Rio Tinto And The Pilbara: A Necessary Conversation On Sustainability
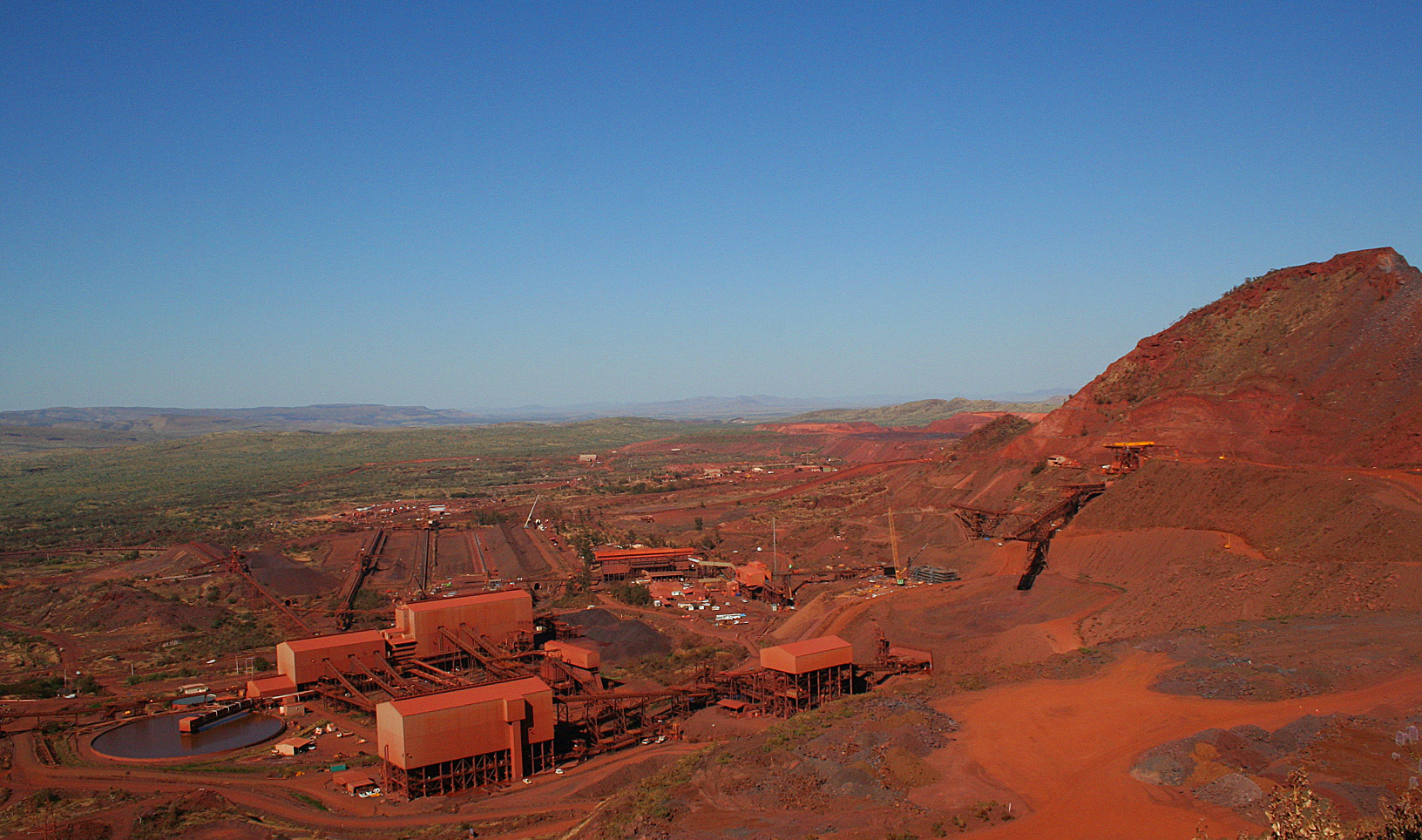

Table of Contents
The Environmental Impact of Pilbara Mining Operations
The Pilbara's vast iron ore reserves have fueled economic growth, but this prosperity comes at a cost. Understanding and mitigating the environmental impact of Rio Tinto's operations is paramount.
Water Consumption and Management
Water scarcity is a significant concern in the Pilbara. Rio Tinto's operations require substantial water resources for various processes. However, the company is implementing several strategies to minimize its water footprint:
- Water Recycling and Reuse: Advanced water treatment plants recycle and reuse water within their operations, reducing reliance on freshwater sources.
- Desalination Plants: Investing in desalination plants provides a sustainable alternative to freshwater extraction.
- Improved Water Efficiency Technologies: Implementing technologies that optimize water usage in mining processes.
These efforts, while significant, still face challenges. The impact on local ecosystems, such as groundwater depletion and alteration of natural water flows, requires ongoing monitoring and mitigation strategies. Effective Pilbara mining sustainability requires a holistic approach to water management.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions and Climate Change
Rio Tinto's Pilbara operations contribute to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily from energy consumption and heavy machinery. The company has committed to ambitious decarbonization targets, including:
- Renewable Energy Adoption: Investing in renewable energy sources like solar and wind power to reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
- Emissions Reduction Targets: Setting science-based targets to reduce greenhouse gas emissions across their value chain.
- Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS): Exploring and investing in CCS technologies to capture and store CO2 emissions.
Achieving these targets requires significant technological advancements and investment in innovative solutions. The transition to a low-carbon mining model is crucial for Pilbara mining sustainability and tackling climate change.
