The Continuing Involvement Of European Shipyards In Russia's Arctic LNG Trade
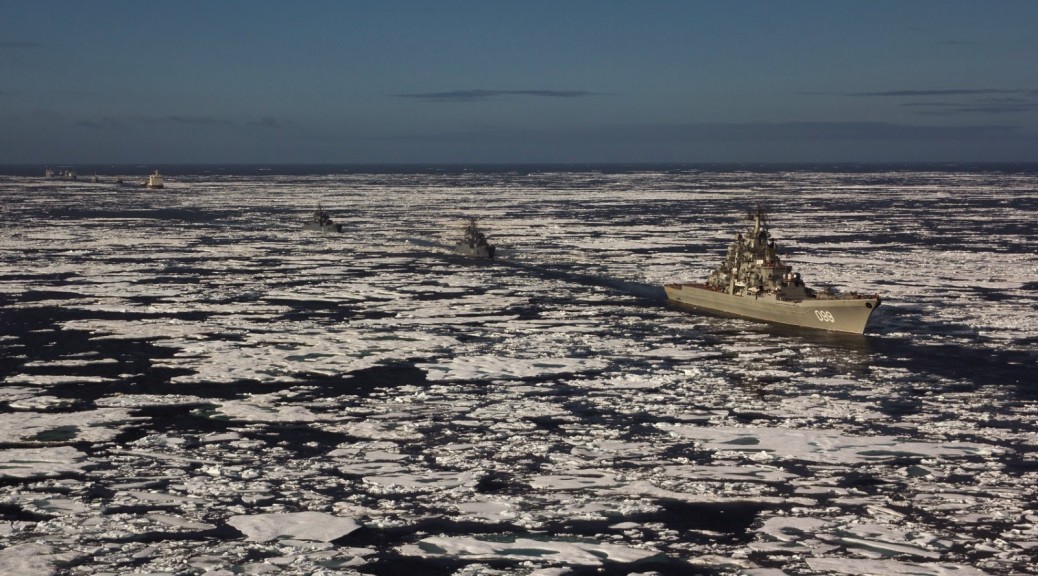

Table of Contents
Economic Incentives for European Shipyard Participation
The continued participation of European shipyards in this sector is driven by powerful economic incentives. The unique challenges and opportunities presented by the Arctic environment create a specific niche where European expertise is highly sought after.
High Demand for Specialized Ice-Class Vessels
The harsh Arctic conditions, characterized by thick ice and extreme weather, necessitate the use of specialized ice-class vessels for safe and efficient LNG transportation. European shipyards have a long history of innovation in shipbuilding, possessing the technological prowess and skilled workforce to construct these robust and sophisticated vessels. This expertise is unmatched globally, making them the preferred choice for Russian energy companies despite geopolitical complexities.
- Superior shipbuilding technology in European yards: European shipyards utilize cutting-edge design and construction techniques, leading to vessels with superior ice-breaking capabilities and enhanced safety features.
- High demand for LNG tankers capable of navigating Arctic ice: The expanding Arctic LNG production requires a significant fleet of ice-class LNG carriers, creating a consistent and lucrative demand for European shipbuilding capabilities.
- Competitive pricing despite sanctions: Despite sanctions, European shipyards often offer competitive pricing and financing options, making them attractive partners for Russian energy companies.
- Long-term contracts with Russian energy companies: Securing long-term contracts with major Russian energy players provides substantial financial stability and predictable revenue streams for European shipyards.
Financial Gains Despite Sanctions
While sanctions against Russia aim to restrict economic activity, loopholes and exemptions allow for continued business in certain areas, providing lucrative opportunities for European shipyards. This often involves indirect involvement, focusing on component supply rather than direct construction.
- Focus on indirect involvement (e.g., supplying components): By supplying crucial components or providing technical expertise, European shipyards can circumvent certain sanctions while still profiting from the Russian Arctic LNG trade.
- Exploitation of legal gray areas in sanctions regimes: The complex nature of sanctions regimes allows for some legal maneuvering, enabling continued engagement with Russian partners within the confines of the law.
- Prioritization of economic gain over geopolitical considerations: The drive for economic profit can sometimes outweigh concerns regarding the geopolitical implications of supporting the Russian energy sector.
- Potential risks of future sanctions escalation: However, this approach carries inherent risks. Any escalation of sanctions could severely jeopardize ongoing projects and future collaborations, leading to substantial financial losses.
Geopolitical Implications of Continued Involvement
The continued involvement of European shipyards in Russia's Arctic LNG infrastructure carries significant geopolitical ramifications, impacting both Russia and the broader global energy landscape.
Supporting Russia's Energy Sector
By participating in the construction and maintenance of Arctic LNG infrastructure, European shipyards indirectly contribute to Russia's economic resilience and its ability to export energy globally, even under the pressure of sanctions.
- Strengthening Russia's energy independence: Access to advanced shipbuilding technologies helps Russia reduce its dependence on other countries for crucial infrastructure development.
