Reactor Power Uprate: A Guide To The NRC Application Process
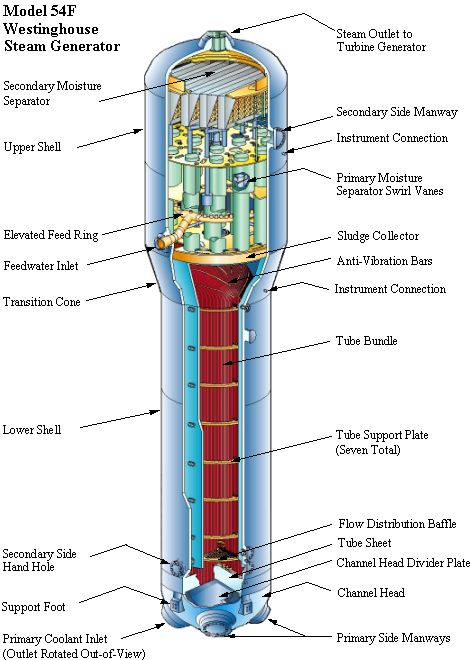
Table of Contents
Understanding the NRC's Regulatory Framework for Reactor Power Uprates
The Nuclear Regulatory Commission (NRC) sets stringent regulations governing reactor power uprates. A successful application requires meticulous attention to detail and a comprehensive understanding of these regulations. Key aspects of the NRC's framework include:
Preliminary Safety Analysis Report (PSAR) Preparation
The PSAR is the cornerstone of your reactor power uprate application. This document provides a detailed assessment of the reactor's current safety systems and analyzes the potential impact of increased power output. Key elements of PSAR preparation include:
- Comprehensive review of existing safety systems: This involves a thorough examination of all safety-related systems, including emergency core cooling systems (ECCS), containment systems, and instrumentation and control systems. A detailed assessment of their capabilities under increased power conditions is essential for the success of a reactor power uprate.
- Identification of potential safety concerns and mitigation strategies: The PSAR should proactively identify potential safety concerns arising from the power uprate and propose effective mitigation strategies to address them. This demonstrates a proactive approach to safety, which is crucial for NRC approval.
- Detailed analysis of thermal-hydraulic performance: A rigorous thermal-hydraulic analysis is necessary to demonstrate that the reactor can operate safely at the increased power level without exceeding design limits. This often involves sophisticated computer modeling and simulations.
- Assessment of structural integrity under increased power conditions: The PSAR must demonstrate that the reactor vessel, piping, and other structural components can withstand the increased stresses associated with higher power operation. This may involve stress analysis and fatigue life assessments.
Meeting NRC Requirements for Technical Specifications
The application must precisely adhere to all technical specifications outlined by the NRC. These specifications cover a wide range of safety and operational aspects of the reactor. Compliance is paramount for a successful reactor power uprate.
- Compliance with all applicable regulations and codes: This includes adherence to industry standards, codes, and guidelines, ensuring your reactor power uprate aligns with established best practices.
- Demonstration of adequate safety margins: The application must demonstrate that even with the increased power output, sufficient safety margins are maintained to account for uncertainties and potential unforeseen events.
- Thorough documentation of all analyses and calculations: All analyses and calculations performed must be thoroughly documented and readily available for NRC review. Detailed records are crucial to ensure transparency and traceability.
- Detailed description of the proposed modifications: The application needs a detailed description of all proposed modifications to the reactor system, including engineering drawings, specifications, and justifications.
Public Participation and Environmental Review
The NRC process includes opportunities for public comment and requires environmental impact assessments. Addressing these aspects is vital for a smooth and successful application.
- Preparation for public hearings and responses to public concerns: The applicant should be prepared to address public concerns and questions about the proposed power uprate during public hearings. Proactive communication is key.
- Conducting environmental impact studies, including potential effects on water bodies and air quality: Environmental impact studies are necessary to assess the potential impact of the power uprate on the surrounding environment. This needs to meet the requirements of the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA).
- Meeting NEPA requirements for environmental review: The application must demonstrate compliance with all NEPA requirements, including the preparation of an environmental impact statement (EIS) if required.
The NRC Application Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The application process itself is multi-stage and requires careful planning and execution. Each stage must be handled with precision and efficiency.
Submitting the Application
The application must be complete, accurate, and address all NRC requirements. This is a critical step that sets the tone for the entire process.
- Preparation of a comprehensive application package including PSAR, technical specifications, and environmental impact assessments: This package needs to be exhaustive and meticulously organized to facilitate NRC review.
- Electronic submission via the NRC's e-submittal system: The NRC utilizes electronic submission systems, requiring familiarity with the online portals and submission procedures.