Biodiversity and Habitat Loss
The Pilbara's unique biodiversity is vulnerable to mining activities. Habitat loss and fragmentation pose significant threats to native flora and fauna. Rio Tinto undertakes several initiatives to mitigate this impact:
- Habitat Restoration and Rehabilitation: Implementing comprehensive programs to restore mined areas and create new habitats.
- Biodiversity Monitoring Programs: Regular monitoring of biodiversity to track the effectiveness of conservation efforts.
- Endangered Species Protection: Implementing specific measures to protect endangered species and their habitats.
Protecting and restoring biodiversity is a long-term commitment that requires careful planning and collaboration with ecological experts. Sustainable mining in the Pilbara must prioritize biodiversity conservation.
Waste Management and Land Rehabilitation
Effective waste management and land rehabilitation are crucial for minimizing the long-term environmental impact of mining. Rio Tinto's approach includes:
- Tailings Management: Implementing innovative tailings management strategies to minimize environmental risks.
- Waste Minimization Techniques: Employing technologies and processes to reduce waste generation.
- Post-Mining Land Rehabilitation: Restoring mined lands to a productive state, often exceeding pre-mining conditions.
Successful land rehabilitation demonstrates responsible mining practices and contributes significantly to Pilbara mining sustainability.
Rio Tinto's Sustainability Initiatives and Commitments
Rio Tinto's commitment to sustainability is reflected in its initiatives and reporting.
Public Reporting and Transparency
Rio Tinto publishes comprehensive sustainability reports, detailing their environmental performance, social impacts, and governance practices. This transparency enables stakeholders to assess the company's progress towards its sustainability goals. Open communication with communities and investors is vital for building trust and ensuring accountability.
Collaboration and Partnerships
Rio Tinto actively collaborates with local communities, NGOs, and research institutions to develop and implement sustainable practices. These partnerships facilitate knowledge sharing and contribute to more effective solutions. Collaborative approaches are crucial for achieving sustainable outcomes.
Investment in Sustainable Technologies
Rio Tinto invests heavily in research and development of sustainable technologies for mining operations. This includes autonomous haulage systems, improved energy efficiency technologies, and advanced water management solutions. These technological advancements are key drivers of Pilbara mining sustainability.
Challenges and Future Outlook for Sustainable Mining in the Pilbara
Sustainable mining in the Pilbara requires navigating complex challenges.
Balancing Economic Development and Environmental Protection
The Pilbara's economy heavily relies on mining. Striking a balance between economic growth and environmental protection requires careful planning, robust regulations, and collaborative efforts. Finding solutions that meet both economic needs and environmental responsibilities is a crucial ongoing challenge.
Technological Advancements and Their Role
Emerging technologies like AI and automation offer significant potential for enhancing mining sustainability. These technologies can improve resource efficiency, reduce emissions, and enhance safety. However, careful consideration of their implementation and potential limitations is necessary.
Policy and Regulatory Frameworks
Strong government regulations and policies are essential to drive sustainable mining practices. These frameworks should incentivize innovation, ensure environmental protection, and promote social equity. Continuous improvement and adaptation of these regulations are vital for a sustainable future.
Conclusion: The Path Towards a Sustainable Future for Rio Tinto and the Pilbara
Sustainable mining practices are not merely an option but a necessity for Rio Tinto's operations in the Pilbara. While significant progress has been made, ongoing challenges remain. The path forward requires continued dialogue and collaboration among Rio Tinto, government bodies, local communities, and other stakeholders. By embracing innovative technologies, strengthening regulations, and fostering transparent communication, a truly sustainable future for Rio Tinto and the Pilbara can be achieved. Join the conversation about creating a truly sustainable future for Rio Tinto and the Pilbara; learn more about their ongoing efforts and how you can contribute to responsible mining practices.

Featured Posts
-
 Confirmed Kieran Culkin To Play Caesar Flickerman In The Hunger Games Sunrise On The Reaping
May 23, 2025
Confirmed Kieran Culkin To Play Caesar Flickerman In The Hunger Games Sunrise On The Reaping
May 23, 2025 -
 Andrew Tate Din Dubai Cu Declaratii Incendiare Despre Conducere
May 23, 2025
Andrew Tate Din Dubai Cu Declaratii Incendiare Despre Conducere
May 23, 2025 -
 Egan Bernals Recovery From A Critical Cycling Accident Insights From Medical Research
May 23, 2025
Egan Bernals Recovery From A Critical Cycling Accident Insights From Medical Research
May 23, 2025 -
 High Level International Cricket Meetings Zimbabwe To Host Key Events
May 23, 2025
High Level International Cricket Meetings Zimbabwe To Host Key Events
May 23, 2025 -
 Tagliafico Blames Man United Players For Ten Hags Struggles
May 23, 2025
Tagliafico Blames Man United Players For Ten Hags Struggles
May 23, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Memorial Day 2025 Sales Event Top Deals And Where To Find Them
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day 2025 Sales Event Top Deals And Where To Find Them
May 23, 2025 -
 Memorial Day 2025 Sales Your Guide To The Best Deals
May 23, 2025
Memorial Day 2025 Sales Your Guide To The Best Deals
May 23, 2025 -
 Is Neal Mc Donough Returning To Tulsa King Season 3 Sylvester Stallone And The Latest News
May 23, 2025
Is Neal Mc Donough Returning To Tulsa King Season 3 Sylvester Stallone And The Latest News
May 23, 2025 -
 Neal Mc Donough From Bull Riding To The Pope His Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025
Neal Mc Donough From Bull Riding To The Pope His Last Rodeo
May 23, 2025 -
 What Date Is Memorial Day In 2025 A Complete Guide
May 23, 2025
What Date Is Memorial Day In 2025 A Complete Guide
May 23, 2025
