School Desegregation: The Justice Department's Decision And Its Broader Implications
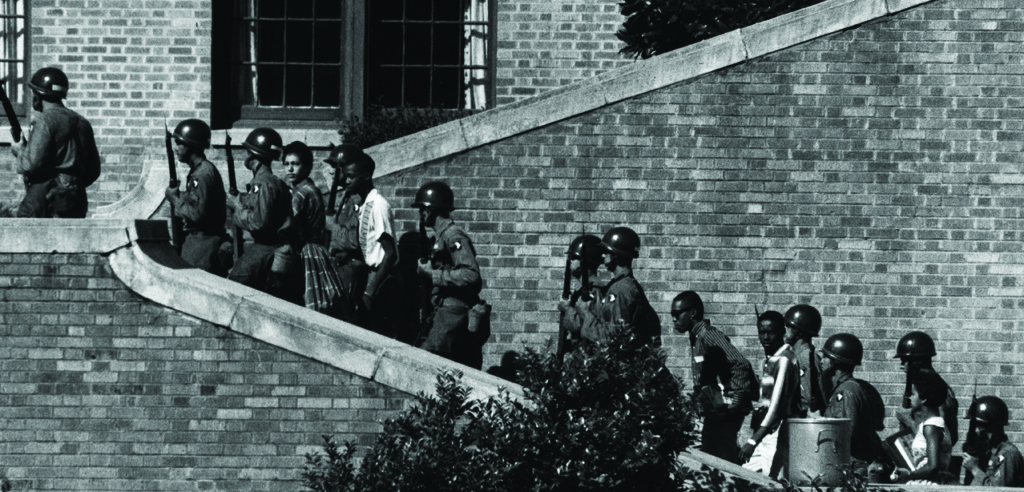

Table of Contents
Fifty years after the landmark Brown v. Board of Education ruling, school segregation remains a stark reality for many American children. Recent data reveals that school segregation is increasing in many parts of the country, highlighting the ongoing struggle for educational equity. This article will examine a recent Justice Department decision concerning school desegregation—specifically, the department's involvement in the Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School District No. 1 case (2007) and its aftermath — and analyze its broader implications for education, society, and future policy. We will explore the impact of this decision on affected school districts, its wider societal consequences, and the potential for future legal challenges and policy changes related to school desegregation. Keywords such as "Justice Department," "school desegregation," "impact," and "policy" will be central to our analysis.
H2: The Justice Department's Recent Decision on School Desegregation:
The Parents Involved in Community Schools v. Seattle School District No. 1 case, decided by the Supreme Court in 2007, significantly impacted the landscape of school desegregation. This case challenged the constitutionality of Seattle and Louisville school districts' student assignment plans, which considered race as one factor in assigning students to schools to promote diversity. The Justice Department, under the Bush administration, sided with the plaintiffs, arguing that the plans violated the Equal Protection Clause of the Fourteenth Amendment.
The legal arguments were complex, pitting the districts' goal of creating diverse student bodies against concerns about reverse discrimination. The Supreme Court's ruling ultimately held that the districts' plans were unconstitutional, stating that the use of race as a primary factor in assigning students to schools was not narrowly tailored to achieve a compelling governmental interest.
- Key points of the ruling: The Court rejected the argument that diversity in schools constituted a compelling governmental interest justifying the use of race.
- Legal precedents cited: The ruling relied on previous Supreme Court decisions, including Brown v. Board of Education, while simultaneously reinterpreting the scope of affirmative action in the educational context.
- Dissenting opinions: Four justices dissented, arguing that the majority opinion ignored the persistent reality of de facto segregation and the need for proactive measures to achieve racial diversity in schools.
H2: Impact on Affected School Districts:
The Parents Involved decision had immediate and lasting consequences for Seattle and Louisville, and indeed, for many other school districts across the country that had implemented similar race-conscious assignment plans. These districts faced the challenge of re-designing their student assignment systems, often resulting in a re-segregation of schools.
- Changes in student demographics: The dismantling of race-conscious assignment plans led to a measurable increase in racial segregation in some schools.
- Budgetary implications: Redesigning assignment plans and addressing potential legal challenges incurred significant costs for school districts.
