Over-the-Counter Birth Control: Implications For Reproductive Rights And Access After Roe V. Wade
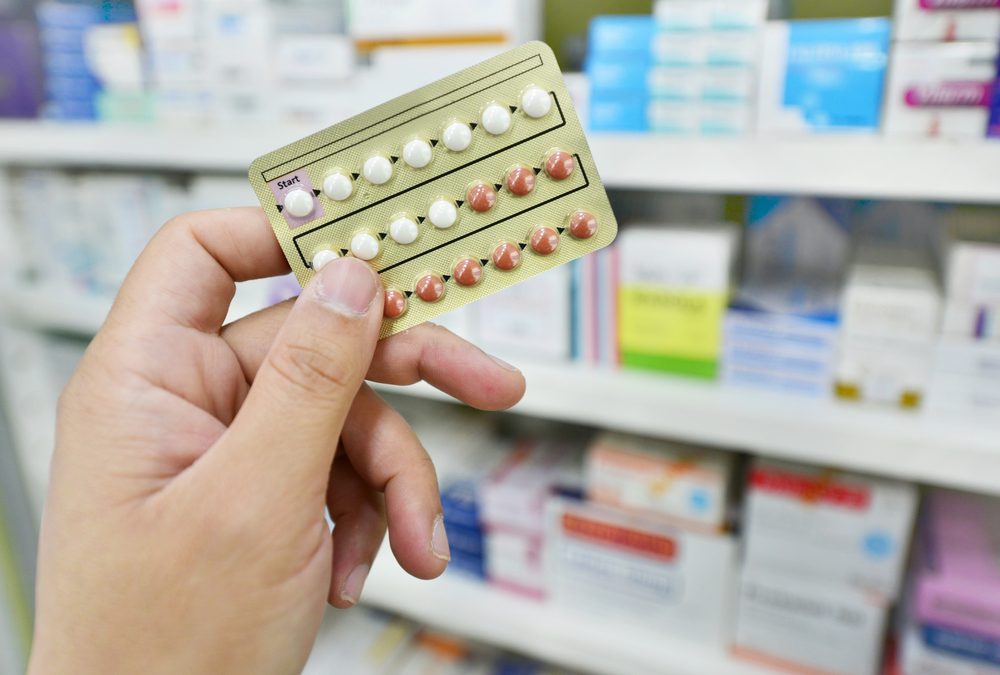
Table of Contents
Increased Access and Convenience
Over-the-counter birth control offers the potential to dramatically improve access to contraception, particularly for underserved populations. Currently, many individuals face significant barriers to accessing birth control, including: financial constraints, geographical limitations (especially in rural areas), and lack of health insurance. Making birth control pills and other contraceptives available OTC could dismantle these barriers, leading to several key improvements:
- Reduced Financial Barriers: The cost of doctor's visits, prescriptions, and even transportation can be prohibitive for many low-income individuals. OTC birth control removes these financial hurdles, making family planning more affordable and accessible.
- Elimination of Geographical Barriers: Access to healthcare providers, particularly specialists offering reproductive services, is unevenly distributed across the US. OTC birth control eliminates the need to travel long distances or navigate complex healthcare systems, especially beneficial for those in rural communities.
- Increased Privacy and Autonomy: For many individuals, seeking birth control requires overcoming social stigma or navigating personal discomfort. OTC access provides greater privacy and control over personal reproductive choices.
- Potential for Improved Adherence to Birth Control Regimens: Easy access could lead to improved adherence to birth control regimens, thereby reducing the risk of unintended pregnancies. This is particularly relevant for contraceptives requiring daily use, such as birth control pills.
The increased accessibility and convenience of OTC contraceptives, including birth control pills and other forms, are undeniable advantages in a system striving for equitable access to family planning.
Potential Drawbacks and Concerns
While increased access is a significant benefit, the potential drawbacks of OTC birth control cannot be ignored. A crucial concern is the potential for misuse and incorrect usage without proper medical guidance. This could lead to several problems:
- Lack of Personalized Medical Advice: A doctor's visit provides an opportunity for personalized medical advice, considering individual health history, potential drug interactions, and pre-existing conditions. OTC access eliminates this crucial consultation.
- Potential for Incorrect Usage and Side Effects: Incorrect usage of contraceptives can significantly reduce their effectiveness and potentially lead to adverse side effects. The absence of professional guidance increases these risks.
