Rising Inflation And Unemployment Fuel Economic Uncertainty

Table of Contents
The Impact of Rising Inflation
High inflation significantly erodes purchasing power, making essential goods and services increasingly unaffordable for many. This cost of living crisis is impacting households and businesses alike.
Eroding Purchasing Power
Inflation reduces the value of money, meaning your money buys less than it did before. This is particularly impactful on those with fixed incomes who struggle to keep pace with rising prices.
- Rising Prices of Essentials: The cost of everyday necessities like gasoline, groceries, and housing is soaring, placing a significant strain on household budgets. Gas prices have increased by [Insert percentage and source], while grocery costs are up by [Insert percentage and source]. Housing costs, including rent and mortgages, have also seen substantial increases.
- Impact on Different Income Groups: Lower-income households are disproportionately affected by high inflation as a larger percentage of their income is spent on essential goods and services. This exacerbates existing inequalities and leads to increased financial hardship for vulnerable populations.
Inflation's Effect on Investment and Savings
Inflation significantly impacts the returns on investments and savings accounts. High inflation diminishes the real value of your savings, reducing their purchasing power over time.
- Impact on Real Interest Rates: When inflation rises faster than interest rates, the real return on savings accounts and other fixed-income investments becomes negative. This means your money is losing value in real terms.
- Strategies for Mitigating Inflation Risk: To protect your savings from inflationary pressures, consider diversifying your investments into assets that historically perform well during periods of high inflation, such as real estate or inflation-protected securities.
The Consequence of Rising Unemployment
Rising unemployment is a clear indicator of a slowing economy and has a ripple effect throughout society. Job losses and economic slowdown often go hand in hand, creating a vicious cycle of reduced consumer spending and further economic contraction.
Job Losses and Economic Slowdown
Increased unemployment reflects a weakening economy. Businesses often reduce their workforce during economic downturns, leading to job losses across various sectors.
- Unemployment Rate Statistics: The current unemployment rate stands at [Insert current unemployment rate and source], indicating [Explain the significance of the number – e.g., a significant increase compared to previous years].
- Industries Most Affected: Industries particularly vulnerable to job losses during economic slowdowns include manufacturing, retail, and hospitality, as these sectors are often highly sensitive to consumer spending patterns.
The Ripple Effect on Consumer Spending
Rising unemployment directly leads to decreased consumer spending. Job losses cause households to tighten their belts, reducing spending on non-essential goods and services.
- Impact on Various Sectors: The reduced consumer spending significantly impacts various sectors, including retail, hospitality, and entertainment, leading to further job losses and business closures.
- Potential for a Deflationary Spiral: A prolonged period of high unemployment and reduced consumer spending can create a deflationary spiral, where falling prices lead to lower wages and further reduced spending, perpetuating the economic downturn.
The Interplay Between Inflation and Unemployment
The relationship between inflation and unemployment is complex and often studied through the lens of the Phillips Curve. However, the current situation presents unique challenges to traditional macroeconomic models.
The Phillips Curve
The Phillips Curve traditionally suggests an inverse relationship between inflation and unemployment: lower unemployment leads to higher inflation, and vice versa. However, this relationship isn't always straightforward and can be influenced by other factors.
Stagflationary Risks
Stagflation, a period of high inflation and high unemployment, is a serious economic risk. It occurs when the economy experiences slow growth, high unemployment, and rising prices simultaneously – a particularly challenging scenario to manage. The current combination of rising inflation and unemployment raises concerns about potential stagflationary pressures.
Conclusion
Rising inflation and unemployment present a significant challenge to global economic stability. The erosion of purchasing power, the consequences of job losses, and the potential for stagflation highlight the severity of the current economic climate. Understanding the dynamics of rising inflation and unemployment is crucial for navigating these uncertain economic times. Stay informed by consulting resources like government websites ([link to relevant government website]) and financial advisors to proactively manage your finances and mitigate the risks associated with rising inflation and unemployment.

