The Bank Of Canada's Inflation Challenge: A Balancing Act

Table of Contents
Understanding the Current Inflationary Environment in Canada
The Causes of Inflation
Canada, like many other countries, is grappling with elevated inflation. Several factors contribute to this challenging inflationary environment:
- Supply chain bottlenecks: The lingering effects of the pandemic continue to disrupt global supply chains, leading to shortages of goods and pushing up prices. Increased shipping costs and port congestion exacerbate this issue.
- Increased energy costs: Global energy prices, particularly for oil and natural gas, have surged, significantly impacting transportation, manufacturing, and household energy bills. This contributes directly to the Canadian Consumer Price Index (CPI).
- Robust consumer spending: Strong consumer demand, fueled by pent-up savings from the pandemic and government stimulus measures, has further pushed up prices. This increased demand outpaces supply in many sectors.
- Rising housing prices: The Canadian housing market has experienced significant price increases in recent years, contributing substantially to overall inflation and impacting the CPI. This is particularly pronounced in major urban centers.
Statistics Canada's CPI data consistently reflects these factors, showing a significant increase in the inflation rate compared to the Bank of Canada's target. For instance, [Insert relevant CPI data and percentage increase from a reliable source].
The Bank of Canada's Mandate
The Bank of Canada's primary mandate is to maintain price stability, which it defines as keeping inflation at around 2 percent, as measured by the CPI. To achieve this mandate, the Bank employs various tools, including:
- Interest rate adjustments: The Bank's key policy instrument is the overnight rate, the target for the interest rate at which commercial banks borrow and lend funds to each other. Raising the overnight rate increases borrowing costs across the economy.
- Quantitative easing/tightening: This involves the Bank buying or selling government bonds to influence the money supply. Quantitative tightening, the current approach, reduces the money supply, aiming to curb inflation.
Currently, the actual inflation rate significantly deviates from the Bank's 2 percent target. [Insert current inflation rate and the deviation from the target]. This discrepancy highlights the urgency of the Bank's actions.
The Bank of Canada's Response to Inflation
Interest Rate Hikes
The Bank of Canada has responded to rising inflation by implementing a series of interest rate hikes. These increases aim to:
- Reduce consumer spending and investment by making borrowing more expensive.
- Cool down the economy and reduce inflationary pressures.
The transmission mechanism of monetary policy involves these interest rate changes impacting borrowing costs for businesses and consumers, influencing investment and spending decisions throughout the economy. The impact on variable-rate mortgages and loans is immediate and significant.
Quantitative Tightening
To further curb inflation, the Bank of Canada is also employing quantitative tightening. This involves reducing the size of its balance sheet by allowing government bonds to mature without reinvestment. This process aims to decrease the money supply and reduce inflationary pressure. Potential side effects include increased volatility in financial markets.
Forward Guidance and Communication
The Bank of Canada’s communication strategy plays a vital role in managing inflation expectations. Clear and consistent communication helps to:
- Anchor inflation expectations.
- Influence market sentiment.
The Bank achieves this through various channels including press conferences, monetary policy reports, and publications explaining its decisions and outlook. This transparency is crucial for maintaining confidence and coordinating economic activity.
The Risks and Challenges of Balancing Inflation and Growth
Recessionary Risks
The Bank of Canada's aggressive monetary policy tightening to combat inflation carries the risk of triggering a recession. The higher interest rates aim to curb spending and investment but could also lead to:
- Job losses.
- Reduced economic growth.
The trade-off between controlling inflation and avoiding a recession is a major challenge for the Bank.
Global Economic Uncertainty
The Canadian economy is intertwined with the global economy, making it vulnerable to external shocks. Global economic factors influencing the Bank of Canada's policy choices include:
- Global inflation: High inflation in other countries can spill over into Canada through imported goods and services.
- Geopolitical risks: Geopolitical instability can disrupt supply chains and increase commodity prices.
These interconnected global dynamics add layers of complexity to the Bank of Canada's challenge in navigating the delicate balance between controlling inflation and supporting economic growth.
Conclusion
The Bank of Canada's inflation challenge is multifaceted and requires ongoing attention. The delicate balance between controlling rising prices and preventing a recession necessitates careful adjustments to monetary policy, including interest rate adjustments and quantitative tightening. The Bank's communication strategy is crucial in managing expectations and maintaining stability. Staying informed about the Bank of Canada's actions and their impact on the Canadian economy is vital for individuals and businesses. Continue to follow updates on the Bank of Canada's inflation control measures and their impact on the Canadian economy to navigate the evolving economic landscape effectively.

