The Powell Fed's Dilemma: Interest Rate Cuts And The Risk Of Delay
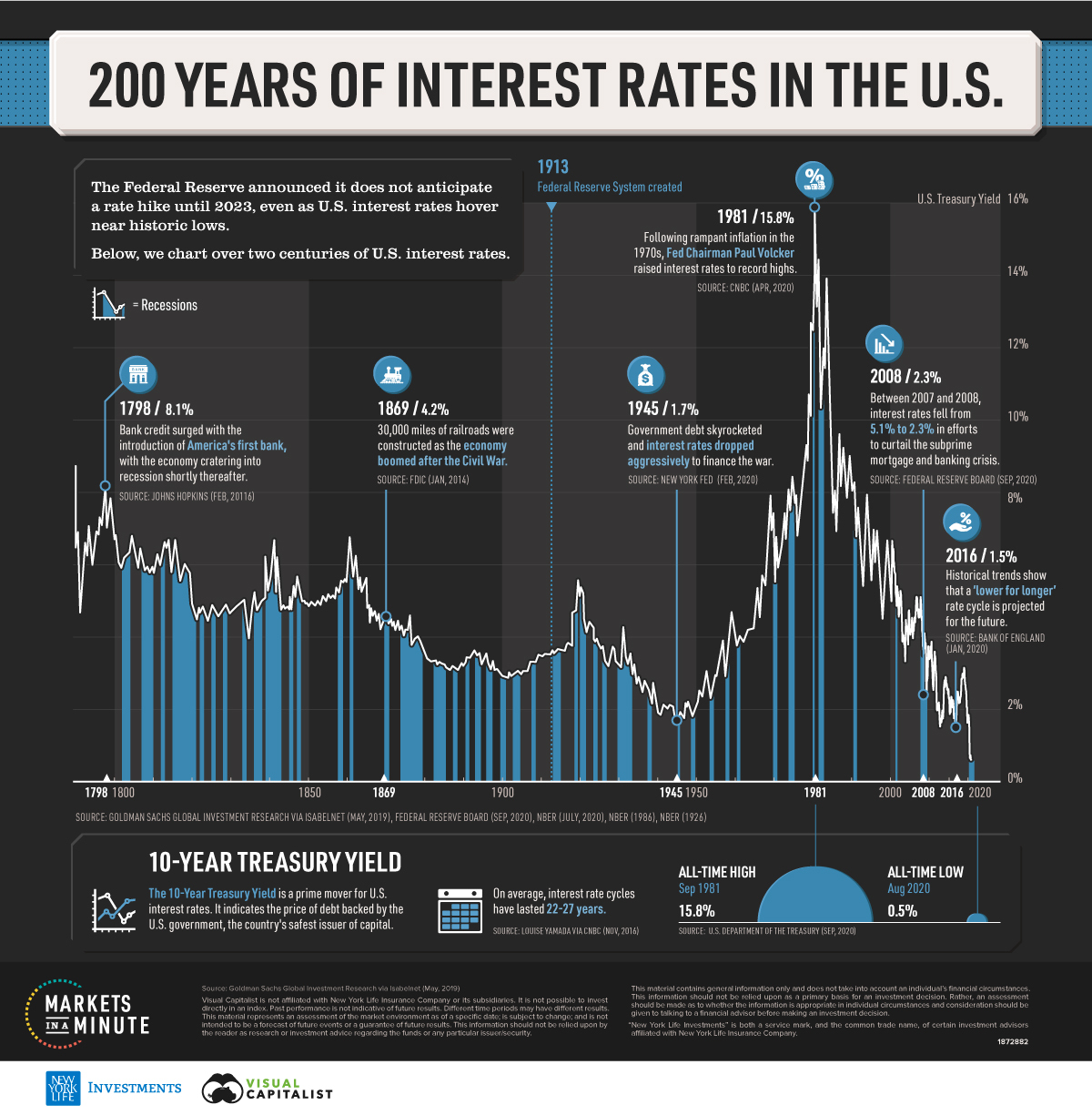
Table of Contents
The Current Economic Landscape: Inflation and Recessionary Fears
The US economy currently presents a mixed bag of indicators, making the Fed's decision on interest rate cuts exceptionally challenging. Inflation, while showing signs of cooling, remains stubbornly above the Fed's target rate of 2%. This persistence is fueled by various factors, including lingering supply chain issues and strong consumer demand. Simultaneously, the labor market exhibits conflicting signals. While unemployment remains historically low, signaling economic strength, there are growing concerns about potential layoffs in certain sectors, hinting at a potential slowdown. This combination of persistent inflation and recessionary fears creates a difficult environment for the Fed to navigate.
