PwC Shuts Down Operations In Nine African Nations: Reasons And Ramifications

Table of Contents
Reasons Behind PwC's Decision to Exit Nine African Nations
PwC's strategic retreat from nine African nations wasn't a spontaneous decision; it's a culmination of several interconnected factors impacting their operational viability and strategic priorities.
Economic Challenges and Market Volatility
Many of the affected African nations grapple with significant economic instability. Fluctuating market conditions make long-term planning and investment extremely challenging for businesses, including large multinational firms like PwC.
- High Inflation: Soaring inflation rates erode profit margins and make it difficult to maintain competitive pricing.
- Currency Devaluation: Frequent currency fluctuations increase operational costs and create uncertainty in financial forecasting.
- Political Risks: Political instability, corruption, and regulatory uncertainty create significant operational risks and deter investment.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Complex and ever-changing regulations add layers of administrative burden and compliance costs.
- Limited Growth Prospects: Slower than anticipated economic growth in some regions reduces the potential for expansion and return on investment.
For example, the recent economic downturns in [mention specific country examples and relevant data, e.g., "X experienced a Y% contraction in GDP last year, impacting PwC's client base and revenue streams."] This highlights the significant economic challenges influencing PwC's decision.
Strategic Restructuring and Prioritization
PwC's decision also reflects a broader strategic restructuring and prioritization of its global operations. The firm likely assessed its portfolio of global markets and decided to focus its resources on more profitable and stable regions.
- Focus on Key Markets: PwC may be strategically reallocating resources to markets offering higher growth potential and lower risk.
- Resource Allocation: Optimizing resource allocation involves focusing investments on areas delivering the highest returns.
- Optimization of Operational Efficiency: Centralizing operations or streamlining processes in certain regions might have been deemed more efficient than maintaining smaller, geographically dispersed operations.
- Global Expansion Plans: PwC's global expansion strategy might favor investment in faster-growing, less volatile markets.
This strategic shift underscores the competitive pressures faced by multinational professional services firms and their need for constant adaptation and optimization.
Operational Challenges and Infrastructure Limitations
Maintaining a robust operational presence in certain African nations presents considerable infrastructural challenges that impact service delivery and efficiency.
- Lack of Reliable Internet: Limited internet access hinders seamless communication, data transfer, and collaboration, crucial aspects of providing professional services.
- Power Outages: Frequent power outages disrupt operations, affecting productivity and potentially leading to data loss.
- Logistical Challenges: Poor infrastructure and unreliable transportation networks can hinder client access and the timely delivery of services.
- Security Concerns: Security risks, including cyber threats and physical insecurity, add operational complexities and costs.
[Provide specific examples illustrating these challenges; for instance, mention specific countries with unreliable infrastructure and the impact it has on business operations.] These factors cumulatively contribute to increased operational costs and decreased efficiency, influencing PwC's decision.
Ramifications of PwC's Withdrawal from Nine African Nations
PwC's withdrawal carries significant ramifications for various stakeholders, extending beyond the firm's immediate operations.
Impact on Local Economies and Employment
The immediate impact is job losses for PwC employees in the affected nations. This triggers a ripple effect through the economy.
- Loss of Jobs: Direct job losses among PwC staff and a potential decline in associated employment in related sectors.
- Decreased Tax Revenue: Reduced tax revenue for governments due to the loss of PwC's economic contribution.
- Reduced Foreign Investment: PwC's departure could signal to other international investors that these markets present heightened risks.
- Impact on Related Businesses: Businesses that depended on PwC's services might face challenges, leading to potential job losses in these sectors.
The broader economic implications include decreased government revenue and diminished investor confidence, hindering economic growth in the affected countries.
Implications for Clients and Business Continuity
PwC's clients in the affected regions face significant challenges in finding suitable replacement services and ensuring business continuity.
- Difficulty Finding Replacement Services: Finding equivalent professional services might prove difficult, particularly for specialized areas of expertise.
- Disruption of Ongoing Projects: Ongoing projects might face delays or disruptions, impacting business operations and potentially leading to financial losses.
- Loss of Expertise: The departure of PwC's experienced professionals represents a loss of valuable expertise and knowledge.
- Impact on Financial Reporting: Businesses reliant on PwC for financial reporting and auditing may face challenges in complying with regulatory requirements.
The consequences could range from operational disruptions to long-term financial instability for affected businesses.
Reputational Impact on PwC and the Accounting Profession
PwC's decision may also have reputational implications for both the firm and the broader accounting profession in Africa.
- Damage to Brand Reputation: The withdrawal could negatively impact PwC's image and perception as a reliable and committed partner in African markets.
- Loss of Trust: The move could erode trust in multinational professional services firms among businesses and governments in the region.
- Scrutiny from Regulators: Regulators might scrutinize PwC's actions, raising questions about the firm's commitment to African markets.