- Challenges in Addressing Individual Health Concerns: OTC access doesn't allow for prompt attention to potential health complications or side effects that might require immediate medical intervention.
- Risk of Increased Unintended Pregnancies Due to Improper Use: Improper usage, stemming from a lack of personalized medical advice and guidance, could lead to a rise in unintended pregnancies, negating the positive impact of increased accessibility.
Therefore, ensuring comprehensive education and readily available information about proper usage and potential side effects is paramount to mitigate these risks.
Legal and Ethical Implications
The transition to OTC birth control is not without legal and ethical complexities. The legal landscape surrounding reproductive healthcare is constantly evolving, particularly post-Roe v. Wade, with significant variations across states.
- State-Level Abortion Bans and Their Potential Impact on Birth Control Access: Some states have enacted restrictive abortion laws that could indirectly impact access to birth control, either through limitations on healthcare services or by creating a climate of fear and distrust.
- Debate on the Appropriate Level of Government Regulation: The debate continues regarding the appropriate level of government regulation and the role of the FDA in overseeing the safety and efficacy of OTC contraceptives.
- Ethical Concerns Regarding Access for Minors: Providing access to minors without parental consent raises complex ethical and legal questions.
- The Role of Insurance Coverage in Determining Access: The extent to which insurance companies cover OTC birth control will significantly influence its accessibility for various demographic groups.
Navigating these legal and ethical challenges requires careful consideration of patient autonomy, public health concerns, and the potential impact on vulnerable populations.
The Impact on the Reproductive Healthcare Landscape
The widespread availability of OTC birth control could significantly reshape the reproductive healthcare landscape, particularly in the post-Roe era.
- Shift in the Provider-Patient Relationship: There could be a shift in the provider-patient relationship, with less reliance on traditional healthcare providers for contraceptive services.
- Potential Reduction in Demand for Certain Healthcare Services: The increased accessibility of OTC contraceptives could lead to a reduction in the demand for certain healthcare services, including those related to managing unintended pregnancies.
- Changes in the Overall Cost of Healthcare: The long-term impact on the overall cost of healthcare is uncertain, with potential savings from reduced pregnancy-related expenses balanced against the need for increased public health education and resources.
- The Need for Improved Public Health Education Initiatives: To mitigate the potential risks associated with OTC birth control, significant investment in public health education initiatives is crucial.
These changes necessitate a thoughtful and proactive approach to ensure the safe and effective integration of OTC birth control into the reproductive healthcare system.
Conclusion: The Future of Over-the-Counter Birth Control and Reproductive Rights
The debate surrounding over-the-counter birth control is multifaceted, highlighting the complexities of balancing increased access with concerns about safety and proper usage. While OTC birth control offers the potential to significantly improve access to family planning, particularly for underserved populations, potential drawbacks related to misuse and lack of personalized medical advice must be addressed through robust public health education and accessible resources. The legal and ethical implications, particularly in the post-Roe landscape, necessitate ongoing dialogue and advocacy to ensure equitable access to reproductive healthcare. Stay informed about the evolving legal and regulatory developments, and participate in discussions and support organizations working to protect reproductive rights and ensure access to comprehensive, safe, and affordable birth control options. Your voice matters in shaping the future of over-the-counter birth control and reproductive healthcare in America.

Featured Posts
-
 New Covid 19 Variant Fueling Case Increase In Multiple Countries
May 31, 2025
New Covid 19 Variant Fueling Case Increase In Multiple Countries
May 31, 2025 -
 Susie Wiles Impersonation Exclusive Details From The Federal Investigation
May 31, 2025
Susie Wiles Impersonation Exclusive Details From The Federal Investigation
May 31, 2025 -
 48 Fun Things To Do In Dc This May Pride Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025
48 Fun Things To Do In Dc This May Pride Concerts And Exhibits
May 31, 2025 -
 2025 Giro D Italia Ita Airways Announced As Official Airline
May 31, 2025
2025 Giro D Italia Ita Airways Announced As Official Airline
May 31, 2025 -
 Xbb 1 5 Variant Surge A Slight Increase In Covid 19 Cases Reported Across India
May 31, 2025
Xbb 1 5 Variant Surge A Slight Increase In Covid 19 Cases Reported Across India
May 31, 2025