- Persistent inflation despite rate hikes: Despite aggressive interest rate increases throughout 2022, inflation has proven more resilient than initially anticipated.
- Mixed signals from the labor market: Strong employment numbers are countered by concerns about slowing job growth and potential future layoffs.
- Growing concerns about a potential recession: Economic forecasts vary, but the probability of a recession in the near future remains a significant concern.
- International economic factors impacting the US economy: Global economic instability and geopolitical events add further complexity to the domestic economic outlook, impacting inflation and growth.
Arguments for Interest Rate Cuts
Advocates for interest rate cuts argue that the current economic climate necessitates a shift in monetary policy. They believe that the risks of a deeper recession outweigh the risks of reigniting inflation. Lowering interest rates could provide much-needed stimulus to the economy.
- Boosting consumer confidence and spending: Lower borrowing costs could incentivize consumers to increase spending, bolstering economic activity.
- Encouraging business investment and job creation: Reduced borrowing costs would make it cheaper for businesses to invest in expansion, leading to job creation and economic growth.
- Preventing a sharper economic downturn: Proactive rate cuts could mitigate the severity of a potential recession by preventing a sharp contraction in economic activity.
- Lowering borrowing costs for businesses and consumers: Reduced interest rates directly translate to lower borrowing costs for mortgages, auto loans, and business loans, stimulating demand.
Arguments Against Interest Rate Cuts
Conversely, opponents of interest rate cuts warn of the potential for reigniting inflation. They argue that premature rate reductions could undo the progress made in bringing inflation under control.
- Risk of reigniting inflation and eroding purchasing power: Lower interest rates could increase demand, leading to renewed upward pressure on prices and eroding consumer purchasing power.
- Potential for increased inflationary expectations: If the public believes inflation will rise again, they may adjust their behavior, further fueling inflationary pressure. This creates a self-fulfilling prophecy.
- Weakening of the US dollar and implications for foreign exchange markets: Rate cuts can weaken the dollar, potentially impacting trade balances and increasing import costs.
- Increased market uncertainty and potential for volatility: Uncertainty surrounding the Fed's decisions can lead to increased market volatility and investor anxiety.
The Timing Dilemma: Risks of Delaying Rate Cuts
The timing of any interest rate cuts is crucial. Delaying action carries significant risks, potentially exacerbating an economic downturn and causing lasting damage.
- Increased economic hardship for consumers and businesses: A prolonged period of high interest rates can lead to financial strain for consumers and businesses, potentially resulting in bankruptcies and job losses.
- Potential for a longer and deeper recession: Delayed action could allow a mild recession to morph into a more severe and prolonged downturn.
- Loss of momentum in economic recovery: Delaying stimulus measures can hinder the pace of economic recovery, prolonging the period of economic weakness.
- Damage to consumer and business confidence: Uncertainty and inaction by the Fed can erode consumer and business confidence, further dampening economic activity.
Conclusion
The Powell Fed's dilemma regarding interest rate cuts is a complex balancing act between stimulating economic growth and controlling inflation. Delaying cuts risks a deeper recession, while implementing them prematurely could reignite inflation. A careful analysis of current economic indicators and future projections is crucial. Understanding the nuances of the Powell Fed's dilemma is vital for investors and policymakers alike. The Fed's decision will significantly impact the economic outlook, underscoring the importance of monitoring this situation closely. Stay informed about the latest developments concerning interest rate cuts and the Powell Fed's response to navigate the uncertain economic terrain.

