The Evolution Of Metropolis Japan: From Ancient Cities To Modern Megacities

Table of Contents
Ancient Foundations: The Rise of Early Japanese Cities
The story of Metropolis Japan begins long ago, with the establishment of early settlements influenced heavily by geography. Rivers provided vital transportation and water sources, shaping the location of these nascent urban centers. Two cities stand out as paramount examples of planned ancient capitals: Nara and Heian-kyō (Kyoto).
-
Nara (710-794 AD): Established as Japan's first permanent capital, Nara featured a meticulously planned grid layout, a revolutionary approach for its time. This design, inspired by Chinese models, reflected a desire for order and control, characteristics that continue to influence Japanese urban planning. The city's temples and palaces, showcasing the influence of Buddhism, became central to its urban structure. Keywords: Ancient Japanese Cities, Nara Period, Heian Period.
-
Heian-kyō (Kyoto) (794-1185 AD): The subsequent capital, Heian-kyō, further refined the principles of planned urban development. Its design, also based on a grid system, incorporated palaces, temples, and residential areas in a deliberate arrangement. The city’s layout profoundly impacted subsequent city planning in Japan, leaving a lasting legacy on urban design. The Imperial Court and the flourishing Buddhist monasteries played a significant role in shaping the city's character and its influence on urban development.
Beyond Nara and Kyoto, other important ancient cities existed, each reflecting the unique regional characteristics and development patterns of the time. These early settlements laid the groundwork for the future explosive growth of Metropolis Japan.
The Edo Period (1603-1868): The Dawn of Mega-Urbanization
The Edo period (1603-1868) witnessed an unprecedented surge in urbanization, largely driven by the rise of Edo (present-day Tokyo) as the center of power under the Tokugawa Shogunate. Edo's growth was explosive, transforming from a small fishing village into a mega-city teeming with life.
-
Edo's Urban Infrastructure: The city developed sophisticated urban infrastructure, including extensive canal networks for transportation and efficient waste management, and advanced fire-fighting systems crucial to managing the ever-present risk of devastating fires in densely packed wooden buildings. These systems showcase the ingenuity and adaptive capabilities in managing rapid population growth. Keywords: Edo Period, Edo City, Tokugawa Shogunate, Urbanization Japan.
-
The Merchant Class: A significant merchant class emerged during this era, contributing significantly to Edo's economic dynamism and urban expansion. Their presence shaped the cityscape with the development of bustling merchant districts and vibrant commercial centers. The unique social structure of the Edo period, with its rigid hierarchy, influenced the spatial organization of the city, separating social classes into distinct districts.
Other cities experienced growth during this period, though at a significantly slower pace compared to Edo's meteoric rise. This contrast highlighted the powerful effect of centralized political power and economic activity on urban development.
The Meiji Restoration and Modernization
The Meiji Restoration (1868) marked a turning point in Japanese history and profoundly impacted urban development. Rapid industrialization fueled unprecedented city growth, demanding new approaches to urban planning.
-
Western Influence: Japan adopted Western urban planning techniques, incorporating elements such as grid patterns, broad avenues, and zoning regulations into city designs. This blend of traditional Japanese design principles with Western innovations shaped the urban landscape of many emerging industrial cities. Keywords: Meiji Restoration, Modernization Japan, Industrialization Japan, Urban Planning Japan.
-
Emergence of New Industrial Cities: New industrial cities sprang up across Japan, attracting workers from rural areas and fostering significant population growth. These cities often lacked the careful planning of earlier capitals and experienced challenges related to rapid expansion and inadequate infrastructure.
The 20th and 21st Centuries: From Industrial Hubs to Global Megacities
The 20th and 21st centuries witnessed the transformation of Japanese cities from industrial hubs into global megacities. World War II caused widespread destruction, but the subsequent reconstruction and the post-war economic miracle led to phenomenal urban expansion.
-
Post-War Growth: The post-war period saw remarkable economic growth, fueling a massive population influx into major cities. This expansion led to the development of sophisticated public transportation systems, essential for managing the growing population density. Keywords: Modern Japanese Cities, Post-War Japan, Tokyo Megacity, Osaka Megacity, Urban Sprawl Japan.
-
Global Hubs: Tokyo, Osaka, Nagoya, and other major metropolitan areas emerged as leading global hubs, attracting international businesses, investment, and talent. These cities became centers of innovation, culture, and commerce, showcasing a dynamic interplay of traditional and modern elements.
However, modern Japanese cities face ongoing challenges including overcrowding, environmental concerns, and infrastructure limitations. Addressing these issues requires innovative urban planning solutions to ensure sustainable growth. Many examples of successful urban renewal and sustainable initiatives are constantly being developed and implemented.
Conclusion:
The evolution of Metropolis Japan demonstrates a remarkable journey from planned ancient capitals to dynamic modern megacities. The historical development of Japanese cities, shaped by political, economic, and social factors, reveals a rich tapestry of urban experiences. Understanding this evolution provides valuable insights into the challenges and successes of urban development on a global scale. Delve deeper into the captivating story of Metropolis Japan! Explore the rich history and unique characteristics of its many cities, from ancient settlements to the vibrant megacities of today. Learn more about the fascinating evolution of Japanese urban landscapes and the innovative solutions shaping their future.

