The Relationship Between Dangote Refinery, NNPC, And Petrol Price Fluctuations
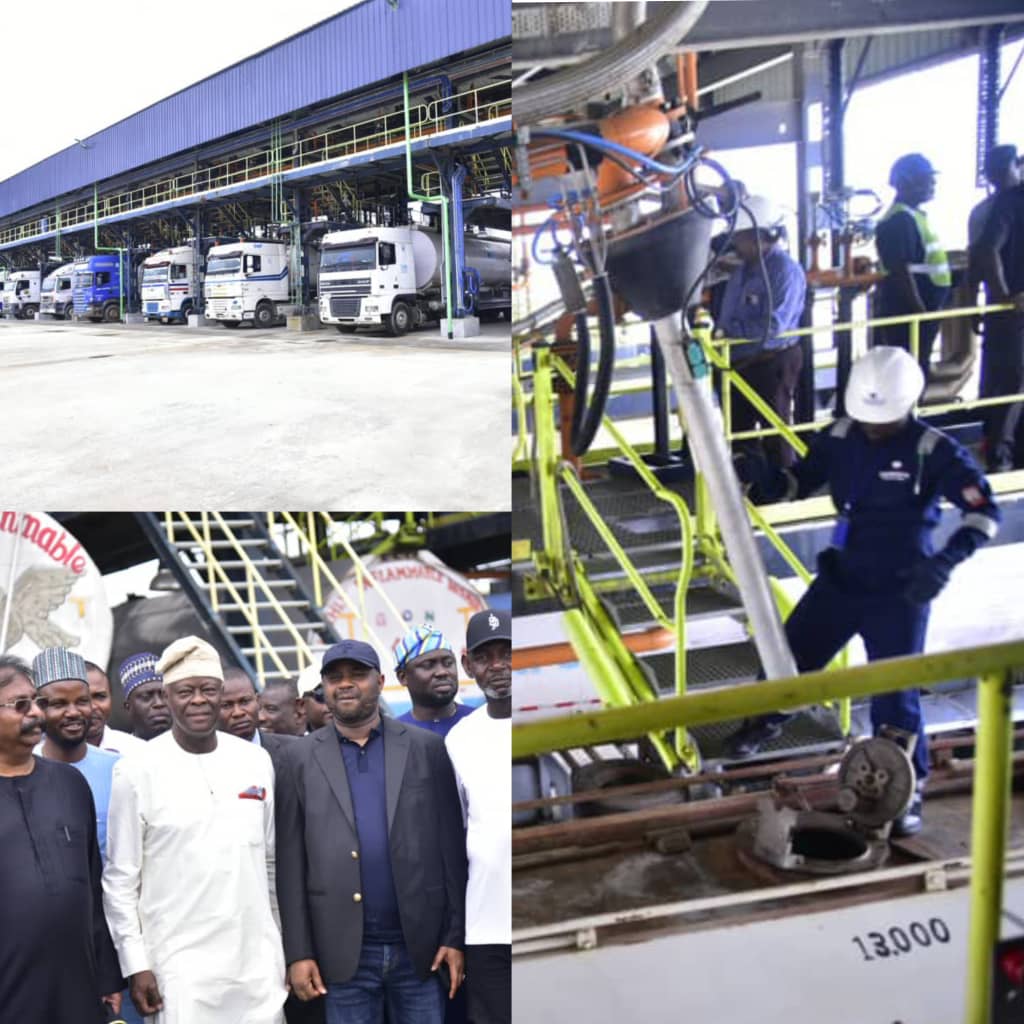

Table of Contents
The NNPC's Historical Dominance and Price Control
NNPC's Monopoly and Subsidy Regime
The Nigerian National Petroleum Corporation (NNPC) has historically held a near-monopoly on the importation and distribution of refined petroleum products in Nigeria. This dominance has been intricately linked to the country's long-standing fuel subsidy regime. For decades, the government subsidized fuel prices to keep them artificially low, cushioning the impact on consumers.
- History of fuel subsidy: The subsidy policy, while aimed at social protection, has created a significant economic burden on the government.
- Economic burden: Billions of Naira have been allocated annually to fuel subsidies, diverting funds from other crucial sectors like healthcare and education.
- Impact on government revenue: The subsidy significantly reduces government revenue and creates fiscal imbalances.
- Political implications of subsidy removal: Past attempts at subsidy removal have sparked widespread protests and social unrest, highlighting the sensitive political nature of fuel pricing.
Details: Estimates suggest that Nigeria spent hundreds of billions of Naira annually on fuel subsidies in the years leading up to significant deregulation efforts. The arguments for removal center on fiscal responsibility and the need to redirect funds to more pressing developmental needs. Conversely, opponents argue that removal disproportionately affects low-income citizens, exacerbating existing inequalities.
NNPC's Infrastructure and Supply Chain
NNPC's infrastructure and supply chain have significantly influenced petrol price stability (or instability). Inefficiencies and bottlenecks within this system have contributed to price volatility.
- Pipeline infrastructure: Deteriorating pipeline infrastructure, susceptible to vandalism and theft, frequently disrupts fuel supply.
- Storage capacity: Limited storage capacity restricts the ability to buffer against supply shocks, leading to price spikes.
- Distribution network efficiency: Inefficient distribution networks often cause delays and shortages, pushing up prices.
- Challenges of logistics and transportation: The logistics and transportation of petroleum products remain a major hurdle, increasing costs and creating price instability.