- Community response: The decision sparked intense debate and divided communities, with some praising the ruling as a victory for equal opportunity and others criticizing it for hindering efforts to achieve racial integration.
H2: Broader Societal Implications of the Decision:
The Parents Involved decision has had profound societal implications, extending far beyond the specific school districts involved. The ruling’s impact on educational equity, racial integration, and social justice continues to be debated.
- Impact on achievement gaps: Studies suggest a correlation between school segregation and persistent achievement gaps between racial and ethnic groups. The Parents Involved decision arguably exacerbated these inequalities.
- Effects on interracial relations: Increased school segregation may negatively impact interracial understanding and social cohesion among students.
- Political ramifications: The decision fueled ongoing debates about affirmative action and the role of government in addressing historical inequalities.
H2: Future Policy and Legal Challenges:
The Parents Involved decision did not end the debate surrounding school desegregation. Future legal challenges are likely, focusing on the interpretation and application of the ruling in various contexts. Moreover, ongoing policy discussions at state and federal levels are crucial for addressing the persistence of school segregation.
- Potential legal challenges: Future litigation might challenge the constitutionality of other school policies or practices that indirectly contribute to segregation.
- Proposed legislative changes: Advocates for educational equity are pushing for legislative changes to promote school integration and address de facto segregation.
- The Justice Department's ongoing role: The Justice Department's enforcement of school desegregation laws and its stance on future cases will continue to shape the landscape of school integration.
Conclusion: The Ongoing Fight for School Desegregation and the Justice Department's Role
The Justice Department's involvement in cases like Parents Involved underscores the ongoing complexities and challenges in achieving school desegregation. The decision, while significant, did not resolve the underlying issue of racial inequality in education. Its broader societal implications highlight the need for continued efforts to promote educational equity and racial justice. Understanding the Justice Department's role in school desegregation is crucial. Stay informed and get involved in advocating for educational equity for all. Support organizations working to dismantle systemic racism and promote racial justice in education. The fight for school desegregation is far from over, and active engagement is essential.

Featured Posts
-
 Googles Future In Jeopardy Sundar Pichai On Doj Antitrust Plan
May 03, 2025
Googles Future In Jeopardy Sundar Pichai On Doj Antitrust Plan
May 03, 2025 -
 Daily Lotto Thursday 17 April 2025 Results
May 03, 2025
Daily Lotto Thursday 17 April 2025 Results
May 03, 2025 -
 Arsenals Havertz A Disappointing Epl Start Souness Criticism
May 03, 2025
Arsenals Havertz A Disappointing Epl Start Souness Criticism
May 03, 2025 -
 La Matinale De Mathieu Spinosi Le Violon En Direct
May 03, 2025
La Matinale De Mathieu Spinosi Le Violon En Direct
May 03, 2025 -
 Winning Numbers Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 03, 2025
Winning Numbers Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 03, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Petunjuk Praktis Mengolah Cangkang Telur Untuk Nutrisi
May 04, 2025
Dari Sampah Menjadi Harta Petunjuk Praktis Mengolah Cangkang Telur Untuk Nutrisi
May 04, 2025 -
 Manfaatkan Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Dan Sumber Kalsium Untuk Tanaman Dan Hewan
May 04, 2025
Manfaatkan Cangkang Telur Pupuk Alami Dan Sumber Kalsium Untuk Tanaman Dan Hewan
May 04, 2025 -
 Kivini Kabugu Tueketimi Faydalari Zararlari Ve Guevenli Hazirlama Teknikleri
May 04, 2025
Kivini Kabugu Tueketimi Faydalari Zararlari Ve Guevenli Hazirlama Teknikleri
May 04, 2025 -
 Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Manfaatnya Untuk Pertumbuhan Tanaman Dan Kesehatan Hewan
May 04, 2025
Daur Ulang Cangkang Telur Manfaatnya Untuk Pertumbuhan Tanaman Dan Kesehatan Hewan
May 04, 2025 -
 Kivinin Kabugu Yenir Mi Yenmez Mi Besin Degerleri Ve Dikkat Edilmesi Gerekenler
May 04, 2025
Kivinin Kabugu Yenir Mi Yenmez Mi Besin Degerleri Ve Dikkat Edilmesi Gerekenler
May 04, 2025
