Rising Federal Debt: How It Impacts Mortgage Borrowers

Table of Contents
The Relationship Between Federal Debt and Interest Rates
Increased government borrowing to finance the national debt significantly influences interest rates. When the government borrows more money, it increases the demand for loans, pushing interest rates higher. This increased demand competes with private sector borrowing, driving up the cost of borrowing across the board. The Federal Reserve (the Fed), the central bank of the US, plays a critical role in managing this.
- Increased demand for loans drives up interest rates: As the government issues more Treasury bonds to finance its debt, it competes with private entities for available capital. This increased competition pushes interest rates upward.
- Investors may demand higher yields on government bonds to compensate for increased risk: Investors perceive a higher risk associated with lending to a government with a large and growing debt burden. To compensate for this perceived risk, they demand higher interest rates on government bonds.
- The Federal Reserve might raise interest rates to combat inflation fueled by government spending: Excessive government spending, often financed by borrowing, can contribute to inflation. To counter inflation, the Fed may raise its benchmark interest rate (the federal funds rate), influencing other interest rates, including mortgage rates.
How Higher Interest Rates Affect Mortgage Rates
The connection between government bond yields (the return on government bonds) and mortgage rates is direct and significant. Mortgage rates are largely influenced by the yield on Treasury bonds, particularly longer-term bonds. When government bond yields rise due to increased federal debt, mortgage rates typically follow suit. The Federal Reserve's actions also play a crucial role. Changes in the federal funds rate directly influence the rates banks charge each other and indirectly impact mortgage rates.
- Mortgage rates typically track Treasury bond yields: Mortgage lenders base their rates on the cost of borrowing money, often reflecting the yields on government bonds. Higher bond yields translate to higher mortgage rates.
- Higher interest rates mean higher monthly mortgage payments: A higher interest rate on a mortgage significantly increases the monthly payment amount, making homeownership less affordable.
- Higher rates can reduce affordability and decrease purchasing power: Increased mortgage rates directly impact affordability, reducing the amount potential homebuyers can borrow and the price range of homes they can afford.
The Impact on Mortgage Affordability and Homeownership
Rising mortgage rates, driven by a growing federal debt, considerably impact the affordability of homes. Potential buyers find themselves facing larger monthly payments and a reduced purchasing power. This can lead to a decrease in homeownership rates, especially among first-time buyers.
- Reduced purchasing power leads to smaller home purchases or inability to buy: Higher rates mean buyers can afford less expensive homes or may be priced out of the market entirely.
- Increased competition among buyers might drive up prices further: Even with reduced purchasing power, demand for housing might remain strong, potentially pushing prices even higher, exacerbating the affordability crisis.
- Potential impact on the overall housing market: A decline in affordability can lead to a slowdown in the housing market, impacting construction, sales, and overall economic activity.
Strategies for Mortgage Borrowers in a High-Debt Environment
Even in a high-interest-rate environment, there are strategies to help borrowers secure a mortgage. Careful planning and informed decision-making are crucial.
- Consider locking in a fixed-rate mortgage before rates rise further: If you anticipate buying soon, securing a fixed-rate mortgage can protect you from further interest rate increases.
- Explore options for improving credit scores to qualify for better rates: A higher credit score can significantly impact the interest rate you qualify for, potentially saving you thousands over the life of the loan.
- Shop around for the best mortgage rates and terms: Different lenders offer varying rates and terms, so comparing offers is essential to find the most favorable option.
- Save a larger down payment to reduce loan amount and monthly payments: A larger down payment reduces the overall loan amount and, consequently, the monthly payments, making the mortgage more manageable.
Rising Federal Debt and Your Mortgage: Key Takeaways and Next Steps
Rising federal debt directly influences interest rates, impacting mortgage rates and affordability for borrowers. Higher interest rates mean higher monthly payments and reduced purchasing power for potential homebuyers. This can lead to decreased homeownership rates and a slowdown in the housing market. Understand how rising federal debt impacts your mortgage by staying informed about economic trends and interest rate changes. Take control of your mortgage options in this environment by planning carefully, improving your credit score, and shopping for the best mortgage rates. Proactive financial planning and awareness of the implications of rising federal debt on personal finances are crucial for securing your financial future and achieving your homeownership goals.

