Recent Detection Of COVID-19 Variants BA.1 And LF.7 In India: An INSACOG Report
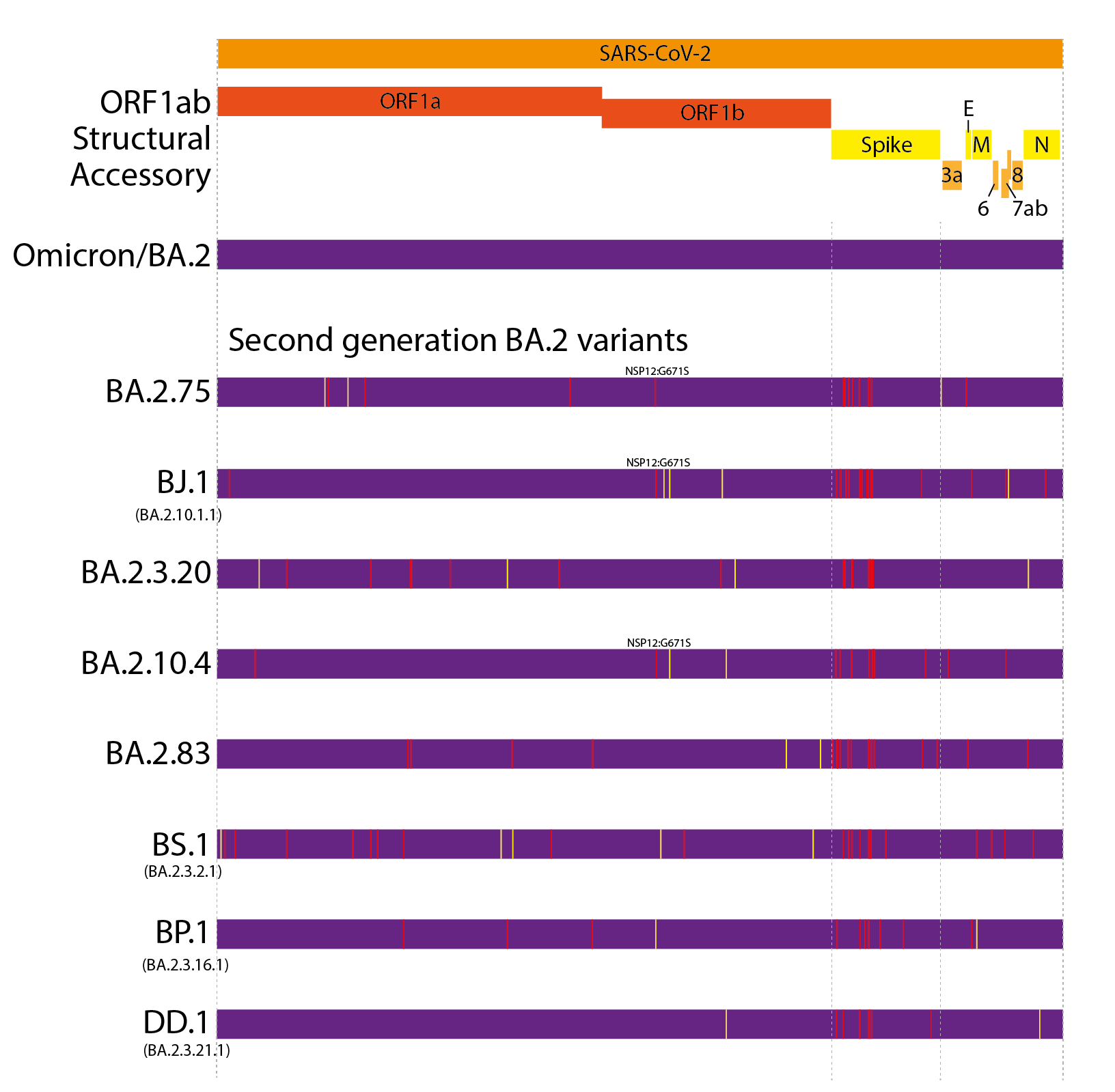
Table of Contents
H2: INSACOG's Role in Variant Surveillance and Detection
The Indian SARS-CoV-2 Consortium on Genomics (INSACOG) plays a pivotal role in India's fight against COVID-19. Its mandate encompasses the comprehensive genomic surveillance of SARS-CoV-2, enabling early detection and tracking of emerging variants. This proactive approach is crucial for informing public health strategies and tailoring interventions effectively.
INSACOG employs a robust methodology for variant detection. This involves collecting samples from across the country, sequencing the viral genome, and analyzing the data to identify new variants and monitor their spread. This meticulous process relies on a network of laboratories across India, working collaboratively to provide a comprehensive national picture.