Featured Posts
-
 April 12th Lotto Jackpot Results Check Winning Numbers
May 07, 2025
April 12th Lotto Jackpot Results Check Winning Numbers
May 07, 2025 -
 20 M Xrp Purchased Whale Activity Signals Potential Price Surge
May 07, 2025
20 M Xrp Purchased Whale Activity Signals Potential Price Surge
May 07, 2025 -
 2000 Yankees Diary Of A Season 500 Mark Reached After Loss
May 07, 2025
2000 Yankees Diary Of A Season 500 Mark Reached After Loss
May 07, 2025 -
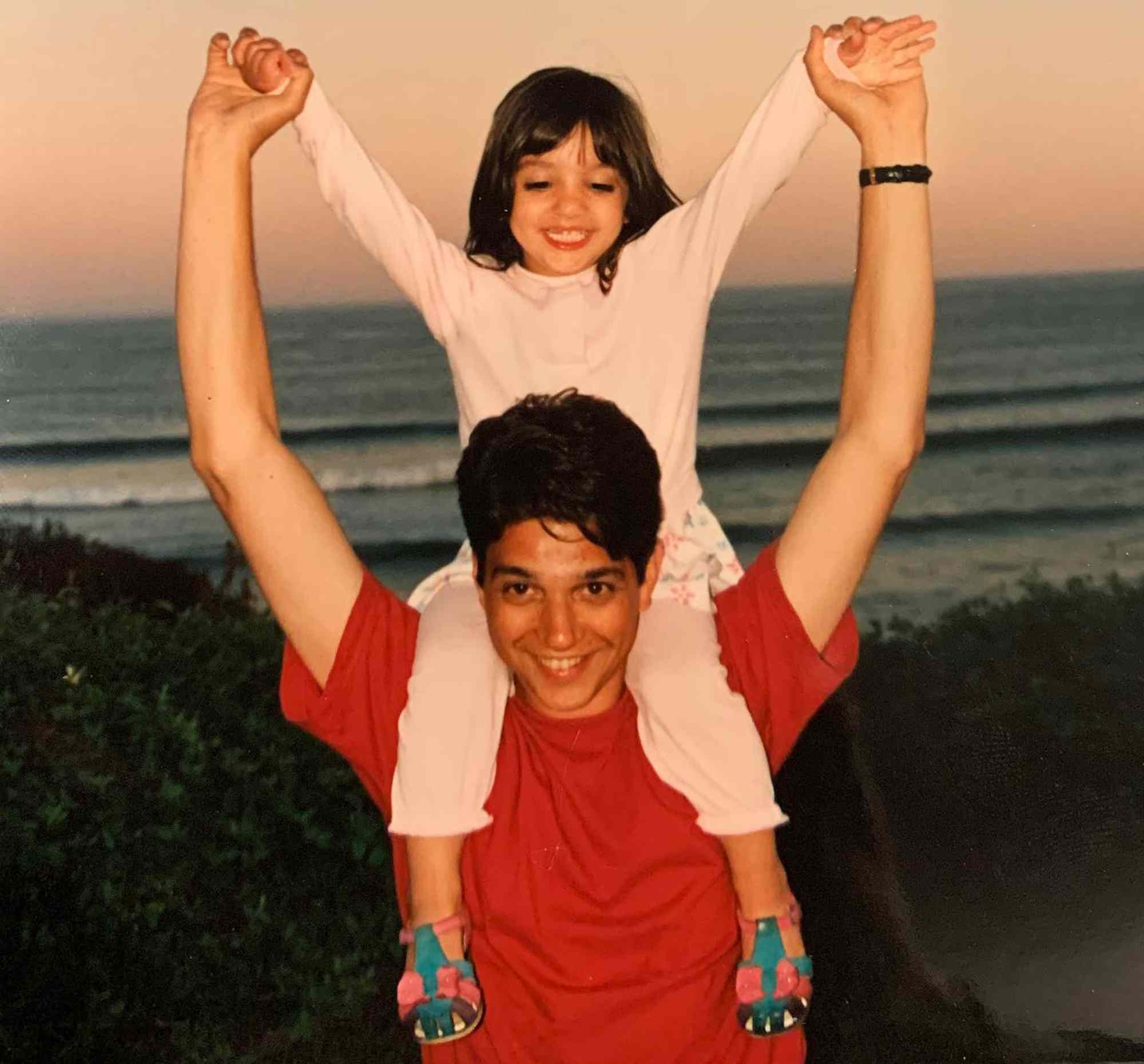 Ralph Macchios Karate Kid 6 Return Excitement And Uncertainty
May 07, 2025
Ralph Macchios Karate Kid 6 Return Excitement And Uncertainty
May 07, 2025 -
 Trumps Movie Tariff Plan A Deeper Look At The Potential Economic Impact
May 07, 2025
Trumps Movie Tariff Plan A Deeper Look At The Potential Economic Impact
May 07, 2025
Latest Posts
-
 Lotto Results Get The Latest Winning Numbers For Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draws
May 08, 2025
Lotto Results Get The Latest Winning Numbers For Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draws
May 08, 2025 -
 Official Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draw Results
May 08, 2025
Official Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Draw Results
May 08, 2025 -
 The Sec Vs Ripple What Does It Mean For Xrps Future
May 08, 2025
The Sec Vs Ripple What Does It Mean For Xrps Future
May 08, 2025 -
 Check Todays Lotto Results Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025
Check Todays Lotto Results Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2
May 08, 2025 -
 Check Your Tickets Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results
May 08, 2025
Check Your Tickets Lotto Lotto Plus 1 And Lotto Plus 2 Results
May 08, 2025