Featured Posts
-
 Dry Weather Could Dampen Easter Bonfire Celebrations
May 18, 2025
Dry Weather Could Dampen Easter Bonfire Celebrations
May 18, 2025 -
 Alex Fines Birthday Cassie Reveals Gender Of Third Child
May 18, 2025
Alex Fines Birthday Cassie Reveals Gender Of Third Child
May 18, 2025 -
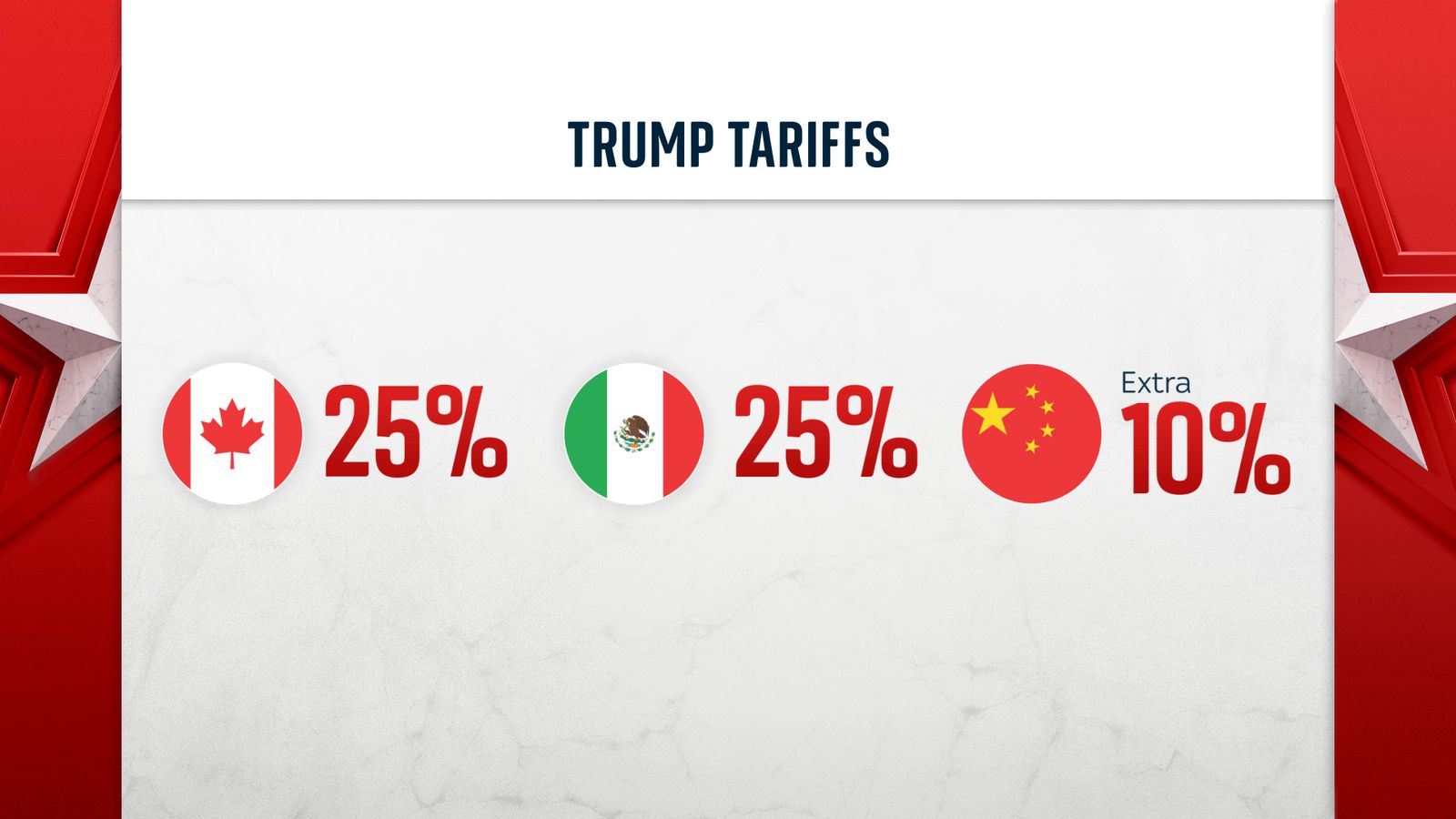 Dutch Public Opinion Opposition To Eu Retaliation Against Trump Tariffs
May 18, 2025
Dutch Public Opinion Opposition To Eu Retaliation Against Trump Tariffs
May 18, 2025 -
 Wildfire Betting A Disturbing Reflection Of Our Times The Los Angeles Case
May 18, 2025
Wildfire Betting A Disturbing Reflection Of Our Times The Los Angeles Case
May 18, 2025 -
 Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting And Its Implications
May 18, 2025
Los Angeles Wildfires The Rise Of Disaster Betting And Its Implications
May 18, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Following Split Claims Kanye West And Bianca Censori Dine In Spain
May 18, 2025
Following Split Claims Kanye West And Bianca Censori Dine In Spain
May 18, 2025 -
 Kanye West Bianca Censoris Spanish Dinner Date Amidst Relationship Speculation
May 18, 2025
Kanye West Bianca Censoris Spanish Dinner Date Amidst Relationship Speculation
May 18, 2025 -
 Kanye West And Bianca Censori A Spanish Restaurant Reunion
May 18, 2025
Kanye West And Bianca Censori A Spanish Restaurant Reunion
May 18, 2025 -
 Persistent Today Show Segment Featuring Jenna Bush Hager Sparks Viewer Debate
May 18, 2025
Persistent Today Show Segment Featuring Jenna Bush Hager Sparks Viewer Debate
May 18, 2025 -
 Instruktsiya Kane Uesta K Sobstvennym Pokhoronam Vdokhnovenie Ot Pashi Tekhnikom
May 18, 2025
Instruktsiya Kane Uesta K Sobstvennym Pokhoronam Vdokhnovenie Ot Pashi Tekhnikom
May 18, 2025