Key achievements of INSACOG include:
- Early detection of the Delta variant, allowing for timely implementation of containment measures.
- Continuous monitoring of variant prevalence, providing crucial data for policymakers.
- Contribution to global genomic surveillance efforts, sharing data with international organizations.
- Development of robust bioinformatics tools for analyzing and interpreting genomic data.
These achievements underscore INSACOG's critical contribution to India's COVID-19 response and its effectiveness in COVID-19 variant detection in India.
H2: Characteristics and Prevalence of BA.1 and LF.7 Variants in India
BA.1, an Omicron subvariant, is characterized by high transmissibility and its ability to evade some immune responses. While generally associated with milder illness compared to earlier variants like Delta, its rapid spread posed a significant challenge to healthcare systems globally.
Information regarding the characteristics of LF.7 is still emerging. Further research is needed to fully understand its transmissibility, severity, and ability to evade immunity compared to BA.1 and other known variants. As more data becomes available from INSACOG and other research institutions, a clearer picture will emerge.
The precise prevalence of BA.1 and LF.7 in different regions of India requires further analysis of the INSACOG report. [Ideally, this section would include a graph or chart illustrating prevalence data if available from the report]. Geographical distribution and prevalence patterns will play a crucial role in understanding the impact of these COVID-19 variants in India.
H2: Public Health Implications and Response to the Detection
The emergence of BA.1 and LF.7 necessitates a proactive public health response. The potential strain on India's healthcare system, particularly in regions with higher prevalence, warrants careful consideration. This includes ensuring adequate hospital bed capacity, oxygen supplies, and medical personnel.
The Indian government's response has focused on several key strategies:
- Accelerated vaccination campaigns targeting vulnerable populations.
- Enhanced testing and contact tracing measures in areas with higher variant detection.
- Reinforcement of public health measures like mask-wearing and social distancing, especially in high-risk settings.
- Strengthening hospital preparedness for managing potential surges in COVID-19 cases.
Continued genomic surveillance remains crucial for monitoring the evolution of the virus and informing future public health strategies. The recommendations and guidelines issued based on the INSACOG report are vital for effective pandemic preparedness.
H2: Comparison with other COVID-19 Variants Circulating in India
Understanding the competitive dynamics between BA.1, LF.7, and other circulating variants in India is crucial. Comparing their transmissibility, severity, and immune evasion capabilities will provide insight into potential dominance shifts. The co-circulation of multiple variants adds complexity to the epidemiological landscape. The patterns of dominance observed can reveal much about viral evolution and adaptation. Further research comparing the observed characteristics and prevalence of BA.1 and LF.7 with other variants like Delta and its sublineages will allow for a more comprehensive understanding of the COVID-19 variant situation in India.
3. Conclusion: The Ongoing Importance of COVID-19 Variant Monitoring in India
The recent detection of COVID-19 variants BA.1 and LF.7 in India highlights the ongoing need for robust genomic surveillance. INSACOG's continued efforts are essential for early detection and tracking of emerging variants. Proactive public health measures remain critical in mitigating potential future outbreaks. Vaccination remains a cornerstone of the strategy, alongside adherence to public health guidelines.
Staying informed about the latest updates on COVID-19 variants in India is crucial. We urge readers to consult official sources like INSACOG and the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare for the most accurate and up-to-date information regarding recent detection of COVID-19 variants and public health advisories. Staying vigilant and informed is our best defense against this evolving pandemic.

Featured Posts
-
 China Us Trade Flow The Impact Of The Tariff Truce
May 31, 2025
China Us Trade Flow The Impact Of The Tariff Truce
May 31, 2025 -
 Duncan Bannatynes Charity Work Supporting Operation Smile In Casablanca
May 31, 2025
Duncan Bannatynes Charity Work Supporting Operation Smile In Casablanca
May 31, 2025 -
 Glastonbury Ticket Resale A 30 Minute Sell Out Report
May 31, 2025
Glastonbury Ticket Resale A 30 Minute Sell Out Report
May 31, 2025 -
 Jaime Munguia Wins Points Victory Over Bruno Surace In Riyadh Rematch
May 31, 2025
Jaime Munguia Wins Points Victory Over Bruno Surace In Riyadh Rematch
May 31, 2025 -
 Indias Insacog Detects New Covid Variants Ba 1 And Lf 7 Assessing The Threat
May 31, 2025
Indias Insacog Detects New Covid Variants Ba 1 And Lf 7 Assessing The Threat
May 31, 2025
