Reducing Railway Emissions: The Role Of Wind-Powered Trains

Table of Contents
The Environmental Impact of Traditional Railway Systems
Traditional railway systems, while often lauded for their efficiency, still carry a significant environmental burden. Understanding this impact is crucial to appreciating the potential of wind-powered alternatives.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Locomotives
Locomotives, the workhorses of rail networks, are major sources of greenhouse gas emissions. These emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter, contribute significantly to climate change and air pollution.
- Diesel engines: Many railway systems rely on diesel locomotives, which produce substantial CO2 emissions during operation.
- Electricity generation from fossil fuels: Even electric trains can contribute to greenhouse gas emissions if the electricity used to power them is generated from fossil fuels like coal or natural gas.
The sheer volume of trains globally means that even relatively small emissions per train can translate into a massive overall environmental impact. Studies estimate that railway emissions account for a significant percentage of the transportation sector's overall carbon footprint. Precise figures vary depending on the region and the type of locomotive used.
Noise Pollution from Trains
Beyond greenhouse gas emissions, traditional trains also generate considerable noise pollution. This noise can negatively affect wildlife, disrupting their habitats and behavior, and it can also impact human populations living near railway lines, leading to stress and sleep disturbances.
- Mitigation strategies: Current noise reduction strategies include the use of noise barriers, quieter wheel designs, and speed restrictions in sensitive areas. However, these measures are often insufficient to fully address the problem.
How Wind-Powered Trains Work
Wind-powered trains represent a radical departure from traditional railway technology, aiming to harness the kinetic energy of wind to propel trains along the tracks. Several approaches are being explored:
Harnessing Wind Energy
Several methods are being explored to harness wind energy for train propulsion:
- Integrated wind turbines: This approach involves integrating wind turbines directly into the train's design, allowing the train to generate its own power while in motion. This could involve small turbines on the roof or even larger turbines deployed alongside the track.
- Overhead wind turbines: Another possibility involves using large-scale wind turbines located along the railway line to generate electricity that feeds the train through overhead lines, similar to the current electrical systems in many regions.
(Insert Diagram or Illustration of both approaches here)
Advantages: Reduced reliance on fossil fuels, decreased greenhouse gas emissions. Disadvantages: Intermittency of wind power, potential for reduced speed in low-wind conditions, initial high capital investment.
The technology involved in energy conversion usually incorporates sophisticated systems for capturing the wind's kinetic energy, converting it into electricity, and using this electricity to drive the train's motors. Advanced energy storage systems are crucial for handling variable wind conditions.
Hybrid Systems and Energy Storage
Given the intermittent nature of wind energy, hybrid systems incorporating battery technology or other energy storage solutions are essential for wind-powered trains. These systems provide power during periods of low wind or when additional power is needed for acceleration or climbing inclines.
- Battery technologies: Lithium-ion batteries, known for their high energy density, are a leading candidate for wind-powered trains. Other technologies like solid-state batteries are also being investigated for their potential advantages in terms of safety and longevity.
Challenges remain in managing the weight of batteries and developing efficient charging infrastructure that can support the energy demands of these trains.
Benefits of Wind-Powered Trains
The transition to wind-powered trains offers numerous environmental, economic, and social benefits:
Reduced Carbon Footprint
The most significant advantage of wind-powered trains is their drastically reduced carbon footprint. By relying on a renewable energy source, these trains can significantly decrease greenhouse gas emissions compared to diesel or even conventionally-powered electric trains. Quantifiable data showing percentage reductions in emissions compared to traditional trains would greatly strengthen this point. For example, "A study by [Source] showed that wind-powered trains could reduce CO2 emissions by X% compared to diesel trains".
- Reduced air pollution: Fewer harmful pollutants are released into the atmosphere, improving air quality along railway lines and surrounding areas.
- Lower carbon footprint: The overall contribution to climate change is significantly diminished.
Cost Savings in the Long Run
While the initial investment in wind-powered train technology might be higher, the long-term cost savings can be substantial.
- Reduced fuel consumption: The elimination or reduction of fossil fuel dependence leads to considerable savings on fuel costs.