Featured Posts
-
 Baby Lasagna Njezina Prica I Eurosong
May 19, 2025
Baby Lasagna Njezina Prica I Eurosong
May 19, 2025 -
 Libraries Under Pressure Examining The Effects Of The Trump Order
May 19, 2025
Libraries Under Pressure Examining The Effects Of The Trump Order
May 19, 2025 -
 Experience Uber One In Kenya Free Deliveries And Exclusive Discounts
May 19, 2025
Experience Uber One In Kenya Free Deliveries And Exclusive Discounts
May 19, 2025 -
 The Deteriorating India Bangladesh Relationship A Look At Recent Trade Actions
May 19, 2025
The Deteriorating India Bangladesh Relationship A Look At Recent Trade Actions
May 19, 2025 -
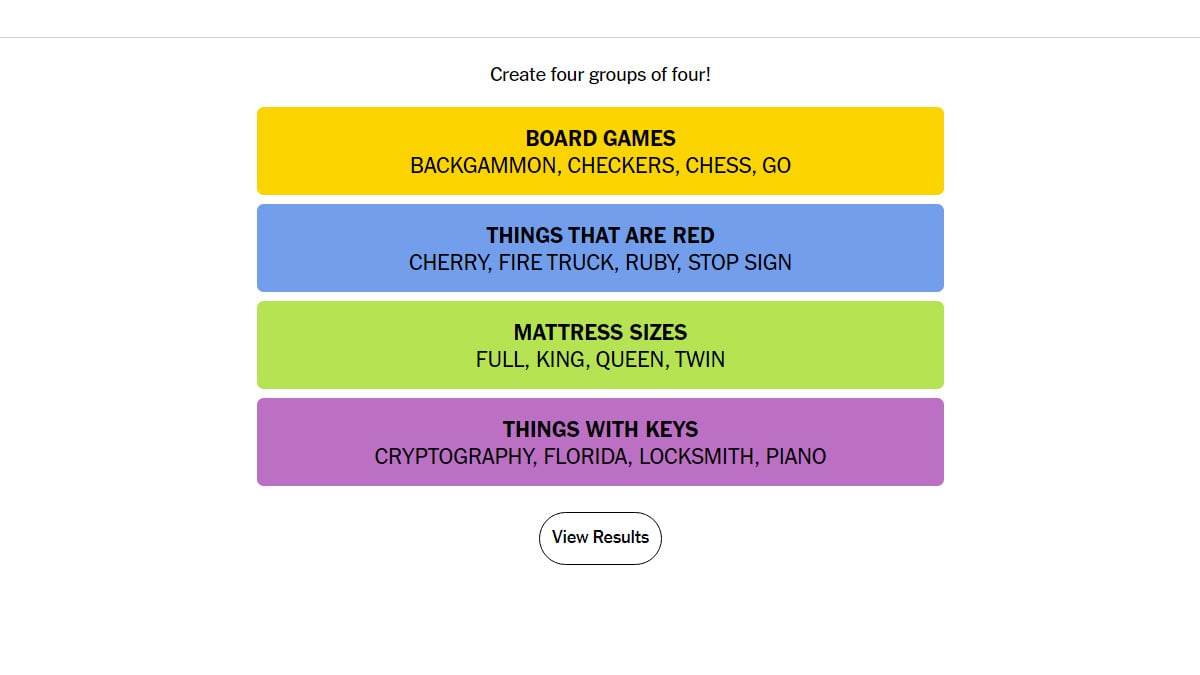 Todays Nyt Connections Puzzle 697 May 8 Hints And Solutions
May 19, 2025
Todays Nyt Connections Puzzle 697 May 8 Hints And Solutions
May 19, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Hamburg Tournament Added To Sinners Comeback Schedule
May 19, 2025
Hamburg Tournament Added To Sinners Comeback Schedule
May 19, 2025 -
 Jennifer Lawrence And Cooke Maroney A Look At Their Relationship
May 19, 2025
Jennifer Lawrence And Cooke Maroney A Look At Their Relationship
May 19, 2025 -
 Sinners Post Ban Return Hamburg Added To Schedule
May 19, 2025
Sinners Post Ban Return Hamburg Added To Schedule
May 19, 2025 -
 Is Cooke Maroney Jennifer Lawrences Husband The Perfect Hot Art Dad
May 19, 2025
Is Cooke Maroney Jennifer Lawrences Husband The Perfect Hot Art Dad
May 19, 2025 -
 Jennifer Lawrences Husband Cooke Maroney The Art Worlds Hot Dad
May 19, 2025
Jennifer Lawrences Husband Cooke Maroney The Art Worlds Hot Dad
May 19, 2025