Details: Pipeline vandalism and fuel theft are rampant, costing the nation billions annually and directly impacting supply and, consequently, pricing. Improving infrastructure and strengthening security measures are crucial to addressing this issue.
The Impact of the Dangote Refinery on the Market
Increased Domestic Refining Capacity
The Dangote Refinery, Africa's largest, represents a significant shift in Nigeria's petroleum landscape. Its commissioning marks a potential turning point in domestic fuel production and self-sufficiency.
- Refinery capacity: With a projected capacity of 650,000 barrels per day, it significantly boosts Nigeria’s refining capacity.
- Projected output: This massive output promises to drastically reduce reliance on imported refined petroleum products.
- Potential to reduce reliance on imports: Less reliance on imports translates to reduced pressure on foreign exchange reserves.
- Impact on foreign exchange reserves: This decreased import bill can free up substantial foreign exchange for other developmental projects.
Details: The refinery's production includes petrol, diesel, kerosene, and other petroleum products, addressing a significant part of Nigeria’s fuel demand. This reduction in imports is expected to have a positive effect on Nigeria's balance of payments.
Potential for Price Competition
The Dangote Refinery's entry into the market introduces much-needed competition in the downstream petroleum sector. This competition has the potential to significantly impact petrol prices.
- Increased supply: Increased supply from the refinery should ease supply constraints and stabilize prices.
- Potential price reduction: The increased competition could lead to price reductions, benefiting consumers.
- Impact on NNPC's market share: NNPC's dominance is expected to decrease as a result of increased competition.
- Influence on market dynamics: The refinery's operations are expected to influence market dynamics, creating a more competitive and efficient market.
Details: The potential for price wars between NNPC and Dangote remains a possibility, ultimately benefiting consumers through lower prices. However, the actual impact on prices will depend on various factors, including the refinery's operational efficiency and government policies.
Government Policy and Market Regulation
Deregulation and Price Liberalization
Government policies on fuel price deregulation are crucial in determining the extent of price volatility. A move towards deregulation aims to foster a more market-driven pricing mechanism.
- Government's approach to deregulation: The government's approach to deregulation involves gradually reducing fuel subsidies and allowing market forces to determine prices.
- Challenges in implementing deregulation: This transition faces significant challenges, including public resistance and political considerations.
- Impact on consumer affordability: Price increases associated with deregulation can negatively impact consumer affordability, especially for low-income households.
Details: The government's commitment to deregulation is key to realizing the full benefits of the Dangote Refinery and creating a more sustainable and efficient fuel market. This will require carefully managed price adjustments and social safety nets to mitigate the negative impacts on vulnerable populations.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory agencies play a critical role in overseeing the petroleum sector, ensuring fair pricing, and preventing market manipulation.
- Regulatory agencies involved: Agencies like the Department of Petroleum Resources (DPR) and the Nigerian Midstream and Downstream Petroleum Regulatory Authority (NMDPRA) are key players.
- Their mandates: These agencies monitor prices, ensure quality control, and prevent monopolistic practices.
- Effectiveness in price monitoring and control: Their effectiveness in price monitoring and control will be vital in preventing price gouging and ensuring a fair market.
- Challenges faced by regulatory bodies: These bodies face challenges such as limited resources, corruption, and political influence.
Details: Strengthening the regulatory framework and enhancing the capacity of these agencies are essential for a fair and transparent fuel market. This will require greater independence, improved enforcement mechanisms, and increased accountability.
Conclusion
The relationship between the Dangote Refinery, NNPC, and petrol price fluctuations is complex and multifaceted. While the Dangote Refinery offers substantial potential to increase domestic refining capacity, reduce import dependency, and stimulate competition – potentially leading to more stable and lower fuel prices – the success of this transformation hinges on effective government policies, robust regulation, and efficient market mechanisms. The interplay of these factors will continue to shape Nigeria's fuel landscape and the price consumers pay at the pump. Further analysis of the Dangote Refinery's operational efficiency and the government's commitment to deregulation will be crucial to fully understanding the long-term impact on petrol price fluctuations and overall energy security in Nigeria. Continued monitoring of the Dangote Refinery's influence on NNPC's market dominance is vital for predicting future fuel price trends. The future of petrol prices in Nigeria is inextricably linked to the successful integration of the Dangote Refinery into the market and the government's continued efforts towards effective deregulation.

Featured Posts
-
 Dijon Agression Au Lac Kir Trois Blesses Graves
May 10, 2025
Dijon Agression Au Lac Kir Trois Blesses Graves
May 10, 2025 -
 Harry Styles Response To A Terrible Snl Impression
May 10, 2025
Harry Styles Response To A Terrible Snl Impression
May 10, 2025 -
 When Is High Potential Returning A Look At Season 2s Episode Count And Renewal
May 10, 2025
When Is High Potential Returning A Look At Season 2s Episode Count And Renewal
May 10, 2025 -
 Hollywood Production Grinds To A Halt Amidst Actors And Writers Strike
May 10, 2025
Hollywood Production Grinds To A Halt Amidst Actors And Writers Strike
May 10, 2025 -
 Indonesias Foreign Exchange Reserves Plummet Two Year Low Amid Rupiah Weakness
May 10, 2025
Indonesias Foreign Exchange Reserves Plummet Two Year Low Amid Rupiah Weakness
May 10, 2025