- Lower maintenance needs: Wind-powered trains may require less maintenance than their diesel counterparts, further reducing operational expenses.
A comprehensive lifecycle cost analysis comparing wind-powered trains with conventional trains is needed to fully assess the economic viability of this technology.
Improved Public Image and Brand Enhancement
Adopting wind-powered trains can significantly enhance a railway company's public image and brand reputation. Consumers are increasingly demanding environmentally friendly transportation options, and the use of green technology can attract environmentally conscious passengers.
- Positive media coverage: The adoption of sustainable technologies often attracts positive media attention, bolstering the company's image.
- Attracting environmentally conscious investors: Green initiatives can attract investors who prioritize environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors.
Challenges and Future Prospects of Wind-Powered Trains
Despite the significant potential of wind-powered trains, several challenges need to be addressed before widespread adoption:
Technological Hurdles
Developing efficient and reliable wind-powered train systems presents considerable technological hurdles.
- Energy capture: Efficiently capturing wind energy, especially at varying speeds and directions, remains a significant engineering challenge.
- Energy storage: Developing lightweight and high-capacity energy storage systems is crucial for managing the intermittent nature of wind power.
- Energy distribution: Effectively distributing the generated power to the train's propulsion systems is essential for smooth and efficient operation.
Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing wind-powered trains may require significant modifications to existing railway infrastructure or the development of new infrastructure.
- Overhead lines (for overhead turbine systems): The installation of wind turbines along railway lines requires careful planning and significant investment.
- Charging stations (for battery-based systems): Providing sufficient charging infrastructure for battery-powered wind-assisted trains is a logistical and financial challenge.
Research and Development
Continued research and development are crucial to overcome the technological hurdles and enhance the efficiency and feasibility of wind-powered trains.
