Record-Breaking Forest Loss: Wildfires Intensify Global Deforestation
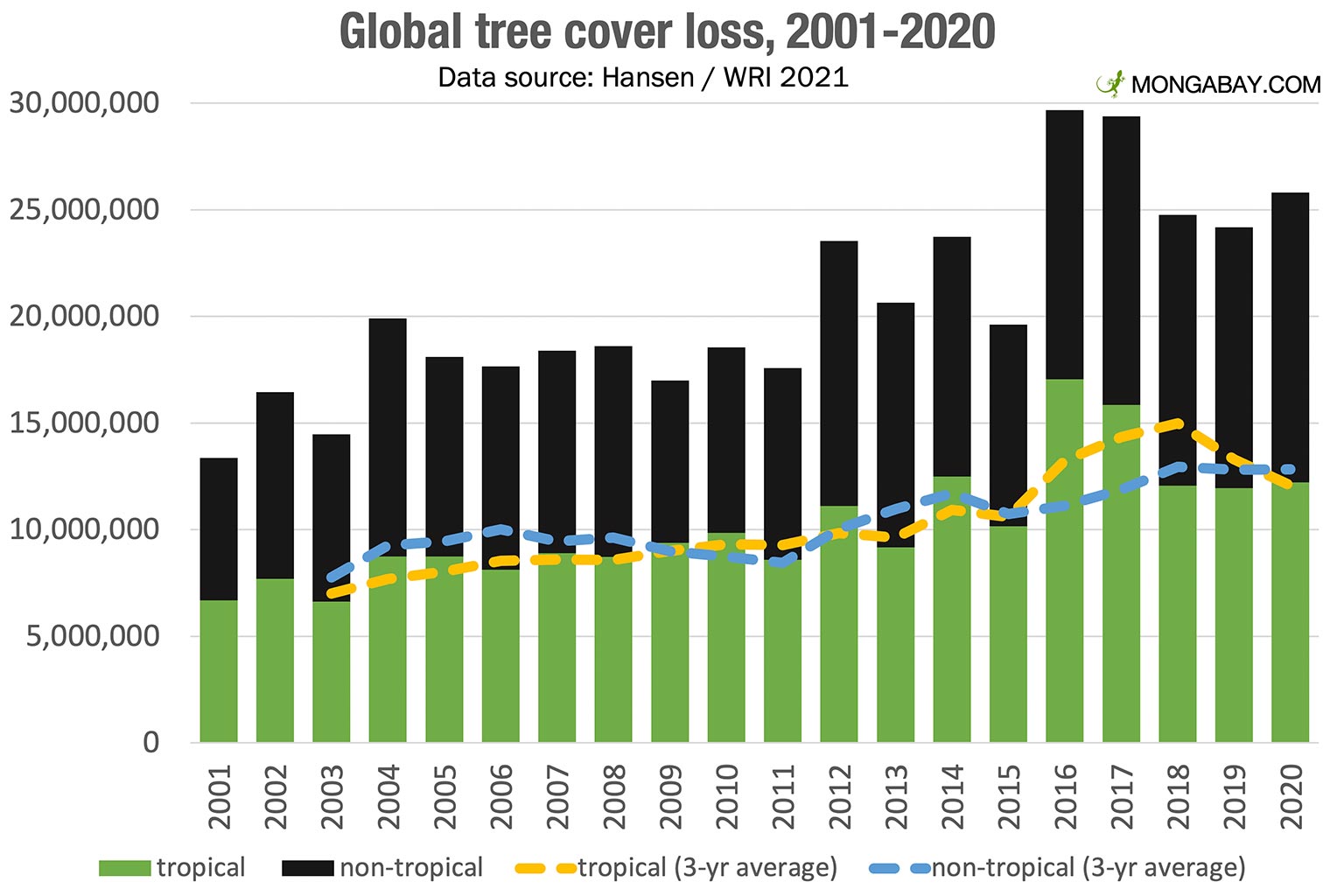
Table of Contents
The Dire Extent of Global Forest Loss
Record-High Deforestation Figures
Global deforestation rates have reached alarming new highs. According to the Global Forest Watch, [insert specific data and source, e.g., "an estimated X million hectares of forest were lost in 2023, a Y% increase compared to 2022" (Source: Global Forest Watch, 2024)]. This represents a significant increase in forest loss compared to previous years, indicating an accelerating crisis.
- Specific numbers on hectares lost: [Insert specific data broken down by region if possible. Example: "The Amazon rainforest alone experienced a loss of Z hectares, while boreal forests in Canada and Russia suffered losses of A and B hectares respectively."]
- Geographic regions most affected: The Amazon rainforest, the Congo Basin, and boreal forests in Siberia and Canada are among the regions experiencing the most significant forest loss.
