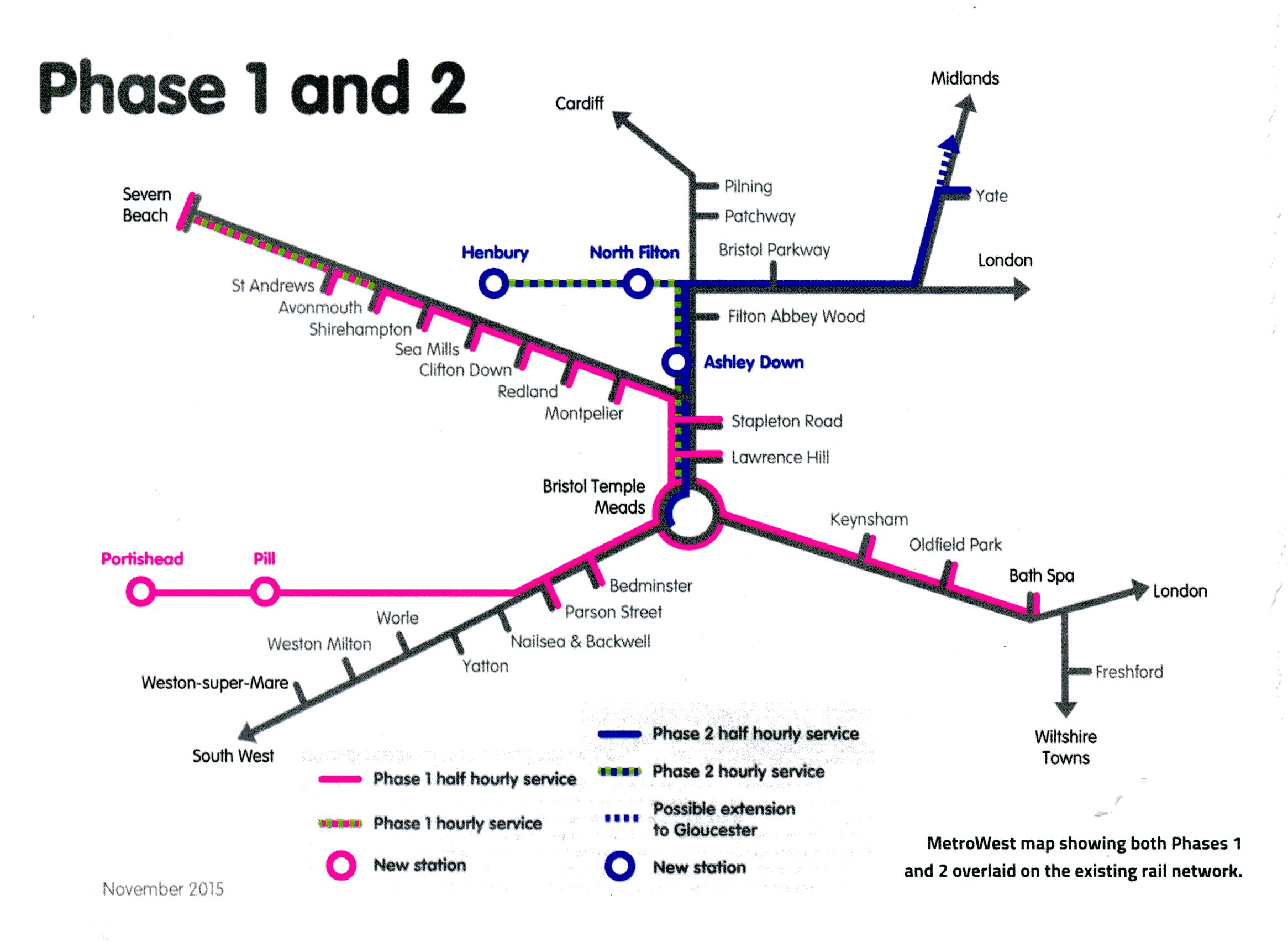 Updated Yate Train Timetable Bristol And Gloucester Connections
Apr 30, 2025
Updated Yate Train Timetable Bristol And Gloucester Connections
Apr 30, 2025 -
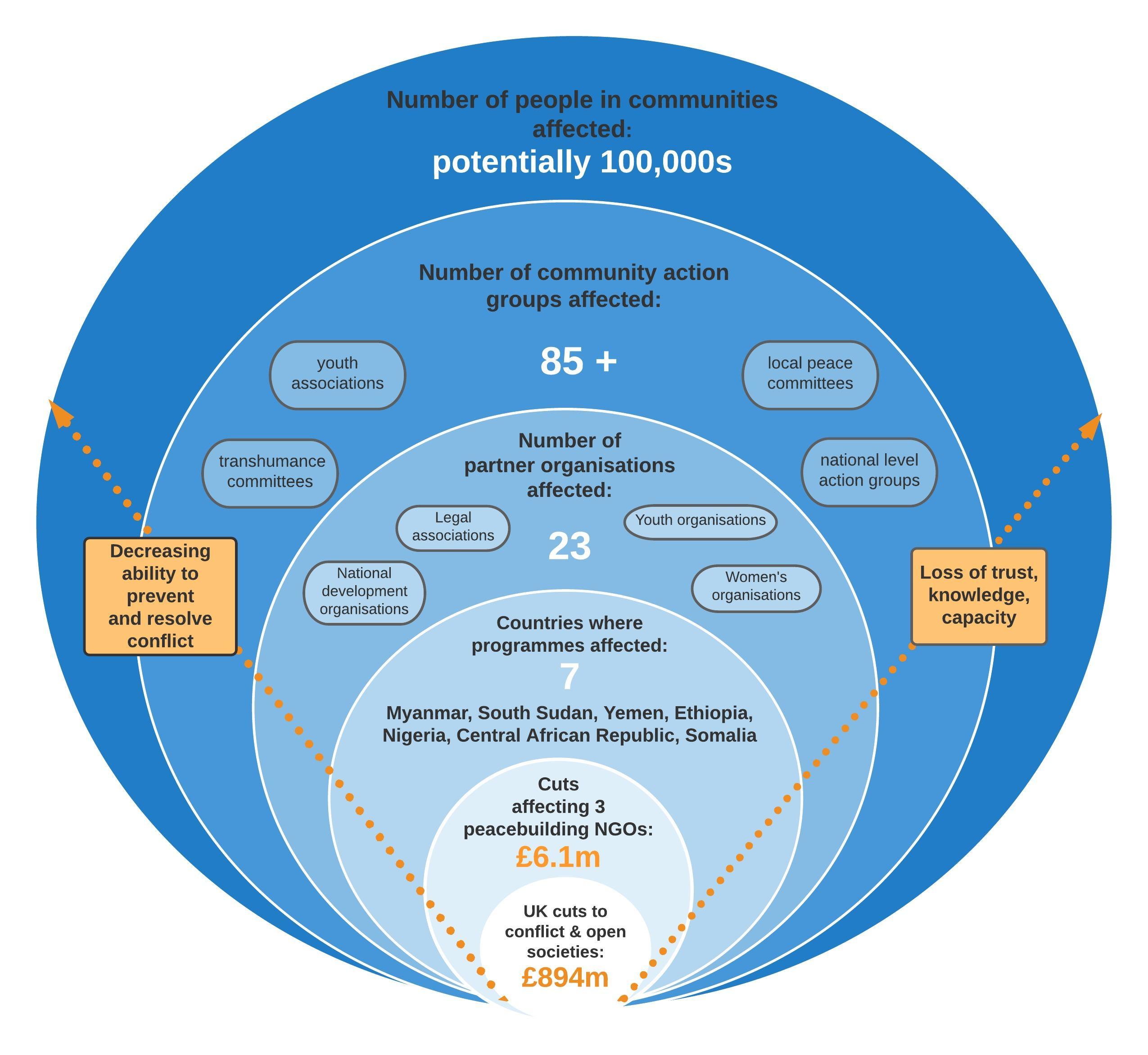 The Ripple Effect Federal Funding Cuts And Their Consequences In Trump Country
Apr 30, 2025
The Ripple Effect Federal Funding Cuts And Their Consequences In Trump Country
Apr 30, 2025 -
 Tarykh Srf Rwatb Abryl 2025 Dlyl Shaml Llmwatnyn
Apr 30, 2025
Tarykh Srf Rwatb Abryl 2025 Dlyl Shaml Llmwatnyn
Apr 30, 2025