- Materials science: Research into lightweight, high-strength materials is vital for optimizing train design and energy efficiency.
- Aerodynamics: Improving the aerodynamic design of trains can further enhance energy efficiency.
Conclusion
Wind-powered trains offer a compelling pathway toward a more sustainable railway system by significantly reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing greenhouse gas emissions. While challenges remain in terms of technology, infrastructure, and research, the potential benefits – environmental, economic, and social – make investing in the research and development of wind-powered trains crucial for a greener future. Let's embrace this innovative solution and pave the way for a more sustainable railway system. Learn more about wind-powered train advancements and support initiatives that promote sustainable transportation today!

Featured Posts
-
 Grab Free Captain America Gear Fortnite Item Shops Limited Time Event
May 03, 2025
Grab Free Captain America Gear Fortnite Item Shops Limited Time Event
May 03, 2025 -
 Kendal Fundraiser For Poppy Atkinson Doubles After Tragedy
May 03, 2025
Kendal Fundraiser For Poppy Atkinson Doubles After Tragedy
May 03, 2025 -
 Tragjedi Ne Ceki Sulm Me Thike Le Dy Te Vdekur Ne Qender Tregtare
May 03, 2025
Tragjedi Ne Ceki Sulm Me Thike Le Dy Te Vdekur Ne Qender Tregtare
May 03, 2025 -
 How Chinas Trade War Impacts Are Being Underreported
May 03, 2025
How Chinas Trade War Impacts Are Being Underreported
May 03, 2025 -
 New Play Station Beta Program Announced By Sony
May 03, 2025
New Play Station Beta Program Announced By Sony
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
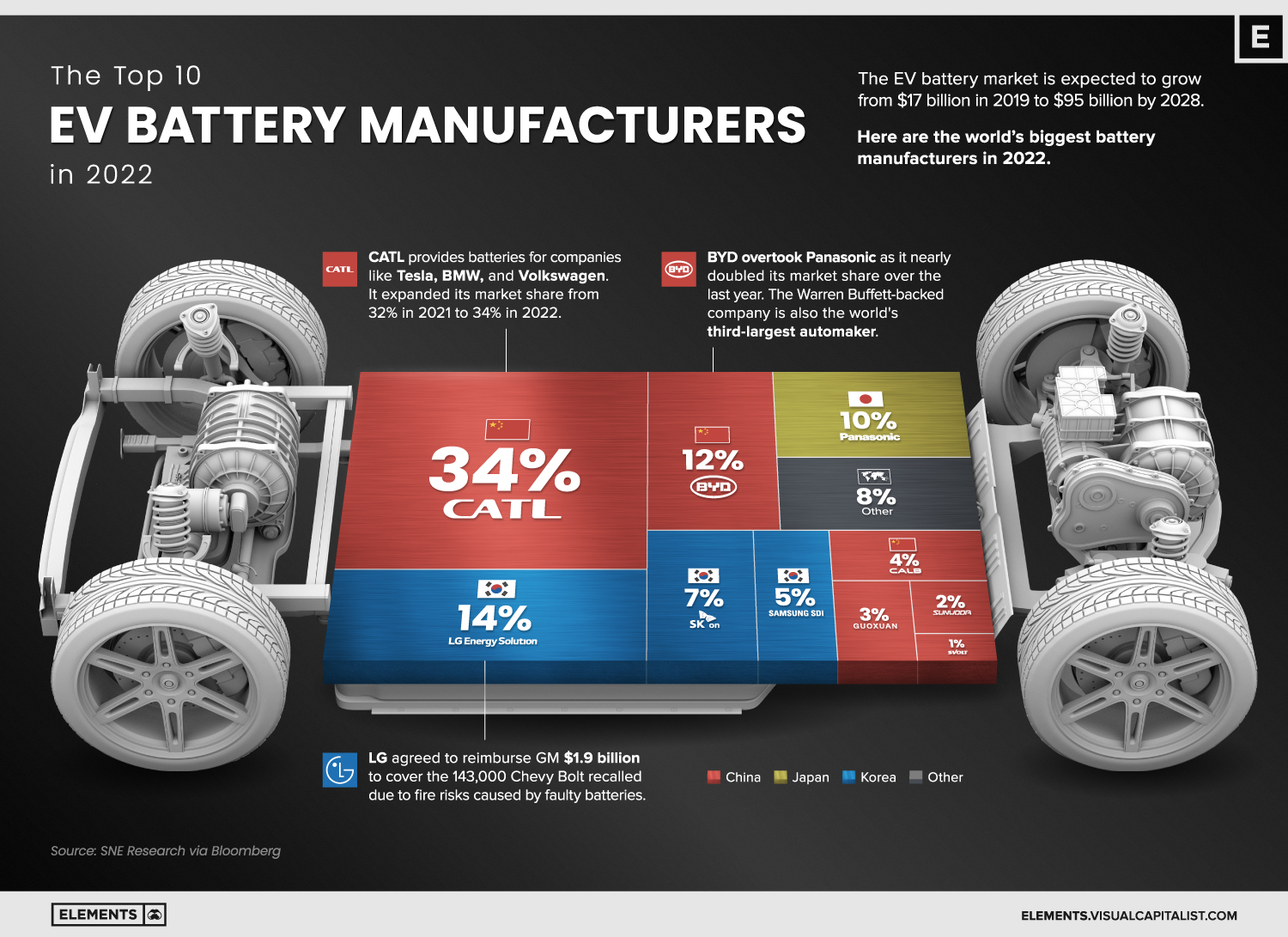 Chinas Ev Revolution Preparing For Global Competition The Us Response
May 04, 2025
Chinas Ev Revolution Preparing For Global Competition The Us Response
May 04, 2025 -
 Singapore Votes Will The Ruling Party Maintain Its Monopoly
May 04, 2025
Singapore Votes Will The Ruling Party Maintain Its Monopoly
May 04, 2025 -
 Lab Owner Admits To Falsifying Covid 19 Test Results
May 04, 2025
Lab Owner Admits To Falsifying Covid 19 Test Results
May 04, 2025 -
 Trumps Tariffs And Their Effect On Norways Sovereign Wealth Fund Under Nicolai Tangen
May 04, 2025
Trumps Tariffs And Their Effect On Norways Sovereign Wealth Fund Under Nicolai Tangen
May 04, 2025 -
 Singapore Elections A Test Of The Paps Grip On Power
May 04, 2025
Singapore Elections A Test Of The Paps Grip On Power
May 04, 2025