- Types of forests impacted: Both tropical rainforests, crucial for biodiversity and carbon sequestration, and temperate and boreal forests are suffering immense damage, impacting global ecosystems and climate stability.
Wildfires as a Primary Driver of Deforestation
The Role of Climate Change in Intensifying Wildfires
Climate change is a major contributor to the increased frequency and intensity of wildfires, significantly driving global deforestation. Rising global temperatures, prolonged drought conditions, and changes in precipitation patterns create ideal conditions for devastating wildfires to ignite and spread rapidly. This creates a dangerous feedback loop: deforestation contributes to climate change, which in turn fuels more intense wildfires, leading to further deforestation.
- The feedback loop between deforestation and climate change: Deforestation reduces the planet's capacity to absorb carbon dioxide, exacerbating climate change and leading to hotter, drier conditions that increase wildfire risk.
- Examples of major wildfires and their impact on forest areas: [Cite specific examples of major wildfires in 2023 and their devastating impact on forest cover. Include sources and quantify the hectares burned.]
- Contribution of human activities: Illegal logging, agricultural expansion, and unsustainable land management practices frequently contribute to the ignition and spread of wildfires, exacerbating the problem of global deforestation.
The Devastating Consequences of Record-Breaking Forest Loss
Biodiversity Loss and Extinction
The destruction of forests leads to catastrophic biodiversity loss. Millions of plant and animal species depend on these ecosystems for survival. Habitat loss caused by deforestation and wildfires drives many species towards extinction, impacting the delicate balance of the global ecosystem.
- Specific endangered species affected: [List specific examples of endangered species affected by deforestation and wildfires in affected regions.]
Climate Change Exacerbation
Deforestation significantly contributes to climate change acceleration. Trees absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. When forests are destroyed, this stored carbon is released back into the atmosphere, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and global warming.
- Contribution of deforestation to carbon emissions: [Quantify the contribution of deforestation to global carbon emissions. Cite relevant studies and data.]
Economic and Social Impacts
The economic consequences of record-breaking forest loss are severe. Local communities that rely on forests for their livelihoods – such as those involved in logging, agriculture, and tourism – suffer significant economic hardship. This can lead to social unrest and displacement.
- Social and economic disruption in affected regions: [Discuss the impact on indigenous communities and local economies. Include examples of social and economic consequences.]
Conclusion
The record-breaking forest loss in 2023, fueled by increasingly intense wildfires, represents a catastrophic environmental crisis. The consequences – from biodiversity loss and climate change exacerbation to severe economic and social disruption – are far-reaching and devastating. We are witnessing an alarming acceleration in global deforestation, demanding immediate and decisive action. We must act now to address this escalating crisis of global deforestation. Learn more about conservation efforts and support organizations working to protect our forests. Preventing deforestation and mitigating wildfire damage through sustainable practices and global cooperation is crucial for securing a healthy planet for future generations. Combating forest loss requires a multifaceted approach, including strengthened environmental policies, sustainable land management, and a global commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions.

Featured Posts
-
 The Bury M62 Relief Road A Forgotten Plan
May 25, 2025
The Bury M62 Relief Road A Forgotten Plan
May 25, 2025 -
 Making The Escape To The Country A Reality A Step By Step Plan
May 25, 2025
Making The Escape To The Country A Reality A Step By Step Plan
May 25, 2025 -
 Mia Farrow Sadie Sink And Photo 5162787 A Broadway Moment
May 25, 2025
Mia Farrow Sadie Sink And Photo 5162787 A Broadway Moment
May 25, 2025 -
 Previsioni Prezzi Moda Usa L Influenza Dei Dazi
May 25, 2025
Previsioni Prezzi Moda Usa L Influenza Dei Dazi
May 25, 2025 -
 Amundi Djia Ucits Etf A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value
May 25, 2025
Amundi Djia Ucits Etf A Deep Dive Into Net Asset Value
May 25, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 George L Russell Jr S Passing A Loss For Marylands Legal And Political Communities
May 25, 2025
George L Russell Jr S Passing A Loss For Marylands Legal And Political Communities
May 25, 2025 -
 Maryland Mourns The Passing Of Legal Luminary George L Russell Jr
May 25, 2025
Maryland Mourns The Passing Of Legal Luminary George L Russell Jr
May 25, 2025 -
 George Russells Mercedes Future Wolff Drops Another Clue
May 25, 2025
George Russells Mercedes Future Wolff Drops Another Clue
May 25, 2025 -
 Mercedes And George Russell Contract Renewal Hinges On This One Factor
May 25, 2025
Mercedes And George Russell Contract Renewal Hinges On This One Factor
May 25, 2025 -
 Toto Wolffs Latest Comments On George Russells Mercedes Future
May 25, 2025
Toto Wolffs Latest Comments On George Russells Mercedes Future
May 25, 2025