Featured Posts
-
 Nissans Classic Nameplate Comeback Is It Really Happening
May 30, 2025
Nissans Classic Nameplate Comeback Is It Really Happening
May 30, 2025 -
 A Widower Under Scrutiny Remy In Fbi Most Wanted Season 6 Sneak Peek
May 30, 2025
A Widower Under Scrutiny Remy In Fbi Most Wanted Season 6 Sneak Peek
May 30, 2025 -
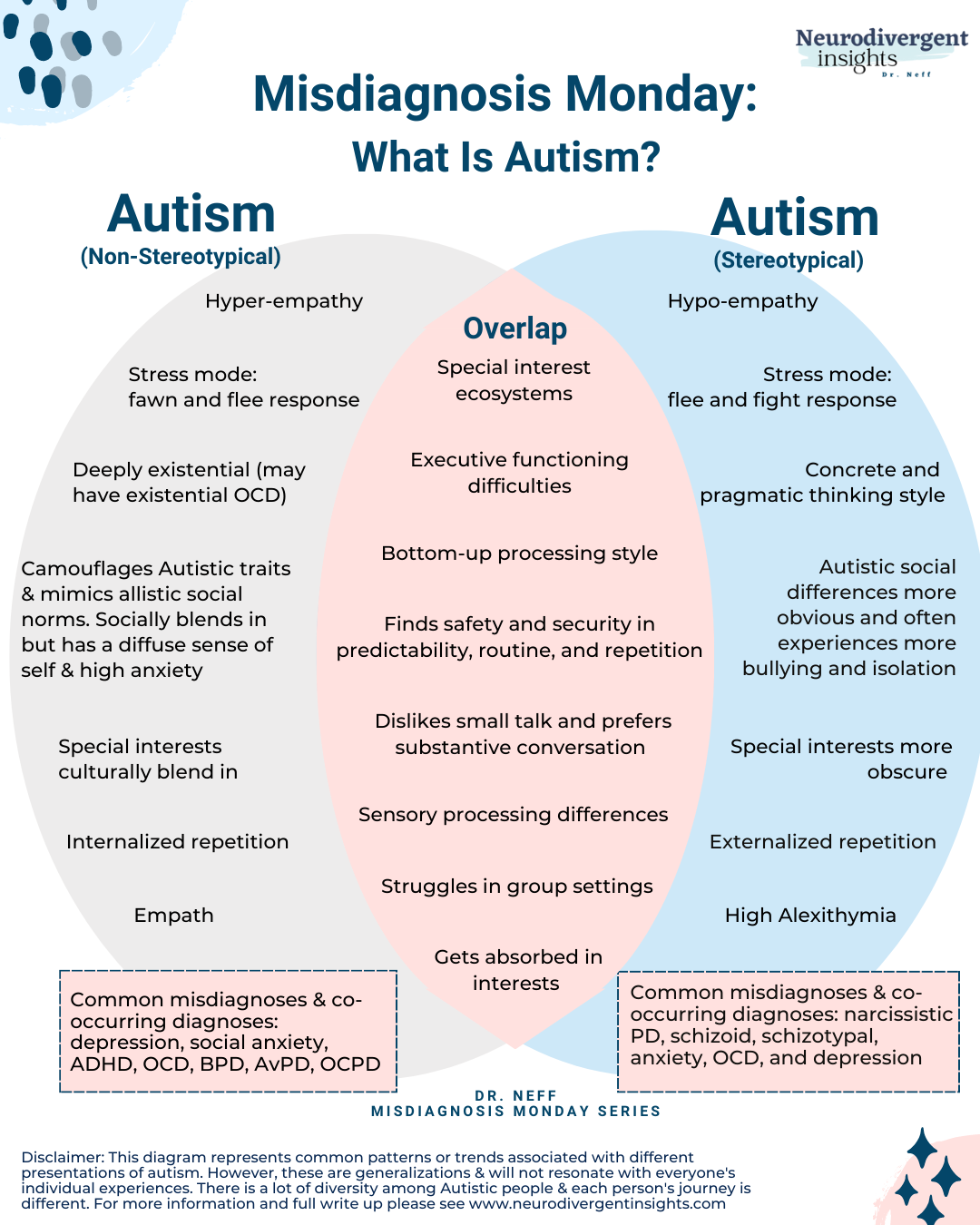 The Transformative Power Of Adult Autism Diagnosis
May 30, 2025
The Transformative Power Of Adult Autism Diagnosis
May 30, 2025 -
 Jack Draper Storms Into Madrid Atp Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025
Jack Draper Storms Into Madrid Atp Clay Court Final
May 30, 2025 -
 Andre Agassi O Declaratie Uluitoare Despre Nervi
May 30, 2025
Andre Agassi O Declaratie Uluitoare Despre Nervi
May 30, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Indian Wells 2024 Tsitsipas Triumphs Medvedev Advances
