Record-Breaking Global Forest Loss: Wildfires And Deforestation
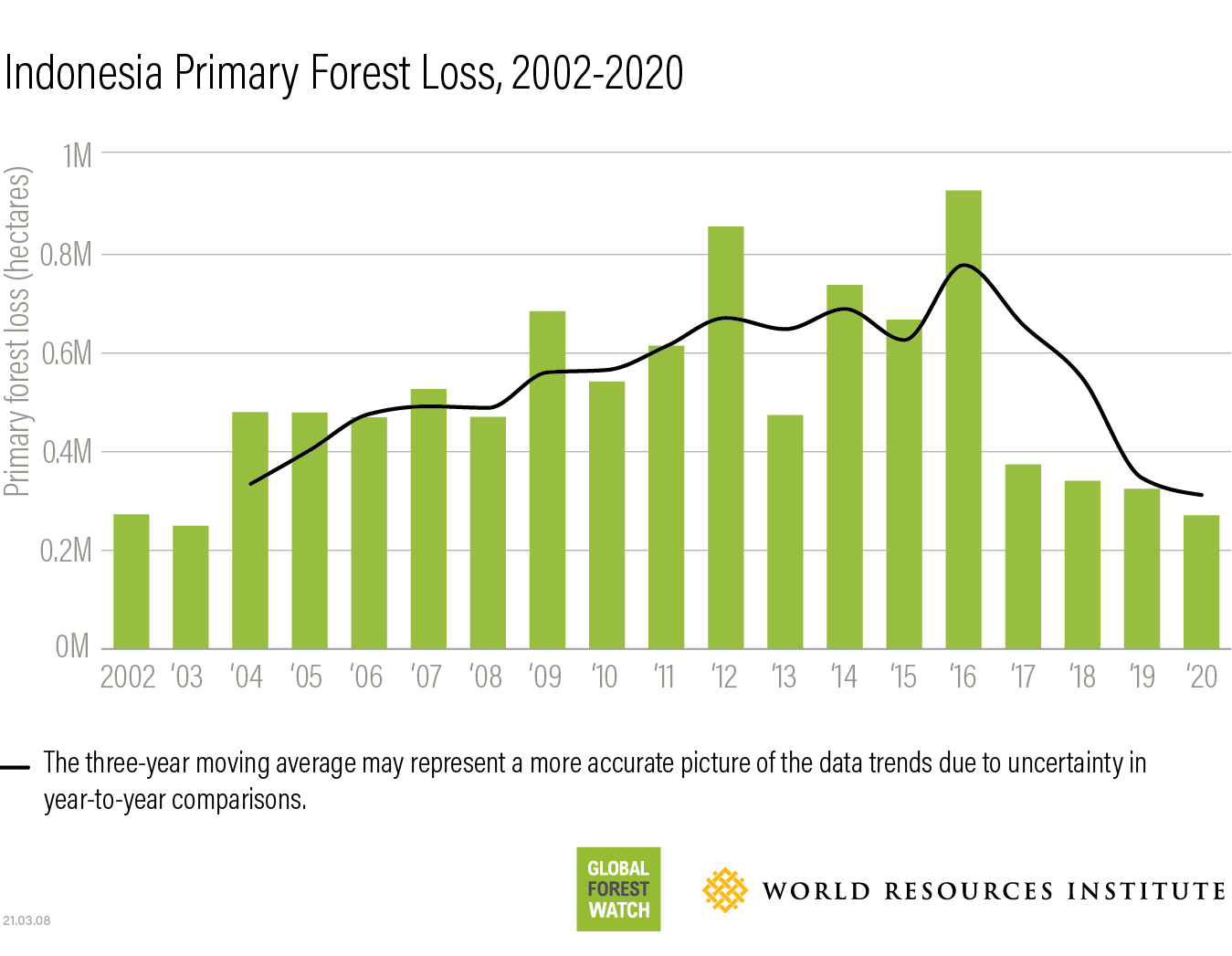
Table of Contents
The Devastating Impact of Wildfires
Increased Frequency and Intensity
The number and severity of wildfires globally are rising dramatically, a trend directly linked to climate change. Longer, hotter, and drier summers, exacerbated by climate change, create ideal conditions for ignition and rapid fire spread. This results in larger, more intense, and longer-lasting wildfire devastation.
- Examples of major wildfires: The 2019-2020 Australian bushfires, the ongoing Amazon rainforest fires, and the frequent California wildfires are stark examples of the increasing scale of these events.
- Statistics: The area burned globally each year has been steadily increasing, with significant variations depending on the region and climate patterns. Detailed statistics can be found from organizations such as the Global Forest Watch.
- Keyword integration: The scale of wildfire devastation is alarming, and the increase in extreme weather events fueled by climate change impact necessitates immediate action for forest fire prevention.
The Role of Climate Change
Climate change plays a crucial role in amplifying wildfire risk. Rising global temperatures lead to drier conditions and prolonged droughts, turning forests into tinderboxes. Higher temperatures also increase the likelihood of lightning strikes, a common wildfire ignition source.
- Feedback Loop: Burned forests release significant amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2), a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere, further exacerbating climate change and creating a dangerous feedback loop.
- Impact on Vulnerable Ecosystems: Many ecosystems, particularly those already stressed by other environmental factors, are particularly vulnerable to the impacts of increased wildfire frequency and intensity.