Featured Posts
-
 Blake Livelys Alleged Blackmail Of Taylor Swift Examining The Baldoni Connection And Leaked Information
May 22, 2025
Blake Livelys Alleged Blackmail Of Taylor Swift Examining The Baldoni Connection And Leaked Information
May 22, 2025 -
 Beklenen Doenues Juergen Klopp Un Gelecegi
May 22, 2025
Beklenen Doenues Juergen Klopp Un Gelecegi
May 22, 2025 -
 Deretan Manajer Liverpool Yang Mengantarkan Gelar Liga Inggris Menuju Musim 2024 2025
May 22, 2025
Deretan Manajer Liverpool Yang Mengantarkan Gelar Liga Inggris Menuju Musim 2024 2025
May 22, 2025 -
 The Federal Result And Its Implications For Saskatchewan Politics
May 22, 2025
The Federal Result And Its Implications For Saskatchewan Politics
May 22, 2025 -
 Is Western Separation Realistic A Saskatchewan Perspective
May 22, 2025
Is Western Separation Realistic A Saskatchewan Perspective
May 22, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Thong Xe Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Chuan Bi Don Lan Song Du Lich Moi
May 22, 2025
Thong Xe Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Chuan Bi Don Lan Song Du Lich Moi
May 22, 2025 -
 At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025
At Be X Ntt Multi Interconnect Ascii Jp
May 22, 2025 -
 Du An Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Khoi Hanh Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025
Du An Cao Toc Dong Nai Vung Tau Khoi Hanh Du Kien 2 9
May 22, 2025 -
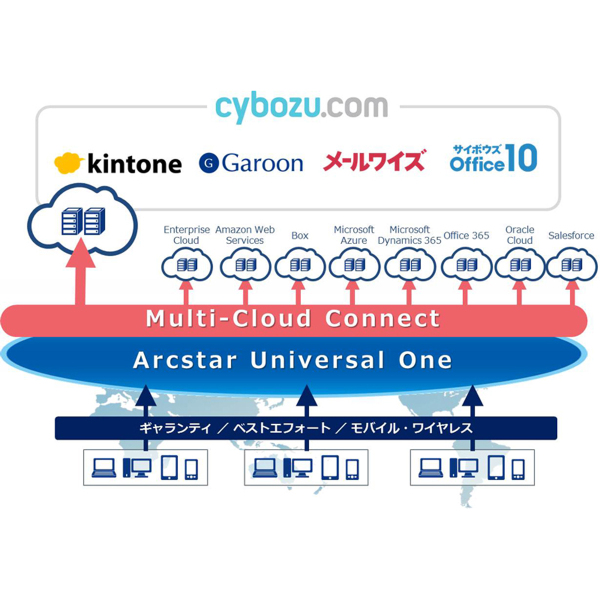 Ascii Jp Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X
May 22, 2025
Ascii Jp Ntt Multi Interconnect At Be X
May 22, 2025 -
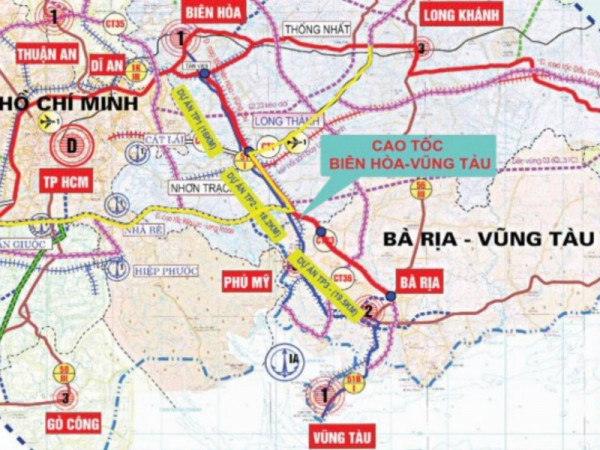 Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Dong Nai Thong Tin Moi Nhat Ve Ngay Thong Xe
May 22, 2025
Cao Toc Bien Vung Tau Dong Nai Thong Tin Moi Nhat Ve Ngay Thong Xe
May 22, 2025