- Strict adherence to NRC filing deadlines: Missing deadlines can cause delays and potentially jeopardize the entire application.
NRC Review and Evaluation
The NRC conducts a rigorous review, which may involve requests for additional information or clarifications. Responding effectively is crucial.
- Responding promptly and completely to NRC requests: Prompt and thorough responses demonstrate cooperation and help to expedite the review process.
- Collaboration with NRC staff to address any identified issues: A collaborative approach with NRC staff helps to resolve any issues efficiently and proactively.
- Potential for on-site inspections and audits: Be prepared for on-site inspections and audits to verify the information provided in the application.
Licensing and Implementation
Upon successful review, the NRC will issue a license amendment. The final stage involves implementation and monitoring.
- Implementing the approved modifications to the reactor system: This phase requires precise execution of the approved modifications, following strict safety protocols.
- Conducting thorough testing and verification procedures: Rigorous testing is necessary to verify that the modifications have been correctly implemented and that the reactor operates safely at the increased power level.
- Post-implementation monitoring and reporting to the NRC: Ongoing monitoring and reporting to the NRC are crucial to demonstrate continued safe operation.
Key Considerations for a Successful Reactor Power Uprate
Several key factors contribute to the success of a reactor power uprate project. Careful planning and expertise are crucial.
Experienced Engineering and Regulatory Expertise
Navigating the complex regulatory landscape requires specialized knowledge and experienced professionals.
- Engaging experienced nuclear engineers and regulatory consultants: Engaging experienced experts provides invaluable support throughout the entire process.
- Utilizing specialized software for safety analysis and simulations: Advanced software is often required for complex safety analyses and simulations.
- Thorough understanding of NRC regulations and guidance: A deep understanding of relevant regulations and guidance is essential for a successful application.
Comprehensive Cost-Benefit Analysis
A thorough cost-benefit analysis determines the economic viability of a power uprate.
- Estimating capital costs, operational costs, and potential revenue increases: This analysis should consider all relevant financial aspects of the project.
- Assessing the impact of potential delays or regulatory challenges: Realistic assessment of potential delays and challenges is critical for sound financial planning.
- Evaluating long-term financial benefits: The long-term financial benefits of the power uprate must outweigh the costs.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the reactor power uprate process requires a detailed understanding of NRC regulations and a meticulously prepared application. By carefully considering all aspects, from the PSAR to post-implementation monitoring, you can significantly increase your energy output and profitability. Don't hesitate to seek expert guidance to ensure a smooth and successful reactor power uprate. Contact us today to discuss your project and learn how we can help you achieve your power uprate goals and optimize your reactor's performance.

Featured Posts
-
 Early Warning Report Riot Platforms Inc Announces Irrevocable Proxy Agreement
May 02, 2025
Early Warning Report Riot Platforms Inc Announces Irrevocable Proxy Agreement
May 02, 2025 -
 Joe Biden And The Economy Assessing The Impact Of His Policies
May 02, 2025
Joe Biden And The Economy Assessing The Impact Of His Policies
May 02, 2025 -
 Analyzing Dragons Den Pitches Lessons For Aspiring Founders
May 02, 2025
Analyzing Dragons Den Pitches Lessons For Aspiring Founders
May 02, 2025 -
 Resolving Nuclear Related Disputes Legal Perspectives And Solutions
May 02, 2025
Resolving Nuclear Related Disputes Legal Perspectives And Solutions
May 02, 2025 -
 Frances Dominant Six Nations Victory A Warning To Ireland
May 02, 2025
Frances Dominant Six Nations Victory A Warning To Ireland
May 02, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Christina Aguileras Photoshopped Pictures Fans React To Unrecognizable New Photoshoot
May 02, 2025
Christina Aguileras Photoshopped Pictures Fans React To Unrecognizable New Photoshoot
May 02, 2025 -
 Fans Accuse Christina Aguilera Of Excessive Photoshopping In Recent Photoshoot
May 02, 2025
Fans Accuse Christina Aguilera Of Excessive Photoshopping In Recent Photoshoot
May 02, 2025 -
 Photoshop Controversy Christina Aguileras Unrecognizable New Look
May 02, 2025
Photoshop Controversy Christina Aguileras Unrecognizable New Look
May 02, 2025 -
 Fans Claim Christina Aguilera Is Unrecognizable In Heavily Edited New Photos
May 02, 2025
Fans Claim Christina Aguilera Is Unrecognizable In Heavily Edited New Photos
May 02, 2025 -
 Christina Aguileras New Photos Photoshop Controversy Erupts
May 02, 2025
Christina Aguileras New Photos Photoshop Controversy Erupts
May 02, 2025