- Keyword integration: Effective climate change mitigation strategies, including reducing greenhouse gas emissions and enhancing carbon sequestration through forest conservation, are critical to reducing ecological damage from wildfires.
The Ongoing Crisis of Deforestation
Drivers of Deforestation
Deforestation, the clearing of forests for other land uses, is another major driver of global forest loss. Several factors contribute to this crisis:
- Agriculture: Cattle ranching and the expansion of palm oil plantations are leading causes of deforestation, particularly in tropical regions.
- Logging: Illegal and unsustainable logging practices contribute significantly to forest loss, often targeting valuable timber species.
- Mining: Mining operations, including both surface and underground mining, often lead to widespread forest clearing.
- Infrastructure Development: The construction of roads, dams, and other infrastructure projects often results in significant habitat destruction.
- Keyword integration: Addressing illegal logging, promoting sustainable agriculture, and preventing further land conversion are essential to curbing deforestation.
The Socioeconomic Factors
Socioeconomic factors play a significant role in driving deforestation. Poverty, lack of land rights, and weak governance often create an environment where unsustainable practices flourish.
- Impact on Indigenous Communities: Indigenous communities, who often depend on forests for their livelihoods and have long-standing traditions of sustainable forest management, are disproportionately affected by deforestation.
- Economic Incentives: The short-term economic benefits associated with clearing forests for agriculture or logging often outweigh the long-term environmental consequences.
- Keyword integration: Promoting sustainable development, supporting community forestry initiatives, and addressing poverty reduction are crucial to changing the socioeconomic drivers of deforestation.
Consequences of Global Forest Loss
Biodiversity Loss
The loss of forests has devastating consequences for biodiversity. Forests are home to a vast array of plant and animal species, and their destruction leads to habitat fragmentation, population declines, and ultimately, extinction.
- Endangered Species: Many endangered species are directly threatened by deforestation and wildfires, further exacerbating the global biodiversity crisis.
- Loss of Ecosystem Services: Forests provide vital ecosystem services, including clean water, air purification, and climate regulation. Their loss undermines these essential functions.
- Keyword integration: Protecting biodiversity conservation, mitigating habitat fragmentation, and safeguarding endangered species are critical to preserving the ecological integrity of our planet and the vital ecosystem services forests provide.
Climate Change Exacerbation
Deforestation and wildfires significantly contribute to climate change by releasing large amounts of stored carbon into the atmosphere.
- Role of Forests in Carbon Sequestration: Forests act as vital carbon sinks, absorbing CO2 from the atmosphere. Their destruction reduces this crucial capacity.
- Positive Feedback Loop: The loss of forests accelerates climate change, which in turn increases the risk of wildfires and further deforestation, creating a dangerous positive feedback loop.
- Keyword integration: Understanding the role of forests in the carbon cycle, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and slowing global warming are essential to mitigating the impacts of climate change.
Conclusion
Record-breaking global forest loss due to wildfires and deforestation poses a grave threat to the environment and human society. The consequences, including biodiversity loss and accelerated climate change, are far-reaching and demand urgent action. We must support organizations dedicated to forest conservation, sustainable forestry practices, and reforestation efforts. Advocating for policies that promote responsible land management and combat climate change is crucial to curbing global forest loss. We can all contribute by reducing our carbon footprint, supporting sustainable consumption, and educating ourselves about the importance of protecting our forests. Let's work together to combat deforestation and prevent wildfires to protect the future of our planet. Learn more and get involved in protecting our forests today.

Featured Posts
-
 Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Benoemen Karin Polman Als Directeur Hypotheken
May 22, 2025
Abn Amro Florius En Moneyou Benoemen Karin Polman Als Directeur Hypotheken
May 22, 2025 -
 Arda Gueler In Kariyeri Real Madrid In Yeni Teknik Direktoeruenuen Etkisi
May 22, 2025
Arda Gueler In Kariyeri Real Madrid In Yeni Teknik Direktoeruenuen Etkisi
May 22, 2025 -
 Is Western Separation Realistic A Saskatchewan Perspective
May 22, 2025
Is Western Separation Realistic A Saskatchewan Perspective
May 22, 2025 -
 Paris Nouvelle Scene Pour La Chanteuse Suisse Stephane
May 22, 2025
Paris Nouvelle Scene Pour La Chanteuse Suisse Stephane
May 22, 2025 -
 Chainalysis Boosts Ai Prowess Through Alterya Acquisition
May 22, 2025
Chainalysis Boosts Ai Prowess Through Alterya Acquisition
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Otter Population Management A Wyoming Case Study
May 22, 2025
Otter Population Management A Wyoming Case Study
May 22, 2025 -
 Wyoming Otter Management A Critical Shift
May 22, 2025
Wyoming Otter Management A Critical Shift
May 22, 2025 -
 Casper Boat Lift Hosts Unexpected Zebra Mussel Invasion
May 22, 2025
Casper Boat Lift Hosts Unexpected Zebra Mussel Invasion
May 22, 2025 -
 A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
A Turning Point For Otter Management In Wyoming
May 22, 2025 -
 The Future Of Otter Populations A Turning Point In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
The Future Of Otter Populations A Turning Point In Wyoming
May 22, 2025