May 31, 2025
Indian Wells 2024 Tsitsipas Triumphs Medvedev Advances
May 31, 2025 -
 Covid 19 In India A Moderate Uptick In Cases Amidst Global Xbb 1 5 Variant Concerns
May 31, 2025
Covid 19 In India A Moderate Uptick In Cases Amidst Global Xbb 1 5 Variant Concerns
May 31, 2025 -
 Tsitsipas Defeats Berrettini Medvedev Moves On At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025
Tsitsipas Defeats Berrettini Medvedev Moves On At Indian Wells
May 31, 2025 -
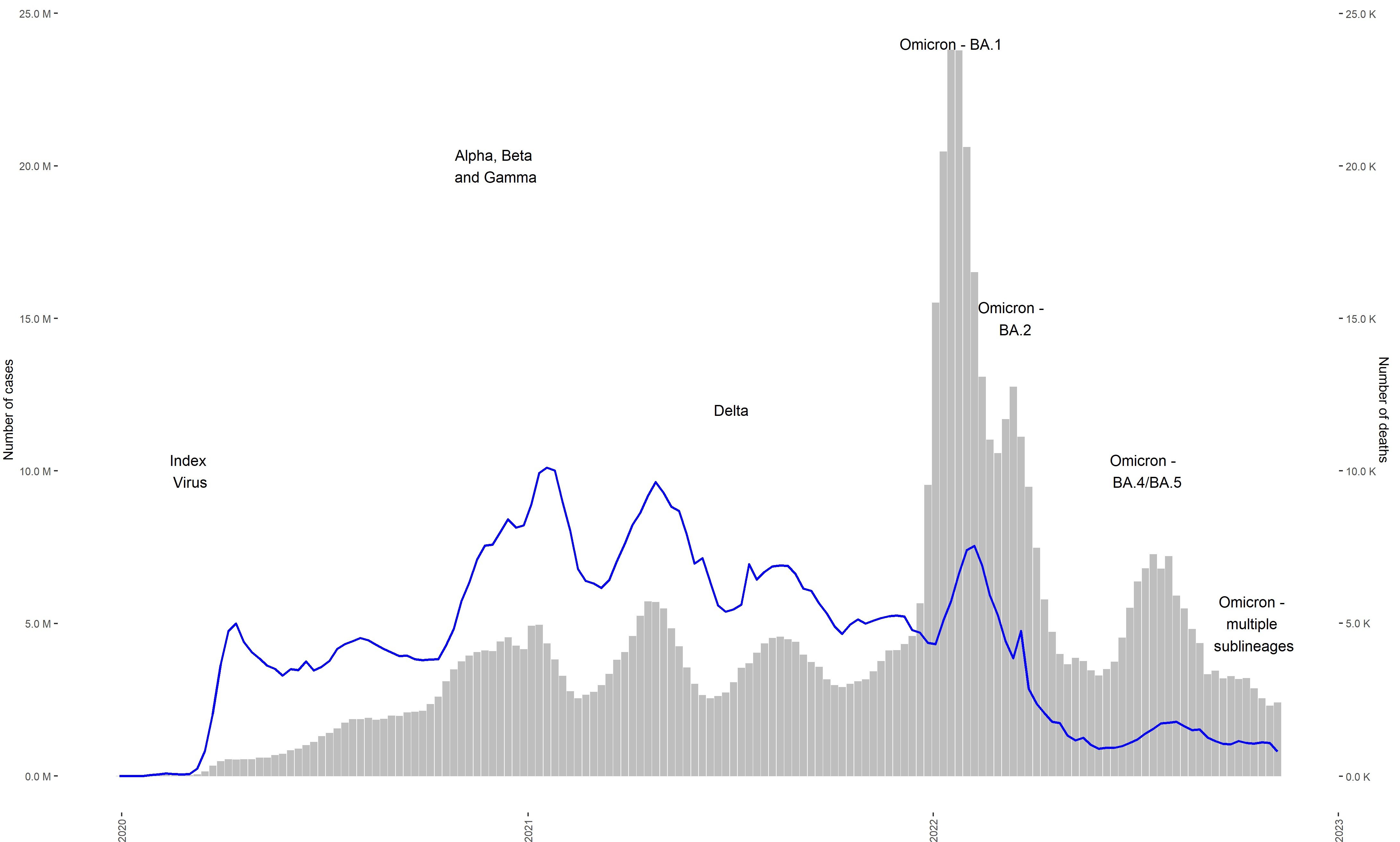 Xbb 1 5 Variant Surge A Slight Increase In Covid 19 Cases Reported Across India
May 31, 2025
Xbb 1 5 Variant Surge A Slight Increase In Covid 19 Cases Reported Across India
May 31, 2025 -
 Davidovich Fokina Falls To Alcaraz In Monte Carlo Masters Semi Final
May 31, 2025
Davidovich Fokina Falls To Alcaraz In Monte Carlo Masters Semi Final
May 31, 2025