- Undermining the effectiveness of Western sanctions: The continued involvement of European companies can be seen as undermining the intended impact of Western sanctions on the Russian economy.
- Potential impact on global energy markets: The increased supply of LNG from Russia's Arctic region, facilitated by European shipbuilding expertise, can influence global energy prices and market dynamics.
- Contribution to Russia's geopolitical influence: A robust energy sector strengthens Russia's position on the international stage, enabling it to exert greater geopolitical influence.
Ethical Considerations and Reputational Risk
The ethical implications of supporting a regime facing accusations of human rights abuses and international aggression are substantial for European shipyards and their stakeholders. This involvement raises significant concerns about corporate social responsibility (CSR).
- Potential damage to corporate social responsibility (CSR) image: Continued involvement in the Russian Arctic LNG trade can damage the reputation of European shipyards among consumers and investors increasingly concerned about ethical sourcing and responsible business practices.
- Backlash from investors and consumers concerned about ethical sourcing: Growing public awareness of human rights violations and geopolitical tensions can lead to boycotts, divestment, and reputational damage for companies involved.
- Potential for future legal challenges related to human rights violations: There's a risk of future legal actions against European shipyards for their contribution to projects linked to human rights abuses.
- Balancing economic benefits with ethical responsibilities: European shipyards face the difficult challenge of balancing the pursuit of economic gain with their ethical responsibilities and the potential for long-term reputational harm.
Future Outlook and Potential Changes
The future of European shipyards' involvement in Russia's Arctic LNG trade is uncertain and hinges on several crucial factors.
Impact of Evolving Sanctions
The trajectory of the relationship will be heavily influenced by changes in international sanctions and the geopolitical climate. Increased enforcement or expansion of sanctions could dramatically alter the landscape.
- Increased scrutiny of financial transactions: Greater scrutiny of financial flows related to Arctic LNG projects could make it more difficult for European shipyards to operate legally and profitably.
- Potential for stricter enforcement of existing sanctions: A stricter enforcement of existing sanctions could lead to significant penalties for European companies involved in the Russian energy sector.
- Implications of future EU policy shifts regarding Russia: Changes in the EU's stance on Russia will significantly impact the legal and regulatory environment for European shipyards.
- Uncertainty surrounding long-term contracts: Existing contracts may face disruptions, renegotiations, or even cancellations due to geopolitical uncertainties.
Alternatives and Diversification Strategies
To mitigate the risks associated with dependence on the Russian Arctic LNG trade, European shipyards need to explore alternative markets and diversify their client base.
- Focus on other renewable energy projects: Investment in renewable energy projects offers a more sustainable and ethically sound path for long-term growth.
- Exploration of LNG projects in other regions: Diversifying into LNG projects in other parts of the world reduces dependence on the Russian market and mitigates geopolitical risks.
- Investment in new technologies and shipbuilding capabilities: Investing in cutting-edge technologies ensures the long-term competitiveness of European shipyards in a rapidly evolving global energy market.
- Development of robust risk management strategies: Implementing robust risk management strategies is essential for navigating the complex geopolitical and economic landscape.
Conclusion
The continued involvement of European shipyards in Russia's Arctic LNG trade highlights a complex interplay of economic incentives, geopolitical considerations, and ethical dilemmas. While substantial financial gains are evident, the reputational risks and the implications for supporting Russia's energy sector are considerable. The future of this relationship remains uncertain, heavily dependent on evolving sanctions, geopolitical shifts, and the choices made by European companies themselves. Understanding the intricacies of European Shipyards & Russia's Arctic LNG Trade is crucial for navigating the complexities of the global energy landscape and formulating effective policy responses. It is vital for stakeholders to carefully consider the ethical and geopolitical implications of this relationship and promote transparency and accountability within the industry. A comprehensive and ongoing analysis of the European Shipyards & Russia's Arctic LNG Trade is essential for shaping a more sustainable and responsible future for the Arctic and global energy markets.

Featured Posts
-
 George Santoss Fraud And Identity Theft Trial A Potential 7 Year Sentence
Apr 26, 2025
George Santoss Fraud And Identity Theft Trial A Potential 7 Year Sentence
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Dave Portnoy Unloads On Gavin Newsom The Full Story
Apr 26, 2025
Dave Portnoy Unloads On Gavin Newsom The Full Story
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Master The Language Of Lente A Springtime Phrasebook
Apr 26, 2025
Master The Language Of Lente A Springtime Phrasebook
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Big Tech Faces Advertising Slowdown Amidst Tariffs
Apr 26, 2025
Big Tech Faces Advertising Slowdown Amidst Tariffs
Apr 26, 2025 -
 Vingegaard Recovers From Concussion Eyes Tour De France Victory
Apr 26, 2025
Vingegaard Recovers From Concussion Eyes Tour De France Victory
Apr 26, 2025