- Implications for Future Business in Africa: Other international firms may hesitate to invest in these markets, fearing similar challenges.
The long-term impact on the trust and confidence in the professional services sector in these regions remains to be seen.
Conclusion: Navigating the Aftermath of PwC's Departure from the African Market
PwC's withdrawal from nine African nations is a complex issue stemming from a confluence of economic challenges, strategic priorities, and infrastructural limitations. The ramifications are far-reaching, impacting local economies, businesses, and the professional services landscape in Africa. Understanding the complexities surrounding this decision is crucial for fostering sustainable business development on the continent. We encourage further discussion, analysis, and investigation into the intricate factors contributing to PwC's withdrawal from the African market and its long-term effects. Explore related articles and resources to gain a deeper understanding. Share your thoughts and insights in the comments below to contribute to a comprehensive understanding of this significant development in the African business world.

Featured Posts
-
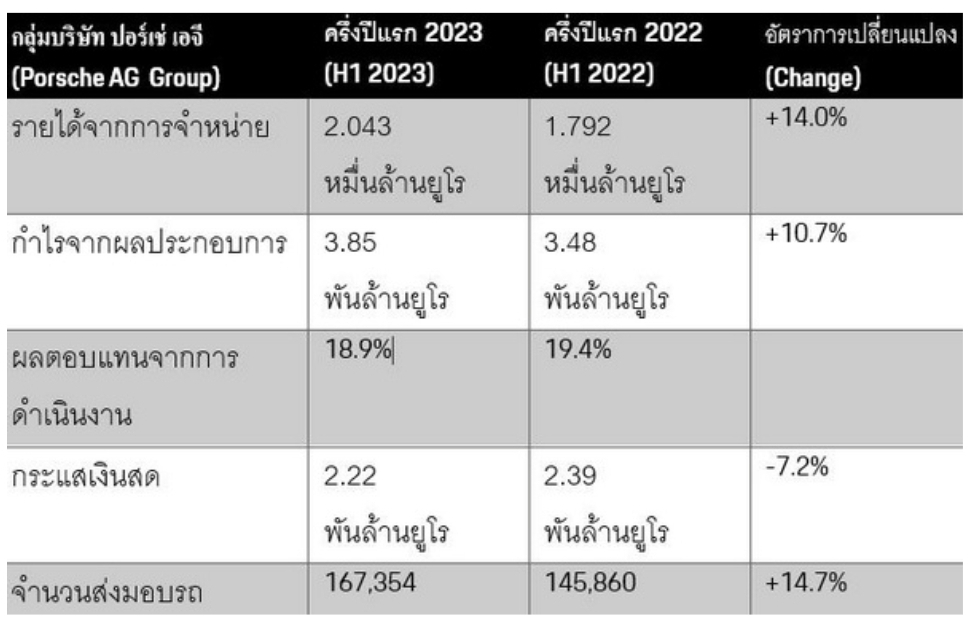 Porsche Ag
Apr 29, 2025
Porsche Ag
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Adhd Aging And Brain Iron Understanding Attention And Cognitive Decline
Apr 29, 2025
Adhd Aging And Brain Iron Understanding Attention And Cognitive Decline
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Shooting At North Carolina University One Dead Six Injured
Apr 29, 2025
Shooting At North Carolina University One Dead Six Injured
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Update Search Continues For British Paralympian Missing In Las Vegas
Apr 29, 2025
Update Search Continues For British Paralympian Missing In Las Vegas
Apr 29, 2025 -
 Understanding Russias Military Strategy And Its Impact On Europe
Apr 29, 2025
Understanding Russias Military Strategy And Its Impact On Europe
Apr 29, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Bharty Hkwmt Ky Kshmyr Palysy Pr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Shdyd Ahtjaj
May 02, 2025
Bharty Hkwmt Ky Kshmyr Palysy Pr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Shdyd Ahtjaj
May 02, 2025 -
 Mqbwdh Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Bhart Ky Palysy Pr Rdeml
May 02, 2025
Mqbwdh Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ka Bhart Ky Palysy Pr Rdeml
May 02, 2025 -
 Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ky Bharty Palysy Pr Skht Nkth Chyny
May 02, 2025
Kshmyr Agha Syd Rwh Allh Mhdy Ky Bharty Palysy Pr Skht Nkth Chyny
May 02, 2025 -
 Aj Ywm Ykjhty Kshmyr Mkhtlf Shhrwn Myn Rylyan Awr Tqrybat
May 02, 2025
Aj Ywm Ykjhty Kshmyr Mkhtlf Shhrwn Myn Rylyan Awr Tqrybat
May 02, 2025 -
 Ywm Ykjhty Kshmyr Kshmyrywn Ky Jdwjhd Ky Hmayt Myn Mzahre
May 02, 2025
Ywm Ykjhty Kshmyr Kshmyrywn Ky Jdwjhd Ky Hmayt Myn Mzahre
May 02, 2025
